您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家介紹怎么在Pytorch中利用CharRNN實現文本分類,內容非常詳細,感興趣的小伙伴們可以參考借鑒,希望對大家能有所幫助。
import torch from torch import nn embedding = nn.Embedding(5, 4) # 假定語料只有5個詞,詞向量維度為3 sents = [[1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 4]] # 兩個句子,how:1 are:2 you:3, are:2 you:3 ok:4 embed = embedding(torch.LongTensor(sents)) print(embed) # shape=(2 ''' tensor([[[-0.6991, -0.3340, -0.7701, -0.6255], [ 0.2969, 0.4720, -0.9403, 0.2982], [ 0.8902, -1.0681, 0.4035, 0.1645]], [[ 0.2969, 0.4720, -0.9403, 0.2982], [ 0.8902, -1.0681, 0.4035, 0.1645], [-0.7944, -0.1766, -1.5941, 0.4544]]], grad_fn=<EmbeddingBackward>) '''
2.2 nn.RNN
RNN是NLP的常用模型,普通的RNN單元結構如下圖所示:
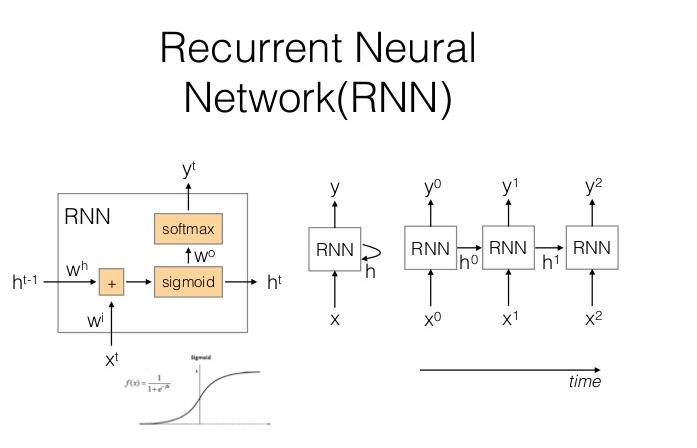
RNN單元還有一些變體,主要是單元內部的激活函數不同或數據使用了不同計算。RNN每個單元存在輸入x與上一時刻的隱層狀態h,輸出有y與當前時刻的隱層狀態。
對RNN單元的改進有LSTM和GRU,這三種類型的模型的輸入數據都需要3D的tensor,,,使用時設置b atch_first為true時,輸入數據的shape為[batch,seq_length, input_dim],第一維為batch的數量不使用時設置為1,第二維序列的長度,第三維為輸入的維度,通常為詞嵌入的維度。
rnn = RNN(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers=1, batch_first, bidirectional)
input_dim 輸入token的特征數量,使用embeding時為嵌入的維度
hidden_dim 隱層的單元數,決定RNN的輸出長度
num_layers 層數
batch_frist 第一維為batch,反之第一堆為seq_len,默認為False
bidirectional 是否為雙向RNN,默認為False
output, hidden = rnn(input, hidden)
input 一批輸入數據,shape為[batch, seq_len, input_dim]
hidden 上一時刻的隱層狀態,shape為[num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_dim]
output 當前時刻的輸出,shape為[batch, seq_len, num_directions*hidden_dim]
import torch from torch import nn vocab_size = 5 embed_dim = 3 hidden_dim = 8 embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_dim) rnn = nn.RNN(embed_dim, hidden_dim, batch_first=True) sents = [[1, 2, 4], [2, 3, 4]] h0 = torch.zeros(1, embeded.size(0), 8) # shape=(num_layers*num_directions, batch, hidden_dim) embeded = embedding(torch.LongTensor(sents)) out, hidden = rnn(embeded, h0) # out.shape=(2,3,8), hidden.shape=(1,2,8) print(out, hidden) ''' tensor([[[-0.1556, -0.2721, 0.1485, -0.2081, -0.2231, -0.1459, -0.0319, 0.2617], [-0.0274, 0.1561, -0.0509, -0.1723, -0.2678, -0.2616, 0.0786, 0.4124], [ 0.2346, 0.4487, -0.1409, -0.0807, -0.0232, -0.4975, 0.4244, 0.8337]], [[ 0.0879, 0.1122, 0.1502, -0.3033, -0.2715, -0.1191, 0.1367, 0.5275], [ 0.2258, 0.4395, -0.1365, 0.0135, -0.0777, -0.5221, 0.4683, 0.8115], [ 0.0158, 0.3471, 0.0742, -0.0550, -0.0098, -0.5521, 0.5923,0.8782]]], grad_fn=<TransposeBackward0>) tensor([[[ 0.2346, 0.4487, -0.1409, -0.0807, -0.0232, -0.4975, 0.4244, 0.8337], [ 0.0158, 0.3471, 0.0742, -0.0550, -0.0098, -0.5521, 0.5923, 0.8782]]], grad_fn=<ViewBackward>) '''
2.3 nn.LSTM
LSTM是RNN的一種模型,結構中增加了記憶單元,LSTM單元結構如下圖所示:
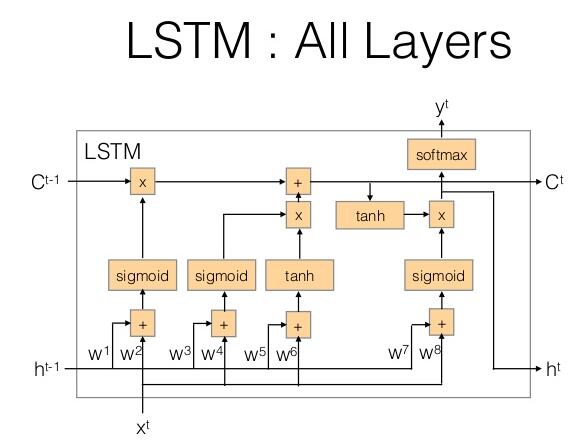
每個單元存在輸入x與上一時刻的隱層狀態h和上一次記憶c,輸出有y與當前時刻的隱層狀態及當前時刻的記憶c。其使用上和RNN類似。
lstm = LSTM(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers=1, batch_first=True, bidirectional)
input_dim 輸入word的特征數量,使用embeding時為嵌入的維度
hidden_dim 隱層的單元數
output, (hidden, cell) = lstm(input, (hidden, cell))
input 一批輸入數據,shape為[batch, seq_len, input_dim]
hidden 當前時刻的隱層狀態,shape為[num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_dim]
cell 當前時刻的記憶狀態,shape為[num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_dim]
output 當前時刻的輸出,shape為[batch, seq_len, num_directions*hidden_dim]
2.4 nn.GRU
GRU也是一種RNN單元,但它比LSTM簡化許多,普通的GRU單元結構如下圖所示:
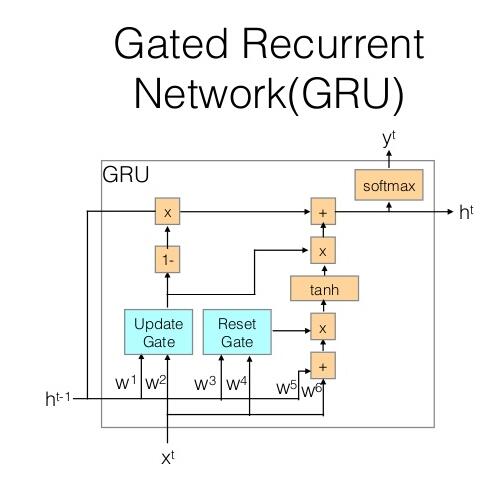
每個單元存在輸入x與上一時刻的隱層狀態h,輸出有y與當前時刻的隱層狀態。
rnn = GRU(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers=1, batch_first=True, bidirectional)
input_dim 輸入word的特征數量,使用embeding時為嵌入的維度
hidden_dim 隱層的單元數
output, hidden = rnn(input, hidden)
input 一批輸入數據,shape為[batch, seq_len, input_dim]
hidden 上一時刻的隱層狀態,shape為[num_layers*num_directions, batch, hidden_dim]
output 當前時刻的輸出,shape為[batch, seq_len, num_directions*hidden_size]
2.5 損失函數
MSELoss均方誤差
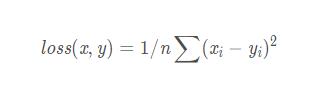
輸入x,y可以是任意的shape,但要保持相同的shape
CrossEntropyLoss 交叉熵誤差
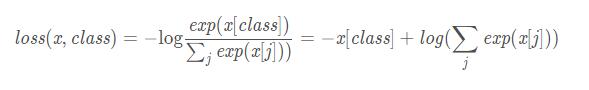
x : 包含每個類的得分,2-D tensor, shape=(batch, n)
class: 長度為batch 的 1D tensor,每個數值為類別的索引(0到 n-1)
3 字符級RNN的分類應用
這里先介紹字符極詞向量的訓練與使用。語料庫使用nltk的names語料庫,訓練根據人名預測對應的性別,names語料庫有兩個分類,female與male,每個分類下對應約4000個人名。這個語料庫是比較適合字符級RNN的分類應用,因為人名比較短,不能再做分詞以使用詞向量。
首次使用nltk的names語料庫要先下載下來,運行代碼nltk.download('names')即可。
字符級RNN模型的詞匯表很簡單,就是單個字符的集合,對于英文來說,只有26個字母,外加空格等會出現在名字中間的字符,見第14行代碼。出于簡化的目的,所有名字統一轉換為小寫。
神經網絡很簡單,一層RNN網絡,用于學習名字序列的特征。一層全連接網絡,用于從將高維特征映射到性別的二分類上。這部分代碼由CharRNN類實現。這里沒有使用embeding層,而是使用字符的one-hot編碼,當然使用Embeding也是可以的。
網絡的訓練和使用封裝為Model類,提供三個方法。train(), evaluate(),predict()分別用于訓練,評估和預測使用。具體見下面的代碼及注釋。
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import sklearn
import string
import random
nltk.download('names')
from nltk.corpus import names
USE_CUDA = torch.cuda.is_available()
device = torch.device("cuda" if USE_CUDA else "cpu")
chars = string.ascii_lowercase + '-' + ' ' + "'"
'''
將名字編碼為向量:每個字符為one-hot編碼,將多個字符的向量進行堆疊
abc = [ [1, 0, ...,0]
[0, 1, 0, ..]
[0, 0, 1, ..] ]
abc.shape = (len("abc"), len(chars))
'''
def name2vec(name):
ids = [chars.index(c) for c in name if c not in ["\\"]]
a = np.zeros(shape=(len(ids), len(chars)))
for i, idx in enumerate(ids):
a[i][idx] = 1
return a
def load_data():
female_file, male_file = names.fileids()
f1_names = names.words(female_file)
f2_names = names.words(male_file)
data_set = [(name.lower(), 0) for name in f1_names] + [(name.lower(), 1) for name in f2_names]
data_set = [(name2vec(name), sexy) for name, sexy in data_set]
random.shuffle(data_set)
return data_set
class CharRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(CharRNN, self).__init__()
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.rnn = nn.RNN(vocab_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
self.liner = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, input):
h0 = torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device) # 初始hidden state
output, hidden = self.rnn(input, h0)
output = output[:, -1, :] # 只使用最終時刻的輸出作為特征
output = self.liner(output)
output = F.softmax(output, dim=1)
return output
hidden_dim = 128
output_dim = 2
class Model:
def __init__(self, epoches=100):
self.model = CharRNN(len(chars), hidden_dim , output_dim)
self.model.to(device)
self.epoches = epoches
def train(self, train_set):
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.RMSprop(self.model.parameters(), lr=0.0003)
for epoch in range(self.epoches):
total_loss = 0
for x in range(1000):# 每輪隨機樣本訓練1000次
name, sexy = random.choice(train_set)
# RNN的input要求shape為[batch, seq_len, embed_dim],由于名字為變長,也不準備好將其填充為定長,因此batch_size取1,將取的名字放入單個元素的list中。
name_tensor = torch.tensor([name], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
# torch要求計算損失時,只提供類別的索引值,不需要one-hot表示
sexy_tensor = torch.tensor([sexy], dtype=torch.long, device=device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
pred = self.model(name_tensor) # [batch, out_dim]
loss = loss_func(pred, sexy_tensor)
loss.backward()
total_loss += loss
optimizer.step()
print("Training: in epoch {} loss {}".format(epoch, total_loss/1000))
def evaluate(self, test_set):
with torch.no_grad(): # 評估時不進行梯度計算
correct = 0
for x in range(1000): # 從測試集中隨機采樣測試1000次
name, sexy = random.choice(test_set)
name_tensor = torch.tensor([name], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
pred = self.model(name_tensor)
if torch.argmax(pred).item() == sexy:
correct += 1
print('Evaluating: test accuracy is {}%'.format(correct/10.0))
def predict(self, name):
p = name2vec(name.lower())
name_tensor = torch.tensor([p], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
with torch.no_grad():
out = self.model(name_tensor)
out = torch.argmax(out).item()
sexy = 'female' if out == 0 else 'male'
print('{} is {}'.format(name, sexy))
if __name__ == "__main__":
model = Model(10)
data_set = load_data()
train, test = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(data_set)
model.train(train)
model.evaluate(test)
model.predict("Jim")
model.predict('Kate')
'''
Evaluating: test accuracy is 82.6%
Jim is male
Kate is female
'''4 基于字符級RNN的文本生成
文本生成的思想是,通過讓神經網絡學習下一個輸出是哪個字符來訓練權重參數。這里我們仍使用names語料庫,嘗試訓練一個生成指定性別人名的神經網絡化。與分類不同的是分類只計算最終狀態輸出的誤差而生成要計算序列每一步計算上的誤差,因此訓練時要逐個字符的輸入到網絡。由于是根據性別來生成人名,因此把性別的one-hot向量concat到輸入數據里,作為訓練數據的一部分。
模型由類CharRNN實現,模型的訓練和使用由Model類實現,提供了train(), sample()方法,前者用于訓練模型,后者用于從訓練中進行采樣生成。
# coding=utf-8
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import string
import random
import nltk
nltk.download('names')
from nltk.corpus import names
USE_CUDA = torch.cuda.is_available()
device = torch.device("cuda" if USE_CUDA else "cpu")
# 使用符號!作為名字的結束標識
chars = string.ascii_lowercase + '-' + ' ' + "'" + '!'
hidden_dim = 128
output_dim = len(chars)
# name abc encode as [[1, ...], [0,1,...], [0,0,1...]]
def name2input(name):
ids = [chars.index(c) for c in name if c not in ["\\"]]
a = np.zeros(shape=(len(ids), len(chars)), dtype=np.long)
for i, idx in enumerate(ids):
a[i][idx] = 1
return a
# name abc encode as [0 1 2]
def name2target(name):
ids = [chars.index(c) for c in name if c not in ["\\"]]
return ids
# female=[[1, 0]] male=[[0,1]]
def sexy2input(sexy):
a = np.zeros(shape=(1, 2), dtype=np.long)
a[0][sexy] = 1
return a
def load_data():
female_file, male_file = names.fileids()
f1_names = names.words(female_file)
f2_names = names.words(male_file)
data_set = [(name.lower(), 0) for name in f1_names] + [(name.lower(), 1) for name in f2_names]
random.shuffle(data_set)
print(data_set[:10])
return data_set
'''
[('yoshiko', 0), ('timothea', 0), ('giorgi', 1), ('thedrick', 1), ('tessie', 0), ('keith', 1), ('carena', 0), ('anthea', 0), ('cathyleen', 0), ('almeta', 0)]
'''
class CharRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(CharRNN, self).__init__()
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.output_size = output_size
# 輸入維度增加了性別的one-hot嵌入,dim+=2
self.rnn = nn.GRU(vocab_size+2, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
self.liner = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, sexy, name, hidden=None):
if hidden is None:
hidden = torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device) # 初始hidden state
# 對每個輸入字符,將性別向量嵌入到頭部
input = torch.cat([sexy, name], dim=2)
output, hidden = self.rnn(input, hidden)
output = self.liner(output)
output = F.dropout(output, 0.3)
output = F.softmax(output, dim=2)
return output.view(1, -1), hidden
class Model:
def __init__(self, epoches):
self.model = CharRNN(len(chars), hidden_dim , output_dim)
self.model.to(device)
self.epoches = epoches
def train(self, train_set):
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.RMSprop(self.model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
for epoch in range(self.epoches):
total_loss = 0
for x in range(1000): # 每輪隨機樣本訓練1000次
loss = 0
name, sexy = random.choice(train_set)
optimizer.zero_grad()
hidden = torch.zeros(1, 1, hidden_dim, device=device)
# 對于姓名kate,將kate作為輸入,ate!作為訓輸出,依次將每個字符輸入網絡,以計算誤差
for x, y in zip(list(name), list(name[1:]+'!')):
name_tensor = torch.tensor([name2input(x)], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
sexy_tensor = torch.tensor([sexy2input(sexy)], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
target_tensor = torch.tensor(name2target(y), dtype=torch.long, device=device)
pred, hidden = self.model(sexy_tensor, name_tensor, hidden)
loss += loss_func(pred, target_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss/(len(name) - 1)
print("Training: in epoch {} loss {}".format(epoch, total_loss/1000))
def sample(self, sexy, start):
max_len = 8
result = []
with torch.no_grad():
hidden = None
for c in start:
sexy_tensor = torch.tensor([sexy2input(sexy)], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
name_tensor = torch.tensor([name2input(c)], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
pred, hidden = self.model(sexy_tensor, name_tensor, hidden)
c = start[-1]
while c != '!':
sexy_tensor = torch.tensor([sexy2input(sexy)], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
name_tensor = torch.tensor([name2input(c)], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
pred, hidden = self.model(sexy_tensor, name_tensor, hidden)
topv, topi = pred.topk(1)
c = chars[topi]
# c = chars[torch.argmax(pred)]
result.append(c)
if len(result) > max_len:
break
return start + "".join(result[:-1])
if __name__ == "__main__":
model = Model(10)
data_set = load_data()
model.train(data_set)
print(model.sample(0, "ka"))
c = input('please input name prefix: ')
while c != 'q':
print(model.sample(1, c))
print(model.sample(0, c))
c = input('please input name prefix: ')關于怎么在Pytorch中利用CharRNN實現文本分類就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。