溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
ConcurrentHashMap,采用了一種“懶加載”的模式,只有到首次插入鍵值對的時候,才會真正的去初始化table數組。1、空構造函數,默認桶大小16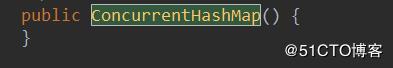
2、指定桶初始容量的構造器,必須是2次冪值
/**
* 指定table初始容量的構造器.
* tableSizeFor會返回大于入參(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1)的 最小2次冪值
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}3、根據已有的Map構造
4、指定table初始容量和負載因子的構造器
5、指定table初始容量、負載因子、并發級別的構造器
/**
* 最大容量.
*/
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* 默認初始容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* 負載因子,為了兼容JDK1.8以前的版本而保留。
* JDK1.8中的ConcurrentHashMap的負載因子恒定為0.75
*/
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* 鏈表轉樹的閾值,即鏈接結點數大于8時, 鏈表轉換為樹.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* 樹轉鏈表的閾值,即樹結點樹小于6時,樹轉換為鏈表.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
/**
* 在鏈表轉變成樹之前,還會有一次判斷:
* 即只有桶大小數量大于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY,才會發生轉換。
* 這是為了避免在Table建立初期,多個鍵值對恰好被放入了同一個鏈表中而導致不必要的轉化。
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
/**
* 在樹轉變成鏈表之前,還會有一次判斷:
* 即只有桶的數量小于MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE,才會發生轉換.
*/
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;
/**
* 用于在擴容時生成唯一的隨機數.
*/
private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
/**
* 可同時進行擴容操作的最大線程數.
*/
private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1;
static final int MOVED = -1; // 標識ForwardingNode結點
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // 標識紅黑樹的根結點
static final int RESERVED = -3; // 標識ReservationNode結點()
static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // usable bits of normal node hash
/**
* CPU核心數,擴容時使用
*/
static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* Node數組,標識整個Map,首次插入元素時創建,大小總是2的冪次.
*/
transient volatile Node<K, V>[] table;
/**
* 擴容后的新Node數組,只有在擴容時才非空.
*/
private transient volatile Node<K, V>[] nextTable;
/**
* 控制table的初始化和擴容.
* 0 : 初始默認值
* -1 : 有線程正在進行table的初始化
* >0 : table初始化時使用的容量,或初始化/擴容完成后的threshold
* -(1 + nThreads) : 記錄正在執行擴容任務的線程數
*/
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
/**
* 擴容時需要用到的一個下標變量.
*/
private transient volatile int transferIndex;
/**
* 計數基值,當沒有線程競爭時,計數將加到該變量上。類似于LongAdder的base變量
*/
private transient volatile long baseCount;
/**
* 計數數組,出現并發沖突時使用。類似于LongAdder的cells數組
*/
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
/**
* 自旋標識位,用于CounterCell[]擴容時使用。類似于LongAdder的cellsBusy變量
*/
private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
/**
* 插入鍵值對,<K,V>均不能為null.
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}/**
* 實際的插入操作
*
* @param onlyIfAbsent true:僅當key不存在時,才插入
*/
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); // 再次計算hash值
/**
* 使用鏈表保存時,binCount記錄table[i]這個桶中所保存的節點數;
* 使用紅黑樹保存時,binCount==2,保證put后更改計數值時能夠進行擴容檢查,同時不觸發紅黑樹化操作
*/
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K, V>[] tab = table; ; ) { // 自旋插入結點,直到成功
Node<K, V> f;
int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) // CASE1: 首次初始化table —— 懶加載
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { // CASE2: table[i]對應的桶為null
// 注意下上面table[i]的索引i的計算方式:[ key的hash值 & (table.length-1) ]
// 這也是table容量必須為2的冪次的原因,讀者可以自己看下當table.length為2的冪次時,(table.length-1)的二進制形式的特點 —— 全是1
// 配合這種索引計算方式可以實現key的均勻分布,減少hash沖突
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, null))) // 插入一個鏈表結點
break;
} else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) // CASE3: 發現ForwardingNode結點,說明此時table正在擴容,則嘗試協助數據遷移
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); // 遷移數據方法
else { // CASE4: 出現hash沖突,也就是table[i]桶中已經有了結點
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) { // 鎖住table[i]結點
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { // 再判斷一下table[i]是不是第一個結點, 防止其它線程的寫修改
if (fh >= 0) { // CASE4.1: table[i]是鏈表結點
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K, V> e = f; ; ++binCount) {
K ek;
// 找到“相等”的結點,判斷是否需要更新value值
if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K, V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) { // “尾插法”插入新結點
pred.next = new Node<K, V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
} else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { // CASE4.2: table[i]是紅黑樹結點
Node<K, V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K, V>) f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i); // 鏈表 -> 紅黑樹 轉換
if (oldVal != null) // 表明本次put操作只是替換了舊值,不用更改計數值
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount); // 計數值加1
return null;
} private final Node<K, V>[] initTable() {
Node<K, V>[] tab;
int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { //自旋直到初始化成功
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) // sizeCtl<0 說明table已經正在初始化/擴容
Thread.yield();
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { // 將sizeCtl更新成-1,表示正在初始化中
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
Node<K, V>[] nt = (Node<K, V>[]) new Node<?, ?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2); // 0.75n,負載因子
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc; // 設置threshold = 0.75 * table.length
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}/**
* 嘗試進行 鏈表 -> 紅黑樹 的轉換.
*/
private final void treeifyBin(Node<K, V>[] tab, int index) {
Node<K, V> b;
int n, sc;
if (tab != null) {
// CASE 1: table的容量 < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(64)時,直接進行table擴容,不進行紅黑樹轉換
if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
tryPresize(n << 1);
// CASE 2: table的容量 ≥ MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(64)時,進行鏈表 -> 紅黑樹的轉換
else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {
synchronized (b) {
if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) {
TreeNode<K, V> hd = null, tl = null;
// 遍歷鏈表,建立紅黑樹
for (Node<K, V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) {
TreeNode<K, V> p = new TreeNode<K, V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((p.prev = tl) == null)
hd = p;
else
tl.next = p;
tl = p;
}
// 以TreeBin類型包裝,并鏈接到table[index]中
setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K, V>(hd));
}
}
}
}
}/**
* 根據key查找對應的value值
*
* @return 查找不到則返回null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K, V>[] tab;
Node<K, V> e, p;
int n, eh;
K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode()); // 重新計算key的hash值
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) { // CASE1、table[i]就是待查找的項,直接返回
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
} else if (eh < 0) //CASE2、hash值<0, 說明遇到非鏈表結點, 調用對應節點的find方法查找
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) { //始終可以按照鏈表方式查找
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}對于CASE2,重點看一下TreeBin結點的查找
1、TreeBin的查找
ConcurrentHashMap采用了一種類似讀寫鎖的方式:當線程持有寫鎖(修改紅黑樹)時,如果讀線程需要查找,不會像傳統的讀寫鎖那樣阻塞等待,而是轉而以鏈表的形式進行查找(TreeBin本身時Node類型的子類,所有擁有Node的所有字段)/**
* 從根結點開始遍歷查找,找到“相等”的結點就返回它,沒找到就返回null
* 當存在寫鎖時,以鏈表方式進行查找
*/
final Node<K, V> find(int h, Object k) {
if (k != null) {
for (Node<K, V> e = first; e != null; ) {
int s;
K ek;
/**
* 兩種特殊情況下以鏈表的方式進行查找:
* 1. 有線程正持有寫鎖,這樣做能夠不阻塞讀線程
* 2. 有線程等待獲取寫鎖,不再繼續加讀鎖,相當于“寫優先”模式
*/
if (((s = lockState) & (WAITER | WRITER)) != 0) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
e = e.next; // 鏈表形式
}
// 讀線程數量加1,讀狀態進行累加
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, LOCKSTATE, s, s + READER)) {
TreeNode<K, V> r, p;
try {
p = ((r = root) == null ? null :
r.findTreeNode(h, k, null));
} finally {
Thread w;
// 如果當前線程是最后一個讀線程,且有寫線程因為讀鎖而阻塞,則喚醒寫線程,嘗試獲取寫鎖
if (U.getAndAddInt(this, LOCKSTATE, -READER) == (READER | WAITER) && (w = waiter) != null)
LockSupport.unpark(w);
}
return p;
}
}
}
return null;
}免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。