溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關怎么在Python中利用多線程同步實現文件讀寫控制,文章內容質量較高,因此小編分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后對相關知識有一定的了解。
1、實現文件讀寫的文件ltz_schedule_times.py
#! /usr/bin/env python
#coding=utf-8
import os
def ReadTimes():
res = []
if os.path.exists('schedule_times.txt'):
fp = open('schedule_times.txt', 'r')
else:
os.system('touch schedule_times.txt')
fp = open('schedule_times.txt', 'r')
try:
line = fp.read()
if line == None or len(line)==0:
fp.close()
return 0
tmp = line.split()
print 'tmp: ', tmp
schedule_times = int(tmp[-1])
finally:
fp.close()
#print schedule_times
return schedule_times
def WriteTimes(schedule_times):
if schedule_times <= 10:
fp = open('schedule_times.txt', 'a+')#10以內追加進去
else:
fp = open('schedule_times.txt', 'w')#10以外重新寫入
schedule_times = 1
print 'write schedule_times start!'
try:
fp.write(str(schedule_times)+'\n')
finally:
fp.close()
print 'write schedule_times finish!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
schedule_times = ReadTimes()
#if schedule_times > 10:
# schedule_times = 0
print schedule_times
schedule_times = schedule_times + 1
WriteTimes(schedule_times)2.1、不加鎖對文件進行多線程讀寫。
file_lock.py
#! /usr/bin/env python #coding=utf-8 from threading import Thread import threading import time from ltz_schedule_times import * #1、不加鎖 def lock_test(): time.sleep(0.1) schedule_times = ReadTimes() print schedule_times schedule_times = schedule_times + 1 WriteTimes(schedule_times) if __name__ == '__main__': for i in range(5): Thread(target = lock_test, args=()).start()
得到結果:
0 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: tmp: tmp: tmp: [[[['1''1''1''1']]]] 11 1 1 write schedule_times start!write schedule_times start! write schedule_times start!write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! write schedule_times finish! write schedule_times finish!write schedule_times finish!
文件寫入結果:
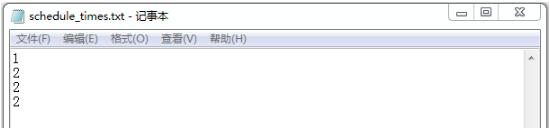
以上結果可以看出,不加鎖多線程讀寫文件會出現錯誤。
2.2、加鎖對文件進行多線程讀寫。
file_lock.py
#! /usr/bin/env python #coding=utf-8 from threading import Thread import threading import time from ltz_schedule_times import * #2、加鎖 mu = threading.Lock() #1、創建一個鎖 def lock_test(): #time.sleep(0.1) if mu.acquire(True): #2、獲取鎖狀態,一個線程有鎖時,別的線程只能在外面等著 schedule_times = ReadTimes() print schedule_times schedule_times = schedule_times + 1 WriteTimes(schedule_times) mu.release() #3、釋放鎖 if __name__ == '__main__': for i in range(5): Thread(target = lock_test, args=()).start()
結果:
0 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: ['1'] 1 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: ['1', '2'] 2 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: ['1', '2', '3'] 3 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish! tmp: ['1', '2', '3', '4'] 4 write schedule_times start! write schedule_times finish!
文件寫入結果:
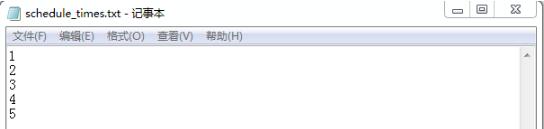
Python是一種跨平臺的、具有解釋性、編譯性、互動性和面向對象的腳本語言,其最初的設計是用于編寫自動化腳本,隨著版本的不斷更新和新功能的添加,常用于用于開發獨立的項目和大型項目。
關于怎么在Python中利用多線程同步實現文件讀寫控制就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。