您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文實例為大家分享了Android實現滑動效果的具體代碼,供大家參考,具體內容如下
坐標系與視圖坐標系相輔相成
1、坐標系:描述了View在屏幕中的位置關系(以屏幕最左上角的頂點作為Android坐標系的原點)
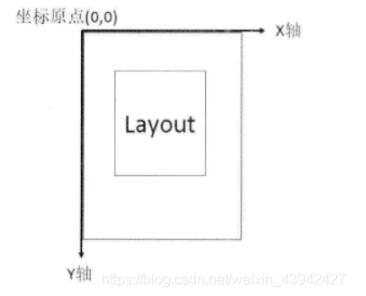
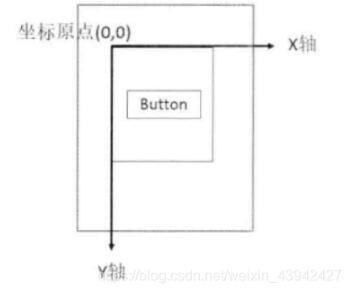
2、視圖坐標系:描述了子視圖在父視圖中的位置關系(以父視圖最左上角為坐標系原點)
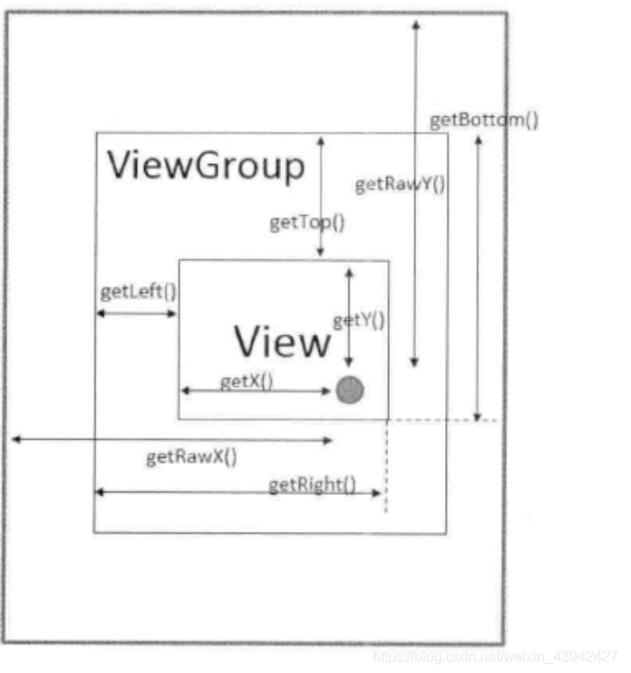
獲取坐標值的方法
1.View提供的獲取坐標方法
getTop():獲取到的是View自身的頂邊到其父布局頂邊的距離
getLeft():獲取到的是View自身的左邊到其父布局頂邊的距離
getRight():獲取到的是View自身的右邊到其父布局頂邊的距離
getBottom():獲取到的是View自身的底邊到其父布局頂邊的距離
2. MotionEvent提供的方法
getX():獲取點擊事件距離控件左邊的距離,即視圖坐標
getY():獲取點擊事件距離控件頂邊的距離,即視圖坐標
getRawX():獲取點擊事件距離整個屏幕左邊的距離,即絕對坐標
getRawY():獲取點擊事件距離整個屏幕右邊的距離,即絕對坐標
實現滑動的七種方法
1.layout方法
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: //計算偏移量 int offsetX=x-lastX; int offsetY=y-lastY; layout(getLeft()+offsetX,getTop()+offsetY,getRight()+offsetX,getBottom()+offsetY); break;
2.offsetLeftAndRight()與 offsetTopAndBottom()
offsetLeftAndRight(offsetX); offsetTopAndBottom(offsetY);
3.LayoutParams
LinearLayout.LayoutParams params= (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) getLayoutParams(); params.leftMargin= getLeft()+offsetX; params.topMargin= getTop()+offsetY; setLayoutParams(params);
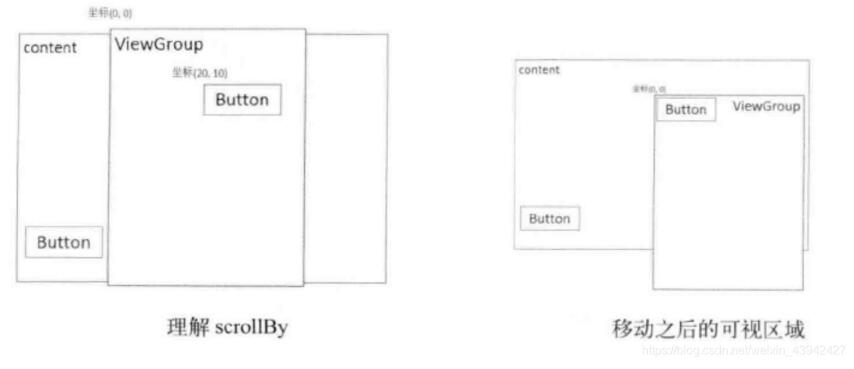
4.scrollBy()與scrollTo()
scrollBy(x,y)表示移動到一個具體的位置
scrollTo(dx,dy)表示移動的增量為dx,dy
int offsetX=x-lastX; int offsetY=y-lastY; View parent= (View) getParent(); parent.scrollBy(-offsetX,-offsetY);
5.Scroller
通過Scroller類可以實現平滑移動的效果,而不是瞬間完成的效果,與動畫的實現原理基本相似
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll();
//判斷scroller是否執行完畢
if (scroller.computeScrollOffset()){
View view= (View) getParent();
//獲得當前的滑動坐標
view.scrollTo(scroller.getCurrX(),scroller.getCurrY());
//通過重繪來不斷調用computeScroll
invalidate();
//invalidate()--->draw()---->computeScroll()
}
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: //手指離開時,執行滑動過程 View viewGroup= (View) getParent(); scroller.startScroll( viewGroup.getScrollX(), viewGroup.getScrollY(), -viewGroup.getScrollX(), -viewGroup.getScrollY(),500); invalidate(); break;
6.屬性動畫
7.ViewDragHelper類
public class DrawGroup extends FrameLayout {
private ViewDragHelper helper;
private View mainView,menuView;
public DrawGroup(@NonNull Context context) {
super(context);
inView();
}
public DrawGroup(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
inView();
}
public DrawGroup(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
inView();
}
private void inView(){
helper=ViewDragHelper.create(this, new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(@NonNull View child, int pointerId) {
//如果當前觸摸的child是mainView時開始檢測
return child==mainView;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(@NonNull View child, int left, int dx) {
//水平方向上的滑動
return left;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(@NonNull View child, int top, int dy) {
//垂直方向上的滑動
return 0;
}
@Override
public void onViewReleased(@NonNull View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
//拖動結束后調用
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
//手指抬起后緩慢移動到指定位置
if (mainView.getLeft()<300){
//關閉菜單
helper.smoothSlideViewTo(mainView,0,0);
//相當于scroller的startScroll方法
}else {
//打開菜單
helper.smoothSlideViewTo(mainView,300,0);
}
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(DrawGroup.this);
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return helper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//將觸摸事件傳遞給ViewDragHelper,此操作必不可少
helper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (helper.continueSettling(true)){
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
}
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate();
//加載完布局調用
menuView=getChildAt(0);
mainView=getChildAt(1);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。