您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“Java程序順序結構中邏輯控制語句的方法教程”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
一.順序結構
二.分支結構
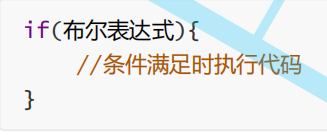
1.if語句
2.switch 語句
三. 循環結構
1 .while 循環
2. break
3. continue
4.for循環
5.do while循環
四.輸入輸出
1.輸出到控制臺
2 .從鍵盤輸入
五.練習
看前欣賞美圖!

上才藝!
目錄 一.順序結構二.分支結構1.if語句2.switch 語句 三. 循環結構1 .while 循環2. break3. continue4.for循環5.do while循環 四.輸入輸出1.輸出到控制臺2 .從鍵盤輸入 五.練習
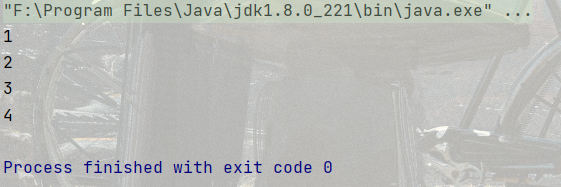
順序結構比較簡單. 像我們之前寫過的代碼就是順序結構的, 按照代碼書寫的順序一行一行執行就可以了
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println("2");
System.out.println("3");
System.out.println("4"); //順序結構`結果:
基本語法形式1
基本語法形式2

基本語法形式3

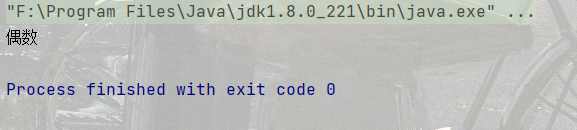
代碼示例: 判定一個數字是奇數還是偶數
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10;
if(n % 2 == 0){ //黃色框框是一個警告,計算機覺得它一定是真的
System.out.println("偶數");
}
else{
System.out.println("奇數");
}
}結果:
基本語法:
switch(整數|枚舉|字符|字符串){
case 內容1 : {
內容滿足時執行語句;
[break;]
}
case 內容2 : {
內容滿足時執行語句;
[break;]
}
…
default:{
內容都不滿足時執行語句;
[break;]
}
}
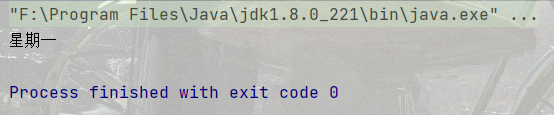
代碼示例: 根據 day 的值輸出星期
public static void main(String[] args) {
int day = 1;
switch(day) {
case 1:
System.out.println("星期一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("星期二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("星期三");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("星期四");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("星期五");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("星期六");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("星期日");
break;
default:
System.out.println("輸入有誤");
break;
}
}結果:
根據 switch 中值的不同, 會執行對應的 case 語句. 遇到 break 就會結束該 case 語句.
如果 switch 中的值沒有匹配的 case, 就會執行 default 中的語句.
我們建議一個 switch 語句最好都要帶上 default
注意事項1 break 不要遺漏, 否則會失去 “多分支選擇” 的效果
注意事項2 switch 中的值只能是 整數|枚舉|字符|字符串
注意事項3 switch 不能表達復雜的條件
注意事項4 switch 雖然支持嵌套, 但是很丑~
基本語法格式:
while(循環條件){
循環語句;
}
循環條件為 true, 則執行循環語句; 否則結束循環。
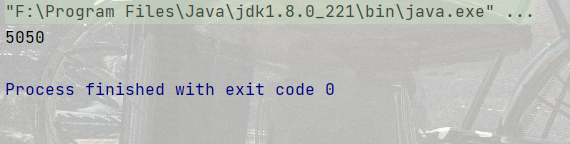
代碼示例1: 計算 1 - 100的數字之和
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1;
int result = 0;
while (n <= 100) {
result += n;
n++;
}
System.out.println(result);
}結果:
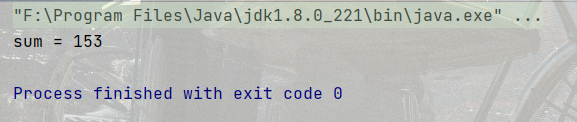
代碼示例2: 計算 1! + 2! + 3! + 4! + 5!
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 1;
int sum = 0;
// 外層循環負責求階乘的和
while (num <= 5) {
int factorResult = 1;
int tmp = 1;
// 里層循環負責完成求階乘的細節.
while (tmp <= num) {
factorResult *= tmp;
tmp++;
}
sum += factorResult;
num++;
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}結果:
這里我們發現, 當一個代碼中帶有多重循環的時候, 代碼的復雜程度就大大提高了. 而比較復雜的代碼就更容易出錯.
后面我們會采用更簡單的辦法來解決這個問題
注意事項
和 if 類似, while 下面的語句可以不寫 { } , 但是不寫的時候只能支持一條語句. 建議還是加上 { }
和 if 類似, while 后面的 { 建議和 while 寫在同一行.
和 if 類似, while 后面不要多寫 分號, 否則可能導致循環不能正確執行
int num = 1;
while (num <= 10); {
System.out.println(num);
num++;
}// 執行結果
[無任何輸出, 程序死循環]
此時 ; 為 while 的語句體(這是一個空語句), 實際的 { } 部分和循環無關. 此時循環條件 num <= 10 恒成立, 導致代碼死循環了.
break 的功能是讓循環提前結束.
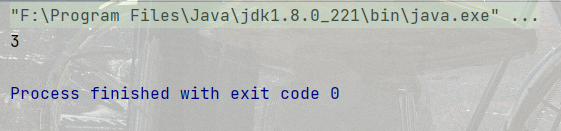
代碼示例: 找到第一個 3 的倍數
//找到第一個被3整除的數
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while(i<=10){
if(i%3==0){
System.out.println(i);
break; //結束所有的循環
}
i++;
}
}結果:
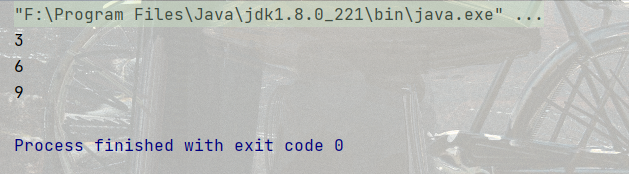
continue 的功能是跳過這次循環, 立即進入下次循環.
代碼示例: 找到 1-10中所有 3 的倍數
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while(i<=10){
if(i%3!=0){
i++;
continue; //結束本趟循環
}
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}結果:
基本語法
for(表達式1;表達式2;表達式3){
循環體;
}
表達式1: 用于初始化循環變量.
表達式2: 循環條件.
表達式3: 更新循環變量.
相比于 while 循環, for 循環將這三個部分合并在一起, 寫代碼時不容易遺漏.
**代碼示例1:**計算1-100的和
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}結果:
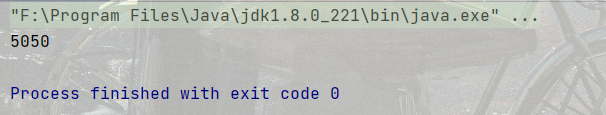
代碼示例2: 計算 5 的階乘
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}結果:
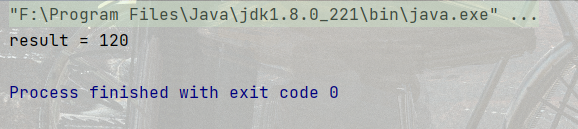
注意事項 (和while循環類似)
和 if 類似, for 下面的語句可以不寫 { } , 但是不寫的時候只能支持一條語句. 建議還是加上 { }
和 if 類似, for 后面的 { 建議和 while 寫在同一行.
和 if 類似, for 后面不要多寫 分號, 否則可能導致循環不能正確執行
基本語法
do{
循環語句;
}while(循環條件);
先執行循環語句, 再判定循環條件
**代碼示例:**打印1-10
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 1;
do {
System.out.print(num+" ");
num++;
} while (num <= 10);
}結果:
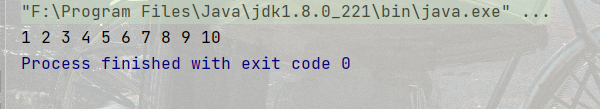
有一點注意一下
public static void main21(String[] args) {
int i=0;
do{
System.out.println("haha");
}while(i!=0); //最少都要執行一次
}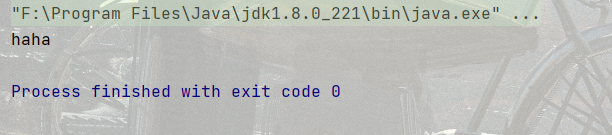
它最少都要執行一次。
注意事項
do while 循環最后的分號不要忘記
一般 do while 很少用到, 更推薦使用 for 和 while.
基本語法
System.out.println(msg); // 輸出一個字符串, 帶換行
System.out.print(msg); // 輸出一個字符串, 不帶換行
System.out.printf(format, msg); // 格式化輸出println 輸出的內容自帶 \n, print 不帶 \n
printf 的格式化輸出方式和 C 語言的 printf 是基本一致的
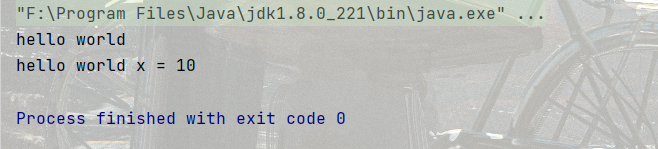
代碼示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello world");
System.out.print("hello world ");
int x = 10;
System.out.printf("x = %d\n", x);
}結果:
格式化字符串
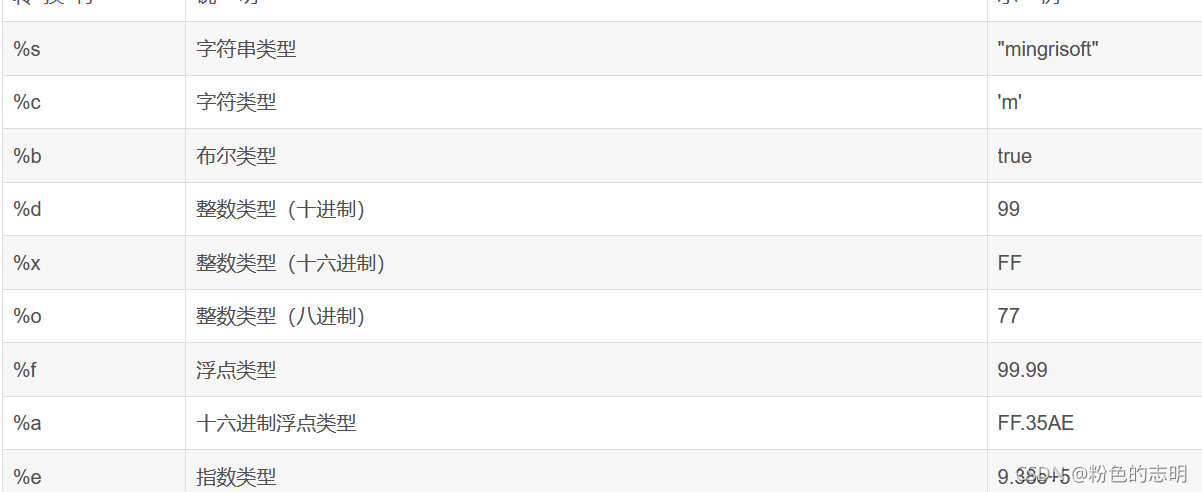
沒必要太用心記,用的時候查一下就知道了。
使用 Scanner 讀取字符串/整數/浮點數
代碼示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入你的姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入你的年齡:");
int age = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("請輸入你的工資:");
float salary = sc.nextFloat();
System.out.println("你的信息如下:");
System.out.println("姓名: "+name+"\n"+"年齡:"+age+"\n"+"工資:"+salary);
sc.close();
}結果:

這里給大家做幾個高頻練習題:
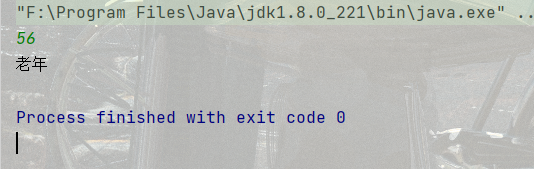
1.根據年齡, 來打印出當前年齡的人是少年(低于18), 青年(19-28), 中年(29-55), 老年(56以上)
代碼實現:
public static void main5(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int Age = scanner.nextInt();
while(Age>0) {
if ( Age <= 18) {
System.out.println("少年");
break;
} else if (Age > 18 && Age <= 28) {
System.out.println("青年");
break;
} else if (Age > 28 && Age <= 55) {
System.out.println("中年");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("老年");
break;
}
}
}打印結果:
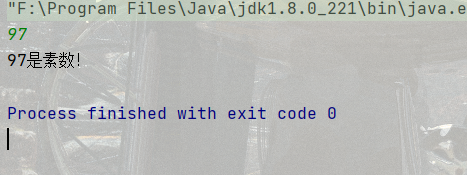
2. 判定一個數字是否是素數
代碼實現:
public static void main4(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int Num = scanner.nextInt();
int i;
for (i = 2; i < Num; i++) {
if (Num % i == 0) {
System.out.println(Num + "不是素數");
break;
}
}
if (Num==i){
System.out.println(Num+"是素數");
}
}打印結果:
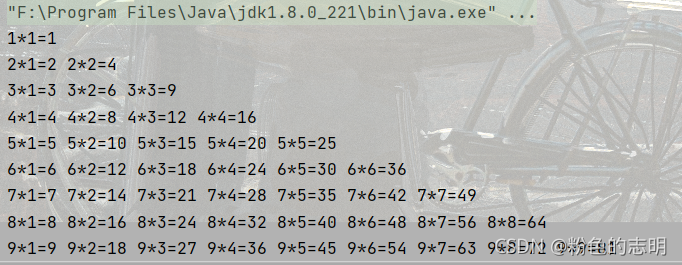
3.輸出乘法口訣表
代碼實現:
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 9 ; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i ; j++) {
System.out.print(i+"*"+j+"="+i*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}打印結果:
4. 編寫代碼模擬三次密碼輸入的場景。 最多能輸入三次密碼,密碼正確,提示“登錄成功”,密碼錯誤, 可以重新輸入,最多輸入三次。三次均錯,則提示退出程序
代碼實現:
public static void login(){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int count = 3;
while(count != 0){
System.out.println("請輸入你的密碼:");
String password = scanner.nextLine();
if(password.equals("123456")){
System.out.println("登陸成功了!");
break;
}else{
count--;
System.out.println("你輸錯密碼了,你還有 "+count+"次機會!");
}
}
}
public static void main16(String[] args) {
login();
}打印結果:

這里用到了方法,后面在說。
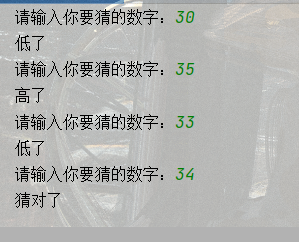
5.猜數字游戲
代碼實現:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int rand = random.nextInt(100);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.print("請輸入你要猜的數字:");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
if (n < rand) {
System.out.println("低了");
} else if (n > rand) {
System.out.println("高了");
} else {
System.out.println("猜對了");
break;
}
}
}打印結果:
“Java程序順序結構中邏輯控制語句的方法教程”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。