溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
在使用深度學習對圖像進行訓練時,對圖像進行隨機旋轉有助于提升模型泛化能力。然而之前在做旋轉等預處理工作時,都是先對圖像進行旋轉后保存到本地,然后再輸入模型進行訓練,這樣的過程會增加工作量,如果圖片數量較多,生成旋轉的圖像會占用更多的空間。直接在訓練過程中便對圖像進行隨機旋轉,可有效提升工作效率節省硬盤空間。
使用TensorFlow對圖像進行隨機旋轉如下:
TensorFlow版本為1.13.1
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
'''
使用TensorFlow進行圖像的隨機旋轉示例
'''
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('tf.jpg')
img = cv2.resize(img,(220,220))
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
def tf_rotate(input_image, min_angle = -np.pi/2, max_angle = np.pi/2):
'''
TensorFlow對圖像進行隨機旋轉
:param input_image: 圖像輸入
:param min_angle: 最小旋轉角度
:param max_angle: 最大旋轉角度
:return: 旋轉后的圖像
'''
distorted_image = tf.expand_dims(input_image, 0)
random_angles = tf.random.uniform(shape=(tf.shape(distorted_image)[0],), minval = min_angle , maxval = max_angle)
distorted_image = tf.contrib.image.transform(
distorted_image,
tf.contrib.image.angles_to_projective_transforms(
random_angles, tf.cast(tf.shape(distorted_image)[1], tf.float32), tf.cast(tf.shape(distorted_image)[2], tf.float32)
))
rotate_image = tf.squeeze(distorted_image, [0])
return rotate_image
global_init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
init = tf.initialize_local_variables()
sess.run([init, global_init])
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
image = tf.placeholder(shape=(220, 220, 3), dtype=tf.float32)
rotate_image = tf_rotate(image, -np.pi/2, np.pi/2)
output = sess.run(rotate_image, feed_dict={image:img})
# print('output:',output)
plt.imshow(output.astype('uint8'))
plt.title('rotate image')
plt.show()
結果如下:
原圖:

隨機旋轉后的圖:
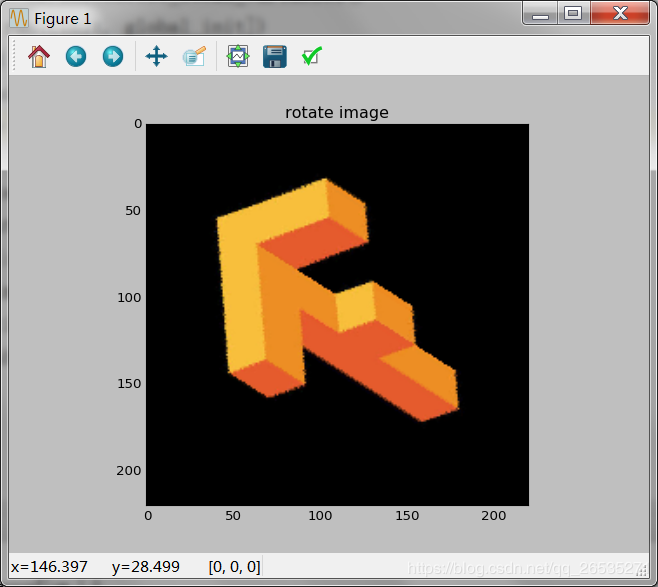
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。