您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家介紹static關鍵字在c++中的作用是什么,內容非常詳細,感興趣的小伙伴們可以參考借鑒,希望對大家能有所幫助。
1 類中的普通成員
類中的成員變量 和 成員函數 是分開存儲的。其中,
1)每個對象都有獨立的成員變量;成員變量可以存儲在 棧空間、堆空間、全局數據區;
2)所有對象共享類的成員函數;成員函數 只能存儲在 代碼段;
類中的靜態成員
1、用 static關鍵字 修飾;
2、可以用 類名::成員名 訪問 靜態成員;
3、靜態成員 屬于 整個類;
4、靜態成員 是所屬類的成員,其它類不能訪問;
5、靜態成員的內存分配 是 唯一的;
1) 靜態成員變量
特征:1、靜態成員變量 屬于 整個類所有;
2、靜態成員變量的生命周期不依賴任何對象;(靜態成員變量的生命周期在程序的運行期)
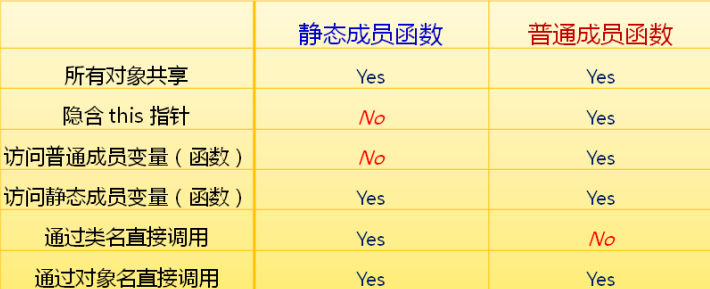
3、所有對象共享類的靜態成員變量;
4、可以通過 類名 直接訪問公有的靜態成員變量;
5、可以通過 對象名 訪問公有的靜態成員變量;
6、靜態成員變量 需要在類外單獨分配空間;(類內聲明、類外定義并初始化)
7、靜態成員變量 在程序內部位于全局數據區,不計入類的內存計算。
原因/好處:使用靜態成員變量實現多個對象之間的數據共享不會破壞隱藏的原則,保證了安全性還可以節省內存。
使用方法:
1、在類的內部,使用 static 修飾普通成員變量;
2、在類的外部(全局作用域),使用 Type ClassName::VarName = value 初始化,并申請存儲空間;
注:靜態成員變量不屬于類的任何對象,所以并不是對象建立時被定義的,所以它不能由類的構造函數初始化,一般也不能在類內初始化;
/*
靜態成員變量 只能在類的內部聲明,在類的外部(全局區)定義和初始化;
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test{
public:
int GetA() const{return a;}
private:
static int a; // 靜態成員變量
};
//int Test::a;如果這樣定義不賦予初值,則初值為零
int Test::a = 1;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Test T;
cout << T.GetA() << endl;
return 0;
}靜態成員變量 被類的所有對象共享,包括派生類對象;
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base{
public:
static int a; // 靜態成員變量
};
// int Test::a;如果這樣定義不賦予初值,則初值為零
int Base::a;
class Derived : public Base{
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Base B;
Derived D;
B.a++;
cout << B.a << endl; // 1
D.a++;
cout << D.a << endl; // 2
return 0;
}靜態成員變量可以作為普通成員函數的默認形參,而普通成員變量則不可以;
class Test{
public:
static int a; //靜態成員變量
int b;
void fun_1(int i = a); //正確
//void fun_2(int i = b); //報錯
};靜態成員變量的類型 可以是所屬類的類型,而普通成員變量則不可以。普通成員變量只能聲明為 所屬類類型的 指針或引用;
class Test{
public:
static Test a; //正確
Test b; //報錯
Test *pTest; //正確
Test &m_Test; //正確
static Test *pStaticObject; //正確
};靜態成員變量在const函數中可以修改,而普通的成員變量是萬萬不能修改的;
/*
const修飾的是當前this指針所指向的對象是const,但是靜態成員變量不屬于任何類的對象,它被類的所有對象修改,所以this指針不修飾靜態的成員變量,所以可以更改。
*/
class Test{
public:
static int a;
int b;
public:
Test():b(0){}
void test() const
{
a++;
//b++; // err // const指的是不能修改當前調用該函數對象的成員變量
}
};
int Test::a;2)靜態成員函數
特征:1、靜態成員函數 屬于 整個類所有;
2、所有對象共享類的靜態成員函數;
2、可以通過 類名 直接訪問公有的靜態成員函數;
3、可以通過 對象名 訪問公有的靜態成員函數;
4、靜態成員函數 只能 訪問靜態成員,不能訪問 非靜態成員;
5、靜態成員函數沒有this指針,也就是說靜態成員函數不能使用修飾符(也就是函數后面的const關鍵字);
原因:處理靜態成員變量;
使用方法:直接用 static 修飾 普通成員函數(類內聲明時),不需要 static 修飾(類外定義時);
總結:
案例分析:
/**
* 統計某班選修課考試的平均成績
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
private:
string name; // 姓名
string gender; // 性別
float score; // 分數
string subject; // 課程
static int total_counts; // 總人數
static float chinese_scores; // 語文分數
static int chinese_counts; // 語文課人數
static float math_scores; // 數學分數
static int math_counts; // 數學課人數
public:
Student(string name, string gender, float score, string subject);
~Student();
static float aveScores(string subject);
void printStudentInfo();
void printAveScores();
};
int Student::total_counts = 0;
float Student::chinese_scores = 0;
int Student::chinese_counts = 0;
float Student::math_scores = 0;
int Student::math_counts = 0;
Student::Student(string name, string gender, float score, string subject)
{
this->name = name;
this->gender = gender;
this->score = score;
this->subject = subject;
if(subject == "chinese" || subject == "語文")
{
chinese_scores += score;
chinese_counts++;
}
else if(subject == "math" || subject == "數學")
{
math_scores += score;
math_counts++;
}
else
{
cout << "this is no the subect:" << subject << endl;
}
total_counts += (chinese_counts + math_counts);
}
Student::~Student()
{
total_counts--;
chinese_counts--;
math_counts--;
}
float Student::aveScores(string subject)
{
float ave_score = 0;
if(chinese_counts > 0 && subject == "chinese" || subject == "語文")
{
ave_score = (chinese_scores / chinese_counts);
//cout << subject << "\t" << chinese_counts << "\t" << chinese_scores << endl;
}
else if(math_counts > 0 && subject == "math" || subject == "數學")
{
ave_score = (math_scores / math_counts);
//cout << subject << "\t" <<math_counts << "\t" << math_scores << endl;
}
return ave_score;
}
void Student::printStudentInfo()
{
cout << name << "\t" << gender << "\t" << score << "\t" << subject << endl;
}
void Student::printAveScores()
{
cout <<subject << " average score: " << aveScores(subject) << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
const int SIZE = 5;
Student stu[SIZE] =
{
Student("10001", "male", 92, "語文"),
Student("10002", "male", 91, "數學"),
Student("10003", "male", 91, "數學"),
Student("10004", "male", 93, "語文"),
Student("10005", "male", 92, "語文"),
};
for(int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
stu[i].printStudentInfo();
}
stu[0].printAveScores();
stu[1].printAveScores();
cout << "語文" << " average score: " << Student::aveScores("語文") << endl;
cout << "數學" << " average score: " << Student::aveScores("數學") << endl;
return 0;
}
靜態成員的案例分析下面看下c語言中的static關鍵字的作用
在我們日常使用過程中,static通常有兩個作用:
1、修飾變量
靜態全局變量:全局變量前加static修飾,該變量就成為了靜態全局變量。我們知道,全部變量在整個工程都可以被訪問(一個文件中定義,其它文件使用的時候添加extern關鍵字聲明 ),而在添加了static關鍵字之后,這個變量就只能在本文件內被訪問了。因此,在這里,static的作用就是限定作用域。
靜態局部變量:局不變量添加了static修飾之后,該變量就成為了靜態局部變量。我們知道局部變量在離開了被定義的函數后,就會被銷毀,而當使用static修飾之后,它的作用域就一直到整個程序結束。因此,在這里static的作用就是限定生命周期。
2、修飾函數
修飾函數則該函數成為靜態函數,函數的作用域僅限于本文件,而不能被其它文件調用。
關于static關鍵字在c++中的作用是什么就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。