您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
[TOC]
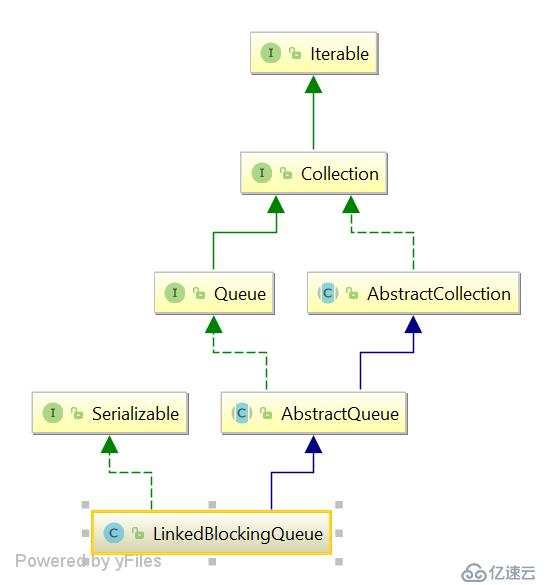
LinkedBlockingQueue 是一個用鏈表實現的有界阻塞隊列;此隊列的默認和最大長度為Integer.MAX_VALUE;此隊列按照先進先出的原則對元素就行排序;隊列有兩個鎖,生成和消費各一把鎖,都是默認的非公平鎖。
static class Node<E> {
// 我們插入的值
E item;
/**
* One of:
* - the real successor Node
* - this Node, meaning the successor is head.next
* - null, meaning there is no successor (this is the last node)
*/
// 下一個node
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) { item = x; }
}
/** 隊列容量 */
private final int capacity;
/** 兩個鎖,需要使用AtomicInteger保證原子性 */
private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
/**
* Head of linked list.
* Invariant: head.item == null
*/
// 頭結點
transient Node<E> head;
/**
* Tail of linked list.
* Invariant: last.next == null
*/
// 尾節點
private transient Node<E> last;
/** Lock held by take, poll, etc */
/** take, poll, etc 的鎖 */
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting takes */
/** 等待在隊列空 */
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
/** Lock held by put, offer, etc */
/** put, offer, etc的鎖 */
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting puts */
/** 等待在隊列滿 */
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition(); // 無參構造
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
// 默認Integer.MAX_VALUE
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
// 有參構造
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
// 創建一個item為null的節點
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
}public boolean offer(E e) {
// e不能為null
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 總數
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 總數等于了容量 返回false
if (count.get() == capacity)
return false;
int c = -1;
// 創建一個node
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
// 獲取鎖
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() < capacity) {
// 插入鏈表
enqueue(node);
// 加1返回舊值
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// c是增加之前的值,然后加1,再判斷有沒有可以存儲的容量
if (c + 1 < capacity)
// 有喚醒下一個線程
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
// 隊列有一個元素了,證明之前隊列為空,可能已經有元素來消費了,所以就需要喚醒一個等待消費的線程
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
return c >= 0;
}
private void enqueue(Node<E> node) {
// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert last.next == null;
last = last.next = node;
}注意:offer 還有一個重載方法,支持中斷,帶有超時時間的限制offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)。
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 不可以為null
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// Note: convention in all put/take/etc is to preset local var
// holding count negative to indicate failure unless set.
int c = -1;
// 構建一個節點
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
// 獲取put鎖
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
// 獲取count
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 調用獲取鎖的方法,支持中斷
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
/*
* Note that count is used in wait guard even though it is
* not protected by lock. This works because count can
* only decrease at this point (all other puts are shut
* out by lock), and we (or some other waiting put) are
* signalled if it ever changes from capacity. Similarly
* for all other uses of count in other wait guards.
*/
// 等于了隊列的容量
while (count.get() == capacity) {
// 進入阻塞隊列
notFull.await();
}
// 入隊
enqueue(node);
// 返回的是自增前的值
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 如果這個元素入隊以后,還有多于的空間,喚醒等待隊列的線程
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
// c==0,證明之前隊列是空的,喚醒一個獲取線程
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
}這次我們看個帶超時時間的poll方法。
// 帶超時時間的消費一個元素
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
E x = null;
int c = -1;
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
// 支持中斷的獲取鎖
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == 0) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
x = dequeue();
// count-- 返回舊值
c = count.getAndDecrement();
// 還有元素,喚醒一個等待獲取的線程
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 隊列還有一個位置,喚醒一個入隊線程
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}
private E dequeue() {
// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert head.item == null;
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC // 自引用
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
} // 獲取元素
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 隊列為null 就阻塞
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 隊列消費一個元素,可以喚醒一個生產線程了
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
} // 獲取第一個元素
public E peek() {
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
Node<E> first = head.next;
if (first == null)
return null;
else
return first.item;
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
}
public int size() {
return count.get();
}LinkedBlockingQueue 可以看做是一個×××隊列,因為最大容量是Integer.MAX_VALUE,這已經很大了,所以使用時一定注意容量問題,避免內存溢出,但是好處就是可以不用我們去初始容量;隊列在入隊和出隊使用了兩把鎖,提高了并發性,相對于一把鎖來說;我們可以發現隊列的底層數據結構采用的是鏈表,對比ArrayBlockingQueue的數組數據結構,在處理數據的同時,節點本身也需要處理垃圾回收,所以相對于數組來的數據來說增加了垃圾回收,可能影響性能;LinkedBlockingQueue 和ArrayBlockingQueue 兩個可以對比學習,追求系統穩定性,性能就使用ArrayBlockingQueue ,追求并發性,可能發生大量請求時(系統不是很穩定)要注意內存溢出就使用LinkedBlockingQueue ,使用場景屬于個人理解,歡迎指正。
《參考 Java 并發編程的藝術》
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。