您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了java Shiro相關知識點有哪些的相關知識,內容詳細易懂,操作簡單快捷,具有一定借鑒價值,相信大家閱讀完這篇java Shiro相關知識點有哪些文章都會有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看吧。
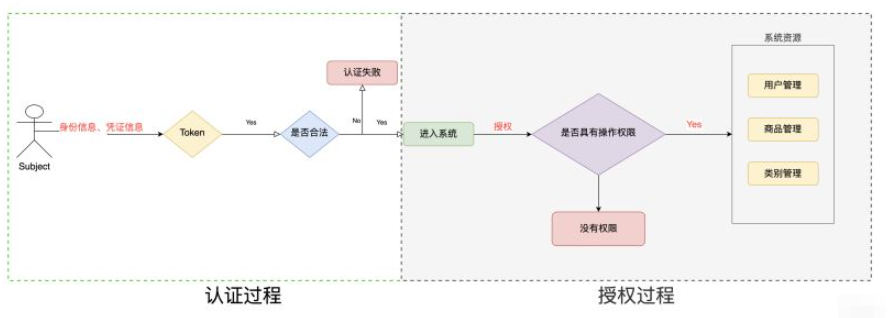
基本上涉及到用戶參與的系統都要進行權限管理,權限管理屬于系統安全的范疇,權限管理實現對用戶訪問系統的控制,按照安全規則或者安全策略控制用戶可以訪問而且只能訪問自己被授權的資源。
權限管理包括用戶身份認證和授權兩部分,簡稱認證授權。對于需要訪問控制的資源用戶首先經過身份認證,認證通過后用戶具有該資源的訪問權限方可訪問。
身份認證,就是判斷一個用戶是否為合法用戶的處理過程。最常用的簡單身份認證方式是系統通過核對用戶輸入的用戶名和口令,看其是否與系統中存儲的該用戶的用戶名和口令一致,來判斷用戶身份是否正確。對于采用指紋等系統,則出示指紋;對于硬件Key等刷卡系統,則需要刷卡。
授權,即訪問控制,控制誰能訪問哪些資源。主體進行身份認證后需要分配權限方可訪問系統的資源,對于某些資源沒有權限是無法訪問的
Apache Shiro™ is a powerful and easy-to-use Java security framework that performs authentication, authorization, cryptography, and session management. With Shiro’s easy-to-understand API, you can quickly and easily secure any application – from the smallest mobile applications to the largest web and enterprise applications.
Shiro 是一個功能強大且易于使用的Java安全框架,它執行身份驗證、授權、加密和會話管理。使用Shiro易于理解的API,您可以快速輕松地保護任何應用程序—從最小的移動應用程序到最大的web和企業應用程序。
Shiro是apache旗下一個開源框架,它將軟件系統的安全認證相關的功能抽取出來,實現用戶身份認證,權限授權、加密、會話管理等功能,組成了一個通用的安全認證框架。
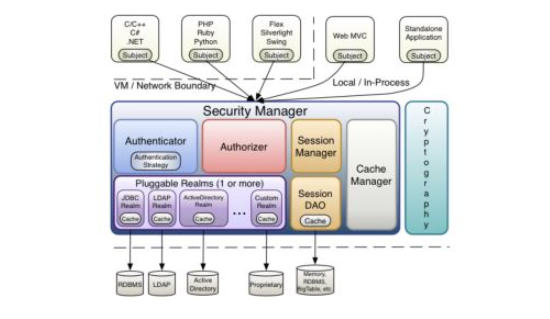
Subject即主體,外部應用與subject進行交互,subject記錄了當前操作用戶,將用戶的概念理解為當前操作的主體,可能是一個通過瀏覽器請求的用戶,也可能是一個運行的程序。 Subject在shiro中是一個接口,接口中定義了很多認證授權相關的方法,外部程序通過subject進行認證授權,而subject是通過SecurityManager安全管理器進行認證授權
SecurityManager即安全管理器,對全部的subject進行安全管理,它是shiro的核心,負責對所有的subject進行安全管理。通過SecurityManager可以完成subject的認證、授權等,實質上SecurityManager是通過Authenticator進行認證,通過Authorizer進行授權,通過SessionManager進行會話管理等。
SecurityManager是一個接口,繼承了Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager這三個接口。
Authenticator即認證器,對用戶身份進行認證,Authenticator是一個接口,shiro提供ModularRealmAuthenticator實現類,通過ModularRealmAuthenticator基本上可以滿足大多數需求,也可以自定義認證器。
Authorizer即授權器,用戶通過認證器認證通過,在訪問功能時需要通過授權器判斷用戶是否有此功能的操作權限。
Realm即領域,相當于datasource數據源,securityManager進行安全認證需要通過Realm獲取用戶權限數據,比如:如果用戶身份數據在數據庫那么realm就需要從數據庫獲取用戶身份信息。
注意:不要把realm理解成只是從數據源取數據,在realm中還有認證授權校驗的相關的代碼。
sessionManager即會話管理,shiro框架定義了一套會話管理,它不依賴web容器的session,所以shiro可以使用在非web應用上,也可以將分布式應用的會話集中在一點管理,此特性可使它實現單點登錄。
SessionDAO即會話dao,是對session會話操作的一套接口,比如要將session存儲到數據庫,可以通過jdbc將會話存儲到數據庫。
CacheManager即緩存管理,將用戶權限數據存儲在緩存,這樣可以提高性能。
Cryptography即密碼管理,shiro提供了一套加密/解密的組件,方便開發。比如提供常用的散列、加/解密等功能。
身份認證,就是判斷一個用戶是否為合法用戶的處理過程。最常用的簡單身份認證方式是系統通過核對用戶輸入的用戶名和口令,看其是否與系統中存儲的該用戶的用戶名和口令一致,來判斷用戶身份是否正確。
Subject:主體
訪問系統的用戶,主體可以是用戶、程序等,進行認證的都稱為主體;
Principal:身份信息
是主體(subject)進行身份認證的標識,標識必須具有唯一性,如用戶名、手機號、郵箱地址等,一個主體可以有多個身份,但是必須有一個主身份(Primary Principal)。
credential:憑證信息
是只有主體自己知道的安全信息,如密碼、證書等。
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId> <version>1.5.3</version> </dependency>
[users] mosin=1234 tom=1234
/**
* @author: mosin
* @version: v1.0
*/
public class ShiroTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建默認的安全管理器
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//創建安全管理器需要的realm對象
IniRealm iniRealm = new IniRealm("classpath:realm.ini");
//安全管理器設置realm對象
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(iniRealm);
//將安全管理器注入安全工具類 用于獲取認證的主體
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
//獲取認證的主體
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//創建令牌
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken("mosin", "1234");
try {
//認證 通過沒有任何的異常
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
//驗證是否通過
boolean authenticated = subject.isAuthenticated();
System.out.println("認證通過:"+authenticated);
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("用戶名錯誤!");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("密碼錯誤!");
}
}
}DisabledAccountException(帳號被禁用)
LockedAccountException(帳號被鎖定)
ExcessiveAttemptsException(登錄失敗次數過多)
ExpiredCredentialsException(憑證過期)等
上邊的程序使用的是Shiro自帶的IniRealm,IniRealm從ini配置文件中讀取用戶的信息,大部分情況下需要從系統的數據庫中讀取用戶信息,所以需要自定義realm。

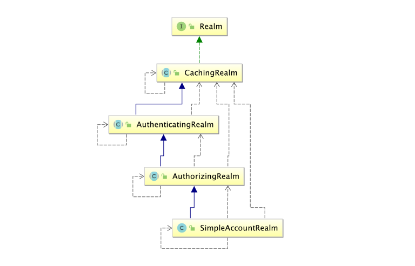
SimpleAccountRealm的部分源碼中有兩個方法一個是 認證 一個是 授權,
public class SimpleAccountRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
UsernamePasswordToken upToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token;
SimpleAccount account = getUser(upToken.getUsername());
if (account != null) {
if (account.isLocked()) {
throw new LockedAccountException("Account [" + account + "] is locked.");
}
if (account.isCredentialsExpired()) {
String msg = "The credentials for account [" + account + "] are expired";
throw new ExpiredCredentialsException(msg);
}
}
return account;
}
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
String username = getUsername(principals);
USERS_LOCK.readLock().lock();
try {
return this.users.get(username);
} finally {
USERS_LOCK.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}/**
* 自定義realm
*/
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//認證方法
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
return null;
}
//授權方法
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal();
if("mosin".equals(principal)){
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal,"123",this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}public class TestAuthenticatorCustomerRealm {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建securityManager
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//IniRealm realm = new IniRealm("classpath:realm.ini");
//設置為自定義realm獲取認證數據
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(new CustomerRealm());
//將安裝工具類中設置默認安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
//獲取主體對象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//創建token令牌
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("mosin", "1234");
try {
subject.login(token);//用戶登錄
System.out.println("登錄成功");
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("用戶名錯誤!!");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("密碼錯誤!!!");
}
}
}實際應用是將鹽和散列后的值存在數據庫中,自動realm從數據庫取出鹽和加密后的值由shiro完成密碼校驗。
/**
* 自定義md5+salt realm
*/
public class CustomerMD5Realm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授權
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
return null;
}
//認證
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//根據用戶名查詢數據庫
if("mosin".equals(principal)){
// 參數1:用戶名 參數2:密碼 參數3:鹽 參數4:自定義realm的名字
System.out.println(this.getName());
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, "800d63a19662b2ba95bc2ffa01ab4804", ByteSource.Util.bytes("mosin"),this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}public class CustomerMD5RealmTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建安全管理器
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//創建自定義MD5Realm對象
CustomerMD5Realm customerMD5Realm = new CustomerMD5Realm();
//創建密碼認證匹配器對象
HashedCredentialsMatcher md5 = new HashedCredentialsMatcher("MD5");
//設置散列的次數
md5.setHashIterations(1024);
//設置密碼認證匹配器對象
customerMD5Realm.setCredentialsMatcher(md5);
//設置安全管理器的 認證安全數據源
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(customerMD5Realm);
//設置安全工具類的安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
//獲取認證的主體
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//創建令牌
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken("mosi", "12345");
//登錄認證
try {
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
System.out.println("認證通過:"+subject.isAuthenticated());
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("用戶名錯誤");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("密碼錯誤!!!");
}
}
}授權,即訪問控制,控制誰能訪問哪些資源。主體進行身份認證后需要分配權限方可訪問系統的資源,對于某些資源沒有權限是無法訪問的。
授權可簡單理解為who對what(which)進行How操作:
Who,即主體(Subject),主體需要訪問系統中的資源。
What,即資源(Resource),如系統菜單、頁面、按鈕、類方法、系統商品信息等。資源包括資源類型和資源實例,比如商品信息為資源類型,類型為t01的商品為資源實例,編號為001的商品信息也屬于資源實例。
How,權限/許可(Permission),規定了主體對資源的操作許可,權限離開資源沒有意義,如用戶查詢權限、用戶添加權限、某個類方法的調用權限、編號為001用戶的修改權限等,通過權限可知主體對哪些資源都有哪些操作許可。
基于角色的訪問控制
RBAC基于角色的訪問控制(Role-Based Access Control)是以角色為中心進行訪問控制
基于資源的訪問控制
RBAC基于資源的訪問控制(Resource-Based Access Control)是以資源為中心進行訪問控制
if(subject.isPermission("user:update:01")){ //資源實例
//對01用戶進行修改
}
if(subject.isPermission("user:update:*")){ //資源類型
//對01用戶進行修改
}權限字符串的規則是:資源標識符:操作:資源實例標識符,意思是對哪個資源的哪個實例具有什么操作,“:”是資源/操作/實例的分割符,權限字符串也可以使用*通配符。
例子:
用戶創建權限:user:create,或user:create:*
用戶修改實例001的權限:user:update:001
用戶實例001的所有權限:user:*:001
編程式
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if(subject.hasRole(“admin”)) {
//有權限
} else {
//無權限
}注解式
@RequiresRoles("admin")
public void hello() {
//有權限
}標簽式
JSP/GSP 標簽:在JSP/GSP 頁面通過相應的標簽完成: <shiro:hasRole name="admin"> <!— 有權限—> </shiro:hasRole> 注意: Thymeleaf 中使用shiro需要額外集成!
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授權
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
String primaryPrincipal = (String) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
System.out.println("primaryPrincipal = " + primaryPrincipal);
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole("admin");
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission("user:update:*");
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission("product:*:*");
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
//認證
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal();
if("xiaochen".equals(principal)){
String password = "3c88b338102c1a343bcb88cd3878758e";
String salt = "Q4F%";
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal,password,
ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt),this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}public class CustomerMD5RealmTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建安全管理器
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//創建自定義MD5Realm對象
CustomerMD5Realm customerMD5Realm = new CustomerMD5Realm();
//創建密碼認證匹配器對象
HashedCredentialsMatcher md5 = new HashedCredentialsMatcher("md5");
//設置加密的次數
md5.setHashIterations(1024);
//設置密碼認證匹配器對象
customerMD5Realm.setCredentialsMatcher(md5);
//設置安全管理器的 認證安全數據源
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(customerMD5Realm);
//設置安全工具類的安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
//獲取認證的主體
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//創建令牌
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken("mosin", "12345");
//登錄認證
try {
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
System.out.println("認證通過:"+subject.isAuthenticated());
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("用戶名錯誤");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("密碼錯誤!!!");
}
//基于角色的控制
//單角色控制
System.out.println("========hasRole==========");
boolean admin = subject.hasRole("admin");
System.out.println("hash admin role:"+admin);
//多角色控制
System.out.println("========hasAllRoles==========");
List<String> roles = Arrays.asList("admin", "user");
boolean booleans = subject.hasAllRoles(roles);
System.out.println("booleans = " + booleans);
// 基于任意角色的控制
System.out.println("========hasRoles==========");
boolean[] booleans1 = subject.hasRoles(roles);
for (boolean b : booleans1) {
System.out.println("b = " + b);
}
//基于權限字符串的權限控制
System.out.println("========isPermitted==========");
boolean permitted = subject.isPermitted("user:update:*");
System.out.println("permitted = " + permitted);
//分別具有哪些權限
boolean[] permitted1 = subject.isPermitted("user:update:*", "product:update:*");
for (boolean b : permitted1) {
System.out.println("b = " + b);
}
//同時具有哪些權限
boolean permittedAll = subject.isPermittedAll("user:update:*", "product:update:*");
System.out.println("permittedAll = " + permittedAll);
}
}關于“java Shiro相關知識點有哪些”這篇文章的內容就介紹到這里,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家對“java Shiro相關知識點有哪些”知識都有一定的了解,大家如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。