溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文實例為大家分享了TensorFlow實現創建分類器的具體代碼,供大家參考,具體內容如下
創建一個iris數據集的分類器。
加載樣本數據集,實現一個簡單的二值分類器來預測一朵花是否為山鳶尾。iris數據集有三類花,但這里僅預測是否是山鳶尾。導入iris數據集和工具庫,相應地對原數據集進行轉換。
# Combining Everything Together
#----------------------------------
# This file will perform binary classification on the
# iris dataset. We will only predict if a flower is
# I.setosa or not.
#
# We will create a simple binary classifier by creating a line
# and running everything through a sigmoid to get a binary predictor.
# The two features we will use are pedal length and pedal width.
#
# We will use batch training, but this can be easily
# adapted to stochastic training.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
# 導入iris數據集
# 根據目標數據是否為山鳶尾將其轉換成1或者0。
# 由于iris數據集將山鳶尾標記為0,我們將其從0置為1,同時把其他物種標記為0。
# 本次訓練只使用兩種特征:花瓣長度和花瓣寬度,這兩個特征在x-value的第三列和第四列
# iris.target = {0, 1, 2}, where '0' is setosa
# iris.data ~ [sepal.width, sepal.length, pedal.width, pedal.length]
iris = datasets.load_iris()
binary_target = np.array([1. if x==0 else 0. for x in iris.target])
iris_2d = np.array([[x[2], x[3]] for x in iris.data])
# 聲明批量訓練大小
batch_size = 20
# 初始化計算圖
sess = tf.Session()
# 聲明數據占位符
x1_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
x2_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
# 聲明模型變量
# Create variables A and b (0 = x1 - A*x2 + b)
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]))
# 定義線性模型:
# 如果找到的數據點在直線以上,則將數據點代入x2-x1*A-b計算出的結果大于0;
# 同理找到的數據點在直線以下,則將數據點代入x2-x1*A-b計算出的結果小于0。
# x1 - A*x2 + b
my_mult = tf.matmul(x2_data, A)
my_add = tf.add(my_mult, b)
my_output = tf.subtract(x1_data, my_add)
# 增加TensorFlow的sigmoid交叉熵損失函數(cross entropy)
xentropy = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=my_output, labels=y_target)
# 聲明優化器方法
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.05)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(xentropy)
# 創建一個變量初始化操作
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# 運行迭代1000次
for i in range(1000):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(iris_2d), size=batch_size)
# rand_x = np.transpose([iris_2d[rand_index]])
# 傳入三種數據:花瓣長度、花瓣寬度和目標變量
rand_x = iris_2d[rand_index]
rand_x1 = np.array([[x[0]] for x in rand_x])
rand_x2 = np.array([[x[1]] for x in rand_x])
#rand_y = np.transpose([binary_target[rand_index]])
rand_y = np.array([[y] for y in binary_target[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x1_data: rand_x1, x2_data: rand_x2, y_target: rand_y})
if (i+1)%200==0:
print('Step #' + str(i+1) + ' A = ' + str(sess.run(A)) + ', b = ' + str(sess.run(b)))
# 繪圖
# 獲取斜率/截距
# Pull out slope/intercept
[[slope]] = sess.run(A)
[[intercept]] = sess.run(b)
# 創建擬合線
x = np.linspace(0, 3, num=50)
ablineValues = []
for i in x:
ablineValues.append(slope*i+intercept)
# 繪制擬合曲線
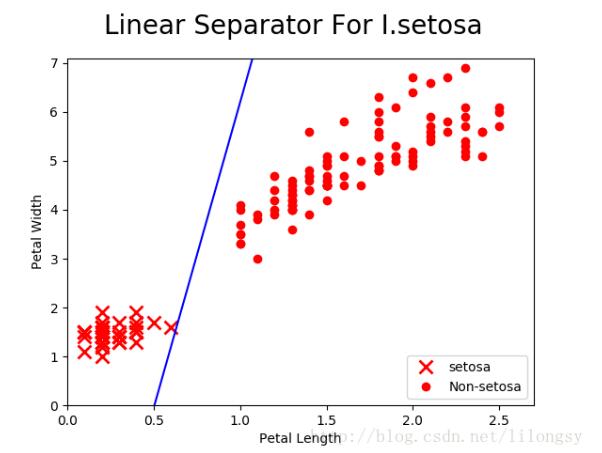
setosa_x = [a[1] for i,a in enumerate(iris_2d) if binary_target[i]==1]
setosa_y = [a[0] for i,a in enumerate(iris_2d) if binary_target[i]==1]
non_setosa_x = [a[1] for i,a in enumerate(iris_2d) if binary_target[i]==0]
non_setosa_y = [a[0] for i,a in enumerate(iris_2d) if binary_target[i]==0]
plt.plot(setosa_x, setosa_y, 'rx', ms=10, mew=2, label='setosa')
plt.plot(non_setosa_x, non_setosa_y, 'ro', label='Non-setosa')
plt.plot(x, ablineValues, 'b-')
plt.xlim([0.0, 2.7])
plt.ylim([0.0, 7.1])
plt.suptitle('Linear Separator For I.setosa', fontsize=20)
plt.xlabel('Petal Length')
plt.ylabel('Petal Width')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
輸出:
Step #200 A = [[ 8.70572948]], b = [[-3.46638322]] Step #400 A = [[ 10.21302414]], b = [[-4.720438]] Step #600 A = [[ 11.11844635]], b = [[-5.53361702]] Step #800 A = [[ 11.86427212]], b = [[-6.0110755]] Step #1000 A = [[ 12.49524498]], b = [[-6.29990339]]
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。