您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
Spring Security是為基于Spring的應用程序提供的一種聲明式安全性框架。它提供了一套完整的安全性解決方案,能夠在Web請求級別和方法調用級別處理身份認證和授權。
Spring Security可以從兩個方面來解決安全性問題:
使用Servlet規范中的Filter保護Web請求并限制URL級別的訪問
使用Spring AOP保護方法調用——借助于對象代理和使用通知,能夠確保只有具備適當權限的用戶才能方法安全保護的方法
下面我將簡單介紹Spring Security的最基礎的入門實例
(1)新建基于Spring MVC的Java Web項目:
導入Spring Security以及一些其他的spring相關的包之后,項目結構如下所示:
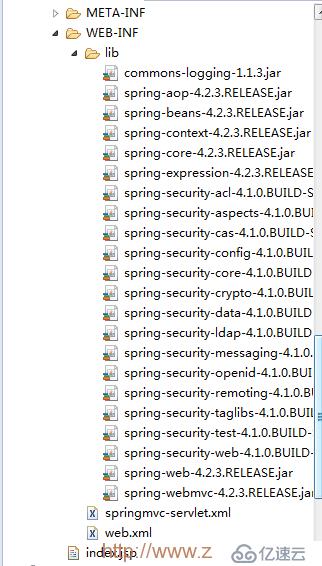
在這個測試項目中不需要再另寫Java文件,同時也不涉及到數據庫操作,實際上涉及到的文件只有:index.jsp、web.xml以及springmvc-servlet.xml文件
(2)web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" version="3.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.html</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> </web-app>
在這個web.xml中,除了定義的一些常規的Spring項目的配置之外,在文件的第30-38行定義了一個名為“springSecurityFilterChain”的filter,這個filter定義之后spring security保護web請求這個作用就開始生效了,spring security將會對請求的url進行攔截并判斷其權限
(3)springmvc-servlet.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:security="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-4.1.xsd">
<security:user-service id="userService">
<security:user name="admin" password="admin"
authorities="ROLE_USER,ROLE_ADMIN" />
<security:user name="zifangsky" password="www.zifangsky.cn"
authorities="ROLE_USER" />
</security:user-service>
<security:authentication-manager>
<security:authentication-provider
user-service-ref="userService" />
</security:authentication-manager>
<security:http pattern="/favicon.ico" security="none" />
<security:http auto-config="true">
<security:intercept-url pattern="/**"
access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')" />
</security:http>
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.zifangsky.* *.controller" />
<context:annotation-config /> <!-- 激活Bean中定義的注解 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
</beans>在這個配置文件中,實際上34行及之后的那些配置都是跟SpringMVC相關的,而之前的那些配置則是在定義spring security的權限校驗規則。
在第29-32行的配置中,“http”定義了一個Web相關的權限配置,同時“intercept-url”標簽則配置了權限控制規則,即:網站根目錄下的所有目錄都需要有“ROLE_USER”的權限才允許訪問。這將導致我們在訪問首頁的index.jsp文件都需要進行權限驗證,也就是說程序運行之后就需要登錄驗證,驗證通過之后才能訪問首頁及其他頁面。當然,這個登錄頁面是spring security默認自帶的,我在后面的文章中再說如何進行自定義這個登錄頁面
既然spring security需要驗證訪客的身份,那么就需要我們提供哪些用戶具有哪些訪問權限,也就是第22-25行配置的“authentication-manager”了,當然真正進行身份驗證的是“authentication-provider”這個元素,從上面代碼可以看出這里只是簡單引用了一個采用硬編碼的“user-service”,其里面定義了兩個角色以及它們所對應的權限。
注:真正生產環境中,用戶及其對應的權限這些信息是需要從數據庫中讀取的,這里為了理解方便就這樣硬編碼了
(4)index.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>Spring Security Demo</title> </head> <body> <div align="center"> Hello Spring Security! </div> </body> </html>
(5)運行測試:
運行項目之后,我們可以發現并沒有直接出現首頁,而是強制轉到了一個默認的登錄頁面:
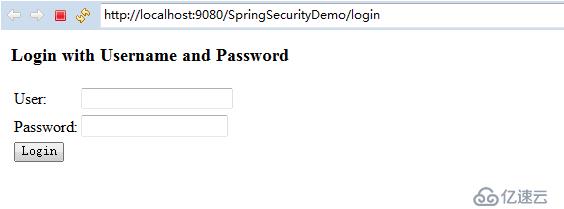
然后輸入上面定義的兩組用戶認證的其中一個,比如:admin/admin,然后就可以跳轉到正常的首頁中去了:
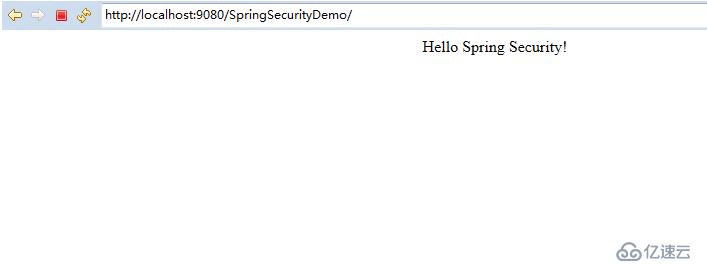
至此,這個最基本的spring security入門實例到此就結束了。不過我將在后面的文章中進一步說明spring security的其他用法
參考文章:
http://haohaoxuexi.iteye.com/blog/2154299
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。