您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“如何使用Java異步編程”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在如何使用Java異步編程問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”如何使用Java異步編程”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
//使用內置線程ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根據supplier構建執行任務 public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) //指定自定義線程,根據supplier構建執行任務 public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
//使用內置線程ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根據runnable構建執行任務 public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) //指定自定義線程,根據runnable構建執行任務 public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
使用示例
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> rFuture = CompletableFuture
.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("hello siting"), executor);
//supplyAsync的使用
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.print("hello ");
return "siting";
}, executor);
//阻塞等待,runAsync 的future 無返回值,輸出null
System.out.println(rFuture.join());
//阻塞等待
String name = future.join();
System.out.println(name);
executor.shutdown(); // 線程池需要關閉
--------輸出結果--------
hello siting
null
hello siting//有時候是需要構建一個常量的CompletableFuture public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> completedFuture(U value)
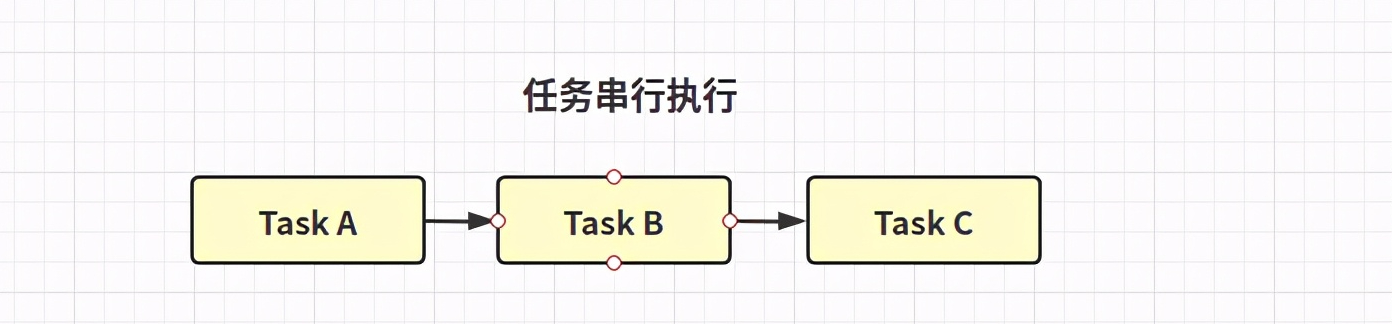
任務完成則運行action,不關心上一個任務的結果,無返回值
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action, Executor executor)
使用示例
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "hello siting", executor)
.thenRunAsync(() -> System.out.println("OK"), executor);
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
OKpublic CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor)
使用示例
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture .supplyAsync(() -> "hello siting", executor) .thenAcceptAsync(System.out::println, executor); executor.shutdown(); --------輸出結果-------- hello siting
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
使用示例
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "hello world", executor)
.thenApplyAsync(data -> {
System.out.println(data); return "OK";
}, executor);
System.out.println(future.join());
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
hello world
OK類似thenApply(區別是thenCompose的返回值是CompletionStage,thenApply則是返回 U),提供該方法為了和其他CompletableFuture任務更好地配套組合使用
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor)
使用示例
//第一個異步任務,常量任務
CompletableFuture<String> f = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("OK");
//第二個異步任務
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "hello world", executor)
.thenComposeAsync(data -> {
System.out.println(data); return f; //使用第一個任務作為返回
}, executor);
System.out.println(future.join());
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
hello world
OK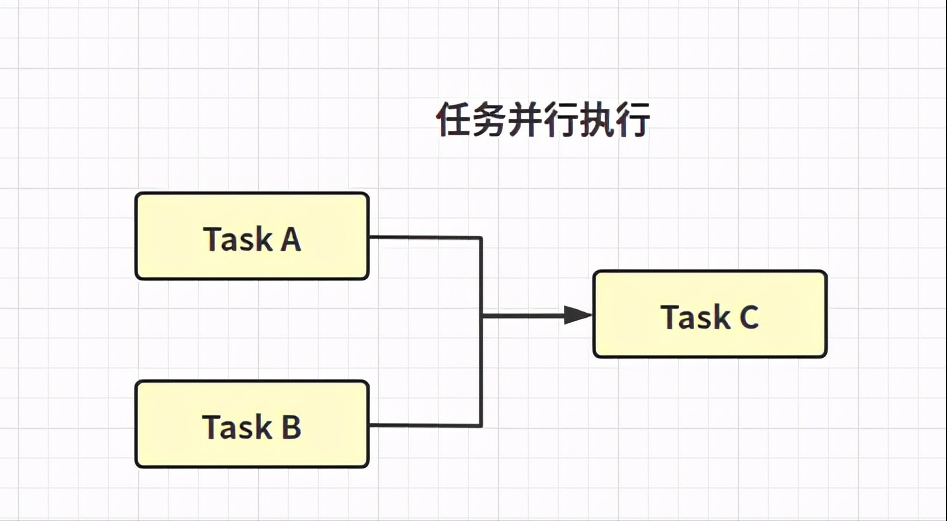
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action) public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action) public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor)
使用示例
//第一個異步任務,常量任務
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello world");
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
//第二個異步任務
.supplyAsync(() -> "hello siting", executor)
// () -> System.out.println("OK") 是第三個任務
.runAfterBothAsync(first, () -> System.out.println("OK"), executor);
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
OK//第一個任務完成再運行other,fn再依賴消費兩個任務的結果,無返回值 public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action) //兩個任務異步完成,fn再依賴消費兩個任務的結果,無返回值 public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action) //兩個任務異步完成(第二個任務用指定線程池執行),fn再依賴消費兩個任務的結果,無返回值 public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor)
使用示例
//第一個異步任務,常量任務
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello world");
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
//第二個異步任務
.supplyAsync(() -> "hello siting", executor)
// (w, s) -> System.out.println(s) 是第三個任務
.thenAcceptBothAsync(first, (s, w) -> System.out.println(s), executor);
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
hello siting//第一個任務完成再運行other,fn再依賴消費兩個任務的結果,有返回值 public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) //兩個任務異步完成,fn再依賴消費兩個任務的結果,有返回值 public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) //兩個任務異步完成(第二個任務用指定線程池執行),fn再依賴消費兩個任務的結果,有返回值 public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor)
使用示例
//第一個異步任務,常量任務
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello world");
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
//第二個異步任務
.supplyAsync(() -> "hello siting", executor)
// (w, s) -> System.out.println(s) 是第三個任務
.thenCombineAsync(first, (s, w) -> {
System.out.println(s);
return "OK";
}, executor);
System.out.println(future.join());
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
hello siting
OK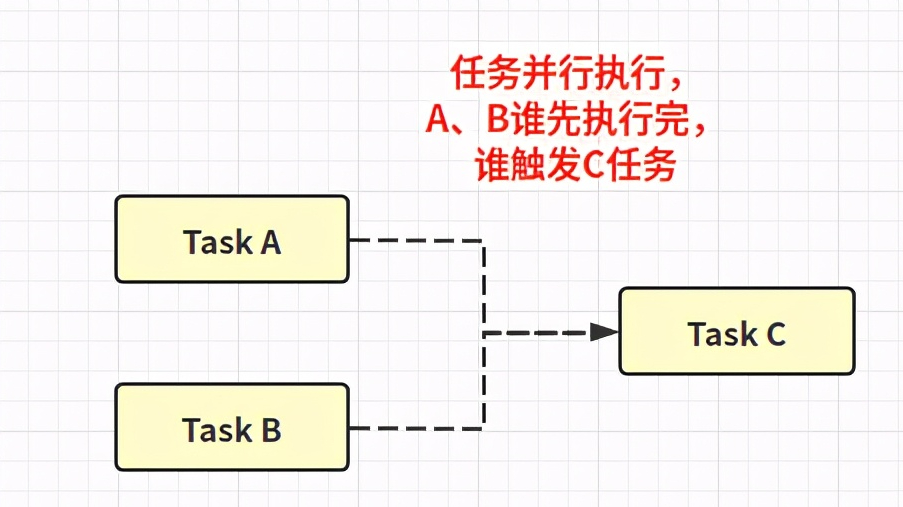
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action) public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action) public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor)
使用示例
//第一個異步任務,休眠1秒,保證最晚執行晚
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (Exception e){}
System.out.println("hello world");
return "hello world";
});
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
//第二個異步任務
.supplyAsync(() ->{
System.out.println("hello siting");
return "hello siting";
} , executor)
//() -> System.out.println("OK") 是第三個任務
.runAfterEitherAsync(first, () -> System.out.println("OK") , executor);
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
hello siting
OKpublic CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action) public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor) public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor)
使用示例
//第一個異步任務,休眠1秒,保證最晚執行晚
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (Exception e){}
return "hello world";
});
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
//第二個異步任務
.supplyAsync(() -> "hello siting", executor)
// data -> System.out.println(data) 是第三個任務
.acceptEitherAsync(first, data -> System.out.println(data) , executor);
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
hello sitingpublic <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn, Executor executor)
使用示例
//第一個異步任務,休眠1秒,保證最晚執行晚
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (Exception e){}
return "hello world";
});
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
//第二個異步任務
.supplyAsync(() -> "hello siting", executor)
// data -> System.out.println(data) 是第三個任務
.applyToEitherAsync(first, data -> {
System.out.println(data);
return "OK";
} , executor);
System.out.println(future);
executor.shutdown();
--------輸出結果--------
hello siting
OK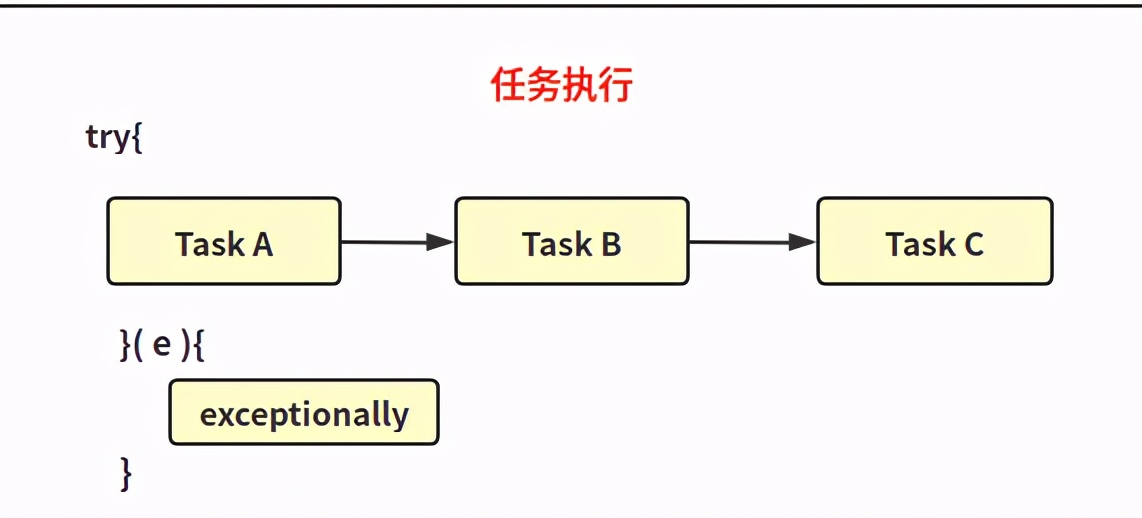
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn)
如果之前的處理環節有異常問題,則會觸發exceptionally的調用相當于 try...catch
使用示例
CompletableFuture<Integer> first = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("main error!");
}
return "hello world";
})
.thenApply(data -> 1)
.exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace(); // 異常捕捉處理,前面兩個處理環節的日常都能捕獲
return 0;
});相比exceptionally而言,即可處理上一環節的異常也可以處理其正常返回值
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
使用示例
CompletableFuture<Integer> first = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (true) { throw new RuntimeException("main error!"); }
return "hello world";
})
.thenApply(data -> 1)
.handleAsync((data,e) -> {
e.printStackTrace(); // 異常捕捉處理
return data;
});
System.out.println(first.join());
--------輸出結果--------
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: main error!
... 5 more
nullwhenComplete與handle的區別在于,它不參與返回結果的處理,把它當成監聽器即可
即使異常被處理,在CompletableFuture外層,異常也會再次復現
使用whenCompleteAsync時,返回結果則需要考慮多線程操作問題,畢竟會出現兩個線程同時操作一個結果
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
使用示例
CompletableFuture<AtomicBoolean> first = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (true) { throw new RuntimeException("main error!"); }
return "hello world";
})
.thenApply(data -> new AtomicBoolean(false))
.whenCompleteAsync((data,e) -> {
//異常捕捉處理, 但是異常還是會在外層復現
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
});
first.join();
--------輸出結果--------
java.lang.RuntimeException: main error!
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: main error!
... 5 morepublic static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
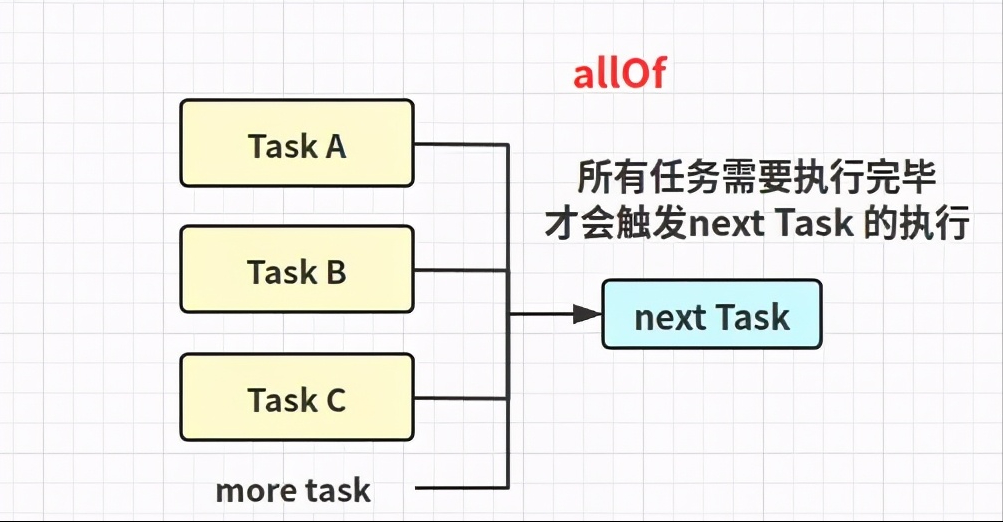
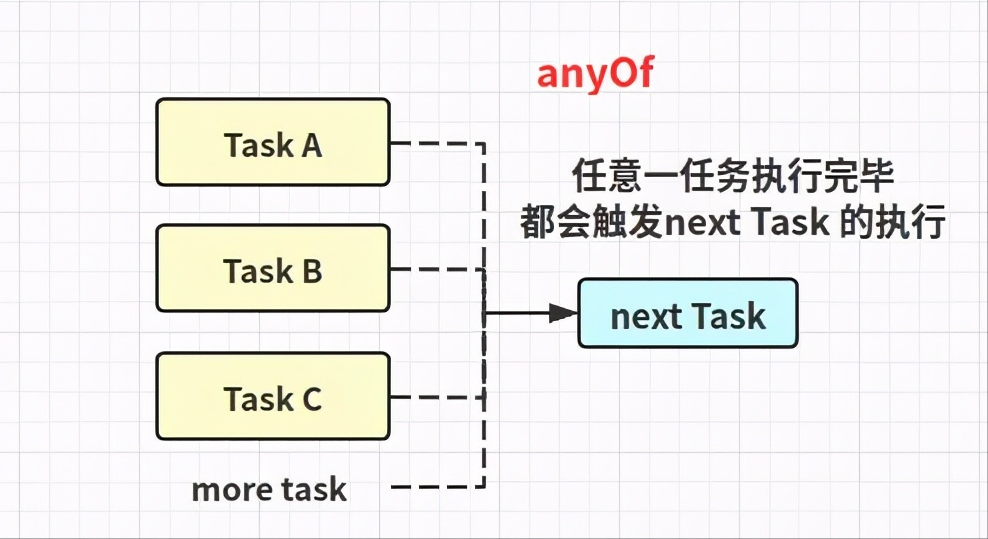
使用示例
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
.allOf(CompletableFuture.completedFuture("A"),
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("B"));
//全部任務都需要執行完
future.join();
CompletableFuture<Object> future2 = CompletableFuture
.anyOf(CompletableFuture.completedFuture("C"),
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("D"));
//其中一個任務行完即可
future2.join();// mayInterruptIfRunning 無影響;如果任務未完成,則返回異常 public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) //任務是否取消 public boolean isCancelled()
使用示例
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (Exception e) { }
return "hello world";
})
.thenApply(data -> 1);
System.out.println("任務取消前:" + future.isCancelled());
// 如果任務未完成,則返回異常,需要對使用exceptionally,handle 對結果處理
future.cancel(true);
System.out.println("任務取消后:" + future.isCancelled());
future = future.exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
});
System.out.println(future.join());
--------輸出結果--------
任務取消前:false
任務取消后:true
java.util.concurrent.CancellationException
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.cancel(CompletableFuture.java:2276)
at Test.main(Test.java:25)
0// 任務是否執行完成 public boolean isDone() //阻塞等待 獲取返回值 public T join() // 阻塞等待 獲取返回值,區別是get需要返回受檢異常 public T get() //等待阻塞一段時間,并獲取返回值 public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) //未完成則返回指定value public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent) //未完成,使用value作為任務執行的結果,任務結束。需要future.get獲取 public boolean complete(T value) //未完成,則是異常調用,返回異常結果,任務結束 public boolean completeExceptionally(Throwable ex) //判斷任務是否因發生異常結束的 public boolean isCompletedExceptionally() //強制地將返回值設置為value,無論該之前任務是否完成;類似complete public void obtrudeValue(T value) //強制地讓異常拋出,異常返回,無論該之前任務是否完成;類似completeExceptionally public void obtrudeException(Throwable ex)
使用示例
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (Exception e) { }
return "hello world";
})
.thenApply(data -> 1);
System.out.println("任務完成前:" + future.isDone());
future.complete(10);
System.out.println("任務完成后:" + future.join());
--------輸出結果--------
任務完成前:false
任務完成后:10到此,關于“如何使用Java異步編程”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。