您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
使用ORM框架我們更多的是使用其查詢功能,那么查詢海量數據則又離不開性能,那么這篇中我們就看下mybatis高級應用之延遲加載、一級緩存、二級緩存。使用時需要注意延遲加載必須使用resultMap,resultType不具有延遲加載功能。
一、延遲加載
延遲加載已經是老生常談的問題,什么最大化利用數據庫性能之類之類的,也懶的列舉了,總是我一提到延遲加載腦子里就會想起來了Hibernate get和load的區別。OK,廢話少說,直接看代碼。 先來修改配置項xml。
注意,編寫mybatis.xml時需要注意配置節點的先后順序,settings在最前面,否則會報錯。
<settings> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> </settings>
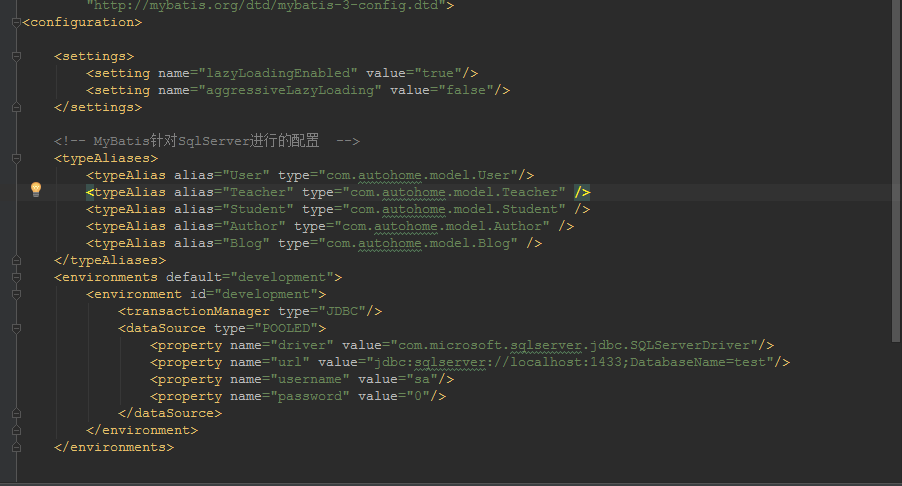
前面提到延遲加載只能通過association、collection來實現,因為只有存在關聯關系映射的業務場景里你才需要延遲加載,也叫懶加載,也就是常說的用的時候再去加載。OK,那么我們來配一個association來實現:
我來編寫一個加載博客列表的同時加載出博客額作者, 主要功能點在id為blogAuthorResumtMap這個resultmap上,其中使用了association,關鍵點是它的select屬性,該屬性也就是你需要懶加載調用的statment id。 當然需要懶加載的statement 返回值當然是resultmap
<resultMap id="blogAuthorResumtMap" type="Blog">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="title" property="title"/>
<result column="category" property="category"/>
<result column="author_id" property="author_id"/>
<!--使用assocition支持延遲加載功能,配置延遲加載關聯關系-->
<association property="author" javaType="Author" select="selectAuthorById" column="author_id"/>
</resultMap>
<!--要使用延遲記載的方法-->
<select id="selectBlogAuthor" resultMap="blogAuthorResumtMap">
SELECT id,title,category,author_id FROM t_blog
</select>
<!--延遲加載查詢博客對應的作者方法-->
<select id="selectAuthorById" parameterType="int" resultType="Author">
SELECT id,name from t_author where id=#{value}
</select>
OK,來看測試結果:
@Test
public void getBlogAuthorByLazyloading(){
SqlSession sqlSession=null;
try{
sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
List<Blog> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectBlogAuthor");
for (Blog blog:list) {
System.out.println("id:"+blog.getId()+",title:"+blog.getTitle()+",category:"+blog.getCategory());
System.out.println("author:"+blog.getAuthor().getName());
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
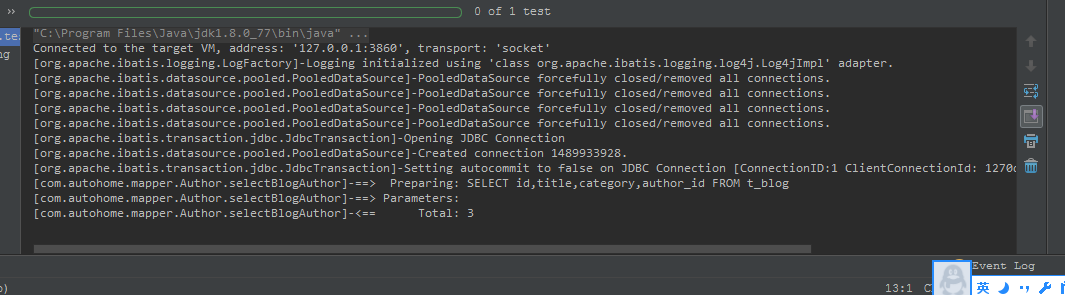
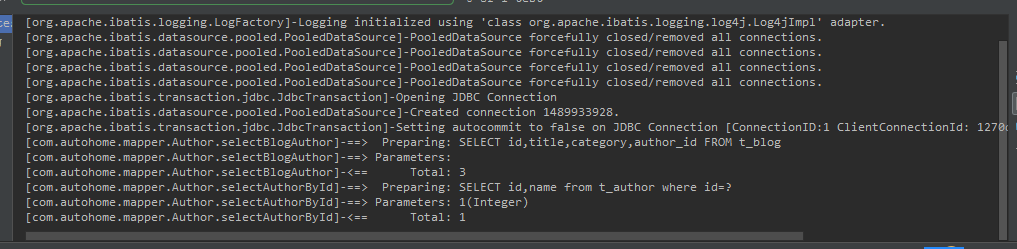
從圖一中看出,執行selectBlogAuthor返回List<Blog>對象時只執行了SQL SELECT id,title,category,author_id from t_blog,循環遍歷時才去執行select id,name from t_author where id=?。
二、一級緩存
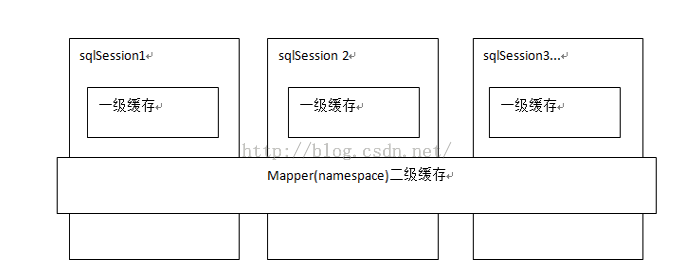
了解緩存前我們先看一張圖片(圖片來源于傳智播客視頻圖片)。從圖中可以了解一級緩存是sqlsession級別、二級緩存是mapper級別。在操作數據庫時我們需要先構造sqlsession【默認實現是DefaultSqlSession.java】,在對象中有一個數據結構【hashmap】來存儲緩存數據。不同的sqlsession區域是互不影響的。 如果同一個sqlsession之間,如果多次查詢之間執行了commit,則緩存失效,mybatis避免臟讀。
OK,在看mybatis一級緩存時,我總是覺的一級緩存有點雞肋,兩個查詢如果得到一樣的數據,你還會執行第二次么,果斷引用第一次的返回值了。 可能還沒了解到一級緩存的奧妙之處。一級緩存默認是開啟的,不需要額外設置,直接使用。
public void testCache(){
SqlSession sqlSession=null;
try{
sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Author author = sqlSession.selectOne("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectAuthorById",1);
System.out.println("作者信息 id:"+author.getId()+",name:"+author.getName());
author = sqlSession.selectOne("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectAuthorById",1);
System.out.println("作者信息2 id:"+author.getId()+",name:"+author.getName());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
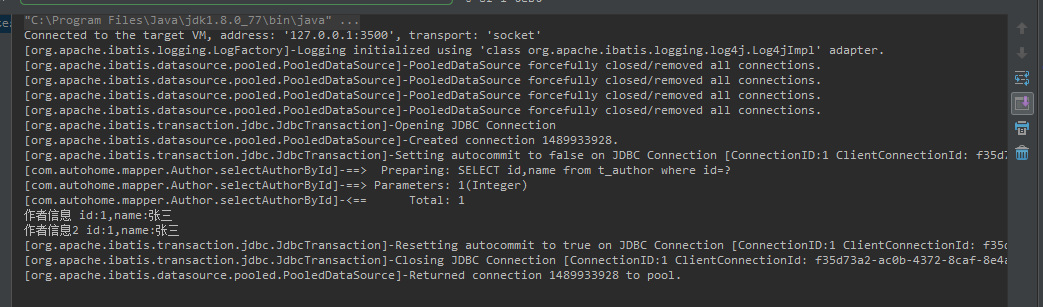
從DEBUG截圖來看,當我們第一次調用方法時執行了SELECT id,name from t_author where id=? 此時緩存中還沒有該數據,則執行數據庫查詢,當再次執行時直接從緩存中讀取。
執行demo后我們來看下這個查詢過程保存到緩存的源碼,先看下DefaultSqlSession.java。我們調用的selectOne(),從代碼中看它是直接調用selectList()然后判斷返回值size大小。
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement) {
return this.<T>selectOne(statement, null);
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
再跟蹤到selectList方法,看到先構造MappedStatement對象,然后看到真正執行query()的是一個executor對象,在DefaultSqlSession.java中executor是成員變量,再翻到org.apache.ibatis.executor包中看到executor實際是一個接口。OK,那么我們debug時發現其引用是CachingExecutor。再打開CachingExecutor.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
從CachingExecutor.java的兩個query()可以看到先去構造CacheKey 再調用抽象類BaseExecutor.query(),這個也是最關鍵的一步。
//先創建CacheKey
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//再執行查詢方法
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
BaseExecutor.java
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
再看其中關鍵代碼queryFromDatabase
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
OK,看了一長串,終于是有點眉目了,我們看到finally中先刪除當前key緩存,然后再調用localCache.putObject把最新的結果集存入HashMap中。
三、二級緩存
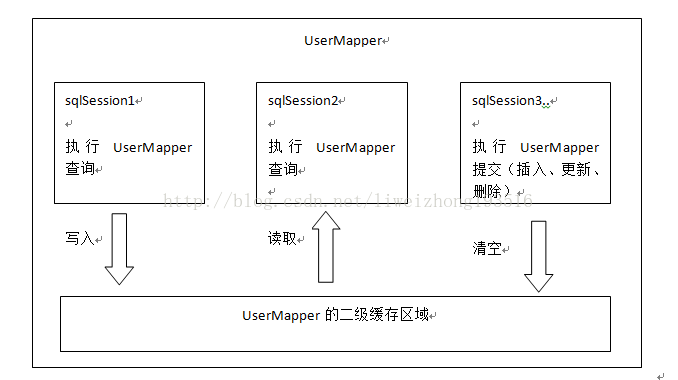
了解二級緩存之前先來看副圖(圖片來自傳智播客視頻,非本人編寫),那么從圖中我們可以看出,mybatis二級緩存是mapper級別,也就是說不同的sqlmapper共享不同的內存區域,不同的sqlsession共享同一個內存區域,用mapper的namespace區別內存區域。
開啟mybatis二級緩存: 1、設置mybatis.xml,也就是說mybatis默認二級緩存是關閉的。
2、設置mapper。在mapper.xml內添加標簽:<cache/>
3、pojo實現接口Serializable。實現該接口后也就說明二級緩存不僅可以存入內存中,還可以存入磁盤。
OK,看一個二級緩存demo:
@Test
public void testCache2(){
SqlSession sqlSession=null;
SqlSession sqlSession2=null;
try{
sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
sqlSession2=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Author author = sqlSession.selectOne("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectAuthorById",1);
System.out.println("作者信息 id:"+author.getId()+",name:"+author.getName());
sqlSession.close();
Author author2 = sqlSession2.selectOne("com.autohome.mapper.Author.selectAuthorById",1);
System.out.println("作者信息2 id:"+author2.getId()+",name:"+author2.getName());
sqlSession2.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
}
}
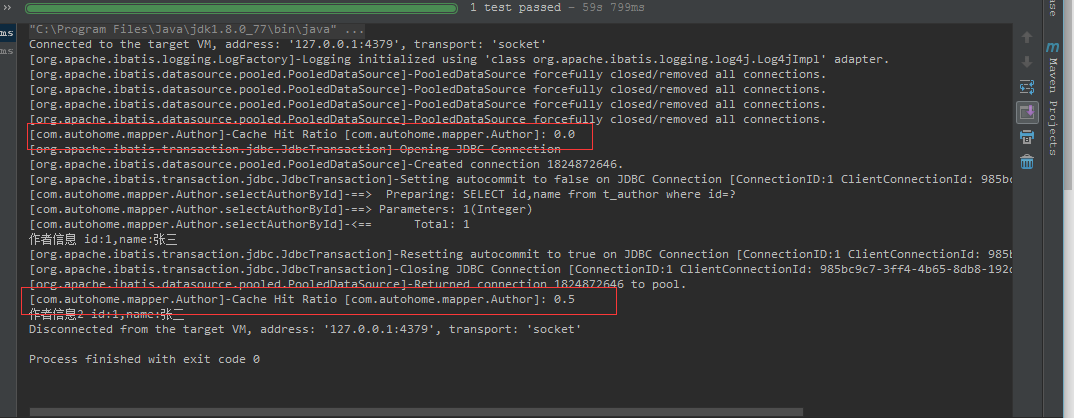
運行demo可以看出二級緩存不同的地方在于Cache Hit Ratio,發出sql查詢時先看是否命中緩存,第一次則是0.0 ,再次查詢時則直接讀取緩存數據,命中率是0.5。當然數據結構還是HashMap。
如果數據實時性要求比較高,可以設置select 語句的
如果數據的查詢實時性要求比較高,則設置select語句的useCache="false",則每次都直接執行sql。
<select id="selectBlogAuthor" resultMap="blogAuthorResumtMap" useCache="false"> SELECT id,title,category,author_id FROM t_blog </select>
以上這篇MyBatis 延遲加載、一級緩存、二級緩存(詳解)就是小編分享給大家的全部內容了,希望能給大家一個參考,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。