您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
用python實現梯度下降算法的方式是什么?這個問題可能是我們日常學習或工作經常見到的。希望通過這個問題能讓你收獲頗深。下面是小編給大家帶來的參考內容,讓我們一起來看看吧!
python版本選擇
這里選的python版本是2.7,因為我之前用python3試了幾次,發現在畫3d圖的時候會報錯,所以改用了2.7。
(推薦教程:Python入門教程)
數據集選擇
數據集我選了一個包含兩個變量,三個參數的數據集,這樣可以畫出3d圖形對結果進行驗證。
部分函數總結
symbols()函數:首先要安裝sympy庫才可以使用。用法:
>>> x1 = symbols('x2')
>>> x1 + 1
x2 + 1在這個例子中,x1和x2是不一樣的,x2代表的是一個函數的變量,而x1代表的是python中的一個變量,它可以表示函數的變量,也可以表示其他的任何量,它替代x2進行函數的計算。實際使用的時候我們可以將x1,x2都命名為x,但是我們要知道他們倆的區別。
再看看這個例子:
>>> x = symbols('x')
>>> expr = x + 1
>>> x = 2
>>> print(expr)
x + 1作為python變量的x被2這個數值覆蓋了,所以它現在不再表示函數變量x,而expr依然是函數變量x+1的別名,所以結果依然是x+1。
subs()函數:既然普通的方法無法為函數變量賦值,那就肯定有函數來實現這個功能,用法:
>>> (1 + x*y).subs(x, pi)#一個參數時的用法
pi*y + 1
>>> (1 + x*y).subs({x:pi, y:2})#多個參數時的用法
1 + 2*pidiff()函數:求偏導數,用法:result=diff(fun,x),這個就是求fun函數對x變量的偏導數,結果result也是一個變量,需要賦值才能得到準確結果。
代碼實現:
from __future__ import division
from sympy import symbols, diff, expand
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
data = {'x1': [100, 50, 100, 100, 50, 80, 75, 65, 90, 90],
'x2': [4, 3, 4, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2],
'y': [9.3, 4.8, 8.9, 6.5, 4.2, 6.2, 7.4, 6.0, 7.6, 6.1]}#初始化數據集
theta0, theta1, theta2 = symbols('theta0 theta1 theta2', real=True) # y=theta0+theta1*x1+theta2*x2,定義參數
costfuc = 0 * theta0
for i in range(10):
costfuc += (theta0 + theta1 * data['x1'][i] + theta2 * data['x2'][i] - data['y'][i]) ** 2
costfuc /= 20#初始化代價函數
dtheta0 = diff(costfuc, theta0)
dtheta1 = diff(costfuc, theta1)
dtheta2 = diff(costfuc, theta2)
rtheta0 = 1
rtheta1 = 1
rtheta2 = 1#為參數賦初始值
costvalue = costfuc.subs({theta0: rtheta0, theta1: rtheta1, theta2: rtheta2})
newcostvalue = 0#用cost的值的變化程度來判斷是否已經到最小值了
count = 0
alpha = 0.0001#設置學習率,一定要設置的比較小,否則無法到達最小值
while (costvalue - newcostvalue > 0.00001 or newcostvalue - costvalue > 0.00001) and count < 1000:
count += 1
costvalue = newcostvalue
rtheta0 = rtheta0 - alpha * dtheta0.subs({theta0: rtheta0, theta1: rtheta1, theta2: rtheta2})
rtheta1 = rtheta1 - alpha * dtheta1.subs({theta0: rtheta0, theta1: rtheta1, theta2: rtheta2})
rtheta2 = rtheta2 - alpha * dtheta2.subs({theta0: rtheta0, theta1: rtheta1, theta2: rtheta2})
newcostvalue = costfuc.subs({theta0: rtheta0, theta1: rtheta1, theta2: rtheta2})
rtheta0 = round(rtheta0, 4)
rtheta1 = round(rtheta1, 4)
rtheta2 = round(rtheta2, 4)#給結果保留4位小數,防止數值溢出
print(rtheta0, rtheta1, rtheta2)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
ax.scatter(data['x1'], data['x2'], data['y']) # 繪制散點圖
xx = np.arange(20, 100, 1)
yy = np.arange(1, 5, 0.05)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(xx, yy)
Z = X * rtheta1 + Y * rtheta2 + rtheta0
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow'))
plt.show()#繪制3d圖進行驗證結果:
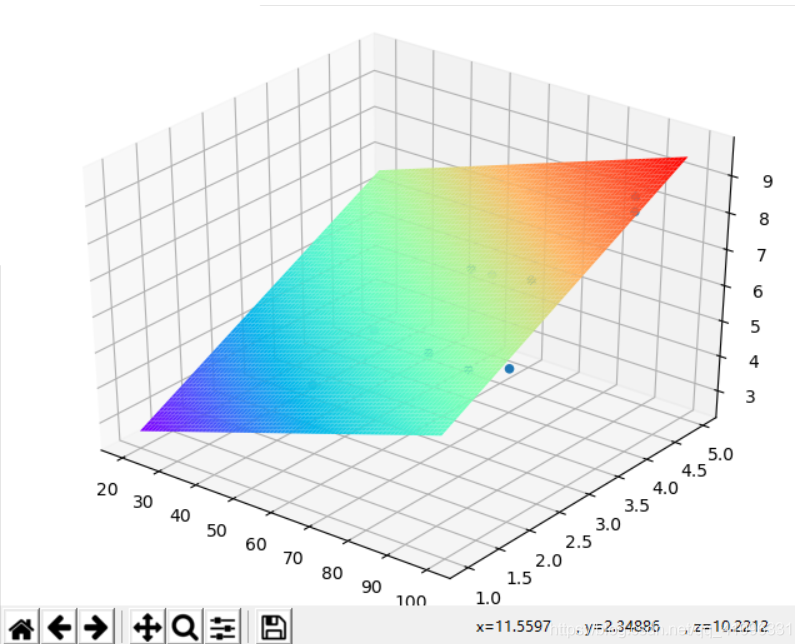
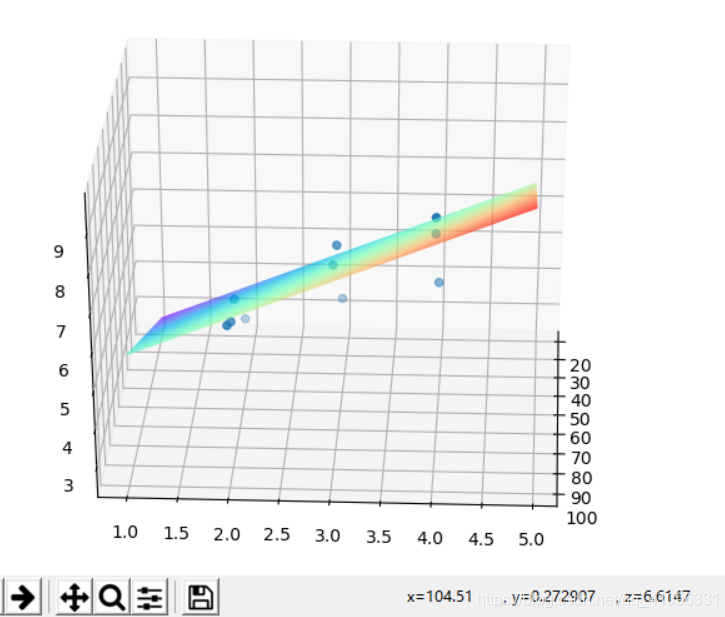
感謝各位的閱讀!看完上述內容,你們對用python實現梯度下降算法的方式是什么大概了解了嗎?希望文章內容對大家有所幫助。如果想了解更多相關文章內容,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。