您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
一、如下方式存在的問題
new?Thread()?{
????@Override
????public?void?run()?{
????????//?業務邏輯
????}
}.start();1、首先頻繁的創建、銷毀對象是一個很消耗性能的事情;
2、如果用戶量比較大,導致占用過多的資源,可能會導致我們的服務由于資源不足而宕機;
3、綜上所述,在實際的開發中,這種操作其實是不可取的一種方式。

二、使用線程池有什么優點
1、線程池中線程的使用率提升,減少對象的創建、銷毀;
2、線程池可以控制線程數,有效的提升服務器的使用資源,避免由于資源不足而發生宕機等問題;

三、線程池的四種使用方式
1、newCachedThreadPool
創建一個線程池,如果線程池中的線程數量過大,它可以有效的回收多余的線程,如果線程數不足,那么它可以創建新的線程。
public?static?void?method()?throws?Exception?{
????ExecutorService?executor?=?Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
????for?(int?i?=?0;?i?<?5;?i++)?{
????????final?int?index?=?i;
????????Thread.sleep(1000);
????????executor.execute(new?Runnable()?{
????????????@Override
????????????public?void?run()?{
????????????????System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()?+?"??"?+?index);
????????????}
????????});
????}
}執行結果
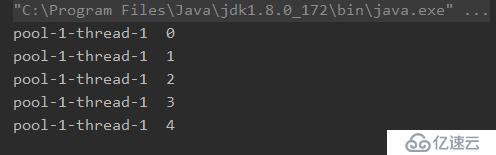
通過分析我看可以看到,至始至終都由一個線程執行,實現了線程的復用,并沒有創建多余的線程。
如果當我們的業務需要一定的時間進行處理,那么將會出現什么結果。我們來模擬一下。
可以明顯的看出,現在就需要幾條線程來交替執行。
不足:這種方式雖然可以根據業務場景自動的擴展線程數來處理我們的業務,但是最多需要多少個線程同時處理缺是我們無法控制的;
優點:如果當第二個任務開始,第一個任務已經執行結束,那么第二個任務會復用第一個任務創建的線程,并不會重新創建新的線程,提高了線程的復用率;
2、newFixedThreadPool
這種方式可以指定線程池中的線程數。舉個栗子,如果一間澡堂子最大只能容納20個人同時洗澡,那么后面來的人只能在外面排隊等待。如果硬往里沖,那么只會出現一種情景,摩擦摩擦...
首先測試一下最大容量為一個線程,那么會不會是我們預測的結果。
public?static?void?method_01()?throws?InterruptedException?{
????ExecutorService?executor?=?Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
????for?(int?i?=?0;?i?<?10;?i++)?{
????????Thread.sleep(1000);
????????final?int?index?=?i;
????????executor.execute(()?->?{
????????????try?{
????????????????Thread.sleep(2?*?1000);
????????????}?catch?(InterruptedException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????????System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()?+?"??"?+?index);
????????});
????}
????executor.shutdown();
}執行結果
我們改為3條線程再來看下結果
優點:兩個結果綜合說明,newFixedThreadPool的線程數是可以進行控制的,因此我們可以通過控制最大線程來使我們的服務器打到最大的使用率,同事又可以保證及時流量突然增大也不會占用服務器過多的資源。
3、newScheduledThreadPool
該線程池支持定時,以及周期性的任務執行,我們可以延遲任務的執行時間,也可以設置一個周期性的時間讓任務重復執行。 該線程池中有以下兩種延遲的方法。
scheduleAtFixedRate
測試一
public?static?void?method_02()?{
????ScheduledExecutorService?executor?=?Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
????executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new?Runnable()?{
????????@Override
????????public?void?run()?{
????????????long?start?=?new?Date().getTime();
????????????System.out.println("scheduleAtFixedRate?開始執行時間:"?+
????????????????????DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new?Date()));
????????????try?{
????????????????Thread.sleep(5000);
????????????}?catch?(InterruptedException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????????long?end?=?new?Date().getTime();
????????????System.out.println("scheduleAtFixedRate?執行花費時間="?+?(end?-?start)?/?1000?+?"m");
????????????System.out.println("scheduleAtFixedRate?執行完成時間:"?+?DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new?Date()));
????????????System.out.println("======================================");
????????}
????},?1,?5,?TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}執行結果

測試二
總結:以上兩種方式不同的地方是任務的執行時間,如果間隔時間大于任務的執行時間,任務不受執行時間的影響。如果間隔時間小于任務的執行時間,那么任務執行結束之后,會立馬執行,至此間隔時間就會被打亂。
scheduleWithFixedDelay
測試一
public?static?void?method_03()?{
????ScheduledExecutorService?executor?=?Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
????executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new?Runnable()?{
????????@Override
????????public?void?run()?{
????????????long?start?=?new?Date().getTime();
????????????System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay?開始執行時間:"?+
????????????????????DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new?Date()));
????????????try?{
????????????????Thread.sleep(1000);
????????????}?catch?(InterruptedException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????????long?end?=?new?Date().getTime();
????????????System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay執行花費時間="?+?(end?-?start)?/?1000?+?"m");
????????????System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay執行完成時間:"
????????????????????+?DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new?Date()));
????????????System.out.println("======================================");
????????}
????},?1,?2,?TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}執行結果

測試二
public?static?void?method_03()?{
????ScheduledExecutorService?executor?=?Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
????executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new?Runnable()?{
????????@Override
????????public?void?run()?{
????????????long?start?=?new?Date().getTime();
????????????System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay?開始執行時間:"?+
????????????????????DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new?Date()));
????????????try?{
????????????????Thread.sleep(5000);
????????????}?catch?(InterruptedException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????????long?end?=?new?Date().getTime();
????????????System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay執行花費時間="?+?(end?-?start)?/?1000?+?"m");
????????????System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay執行完成時間:"
????????????????????+?DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new?Date()));
????????????System.out.println("======================================");
????????}
????},?1,?2,?TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}執行結果
總結:同樣的,跟scheduleWithFixedDelay測試方法一樣,可以測出scheduleWithFixedDelay的間隔時間不會受任務執行時間長短的影響。
4、newSingleThreadExecutor
這是一個單線程池,至始至終都由一個線程來執行。
public?static?void?method_04()?{
????ExecutorService?executor?=?Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
????for?(int?i?=?0;?i?<?5;?i++)?{
????????final?int?index?=?i;
????????executor.execute(()?->?{
????????????try?{
????????????????Thread.sleep(2?*?1000);
????????????}?catch?(InterruptedException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????????System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()?+?"???"?+?index);
????????});
????}
????executor.shutdown();
}執行結果
四、線程池的作用
線程池的作用主要是為了提升系統的性能以及使用率。文章剛開始就提到,如果我們使用最簡單的方式創建線程,如果用戶量比較大,那么就會產生很多創建和銷毀線程的動作,這會導致服務器在創建和銷毀線程上消耗的性能可能要比處理實際業務花費的時間和性能更多。線程池就是為了解決這種這種問題而出現的。

歡迎大家關注我的公種浩【程序員追風】,文章都會在里面更新,整理的資料也會放在里面。
同樣思想的設計還有很多,比如數據庫連接池,由于頻繁的連接數據庫,然而創建連接是一個很消耗性能的事情,所有數據庫連接池就出現了。
最后
歡迎大家一起交流,喜歡文章記得點個贊喲,感謝支持!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。