您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“Babel怎么實現自動生成Attribute文檔”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“Babel怎么實現自動生成Attribute文檔”吧!
利用Babel自動解析源碼屬性上的注釋生成對應Markdown文檔,這個場景的應用主要包括在組件庫文檔對組件屬性的介紹中
2.1.1 創建babel-plugin-auto-attr-doc文件夾;
2.1.2 安裝npm i -g yo generator-babel-plugin-x;
2.1.3 在新建目錄下執行 yo babel-plugin-x:v7-ts;
生成的插件模板如下:
babel-plugin-auto-attr-doc ├─ lib │ └─ index.js ├─ src │ └─ index.ts ├─ __tests__ │ ├─ fixtures │ │ └─ example │ │ ├─ actual.ts │ │ └─ expected.ts │ └─ index.js ├─ package-lock.json ├─ package.json ├─ README.md └─ tsconfig.json
轉換過程:利用Babel將Typescript腳本解析為AST,通過對AST結構分析抽離對應的注釋部分,再拼接Markdown表格風格的語法;
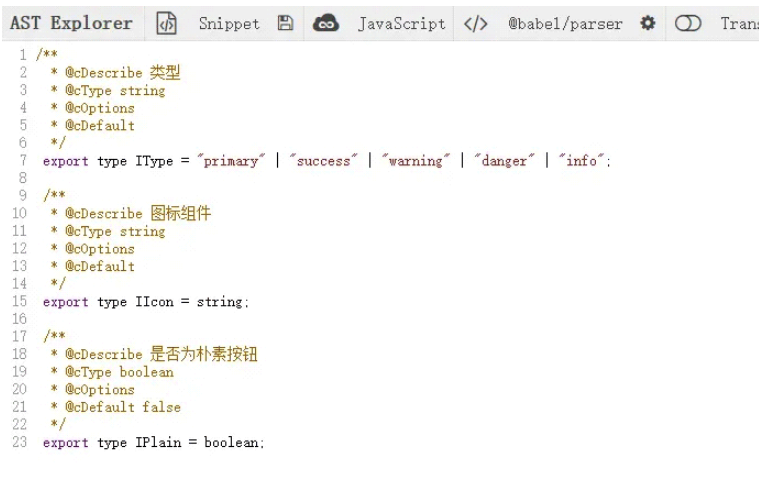
源碼要求:**我們應該將組件涉及到對外提供的屬性統一到對應的types.ts文件管理,分別導出對應的type字段;
注釋要求:**分別定義字段描述、類型、可選項、默認值4項,由于解析器關鍵詞沖突原因,我們應該盡量避免;
/** * @cDescribe 類型 * @cType string * @cOptions * @cDefault */ export type IType = "primary" | "success" | "warning" | "danger" | "info"; /** * @cDescribe 圖標組件 * @cType string * @cOptions * @cDefault */ export type IIcon = string; /** * @cDescribe 是否為樸素按鈕 * @cType boolean * @cOptions * @cDefault false */ export type IPlain = boolean;
Markdown表格:**展示組件的屬性、描述、類型、可選值和默認值這幾項;
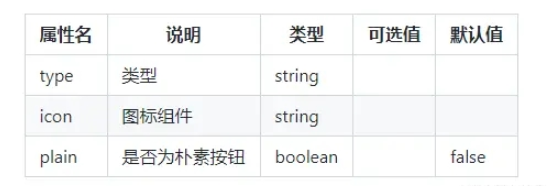
準備插件待解析源碼文件source-code.ts;
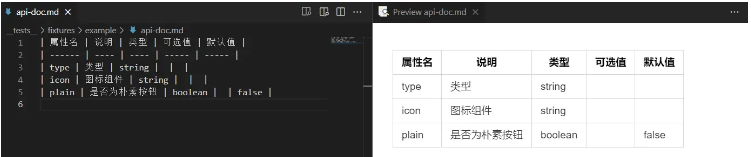
準備實際生成MD后應該顯示的內容文件actual.md;
| 屬性名 | 說明 | 類型 | 可選值 | 默認值 | | ------ | ---- | ---- | ----- | ----- | | type | 類型 | string | | | | icon | 圖標組件 | string | | | | plain | 是否為樸素按鈕 | boolean | | false |
調整單元測試文件讀取:
it(`should ${caseName.split("-").join(" ")}`, () => {
const actualPath = path.join(fixtureDir, "source-code.ts");
// 對源碼進行加載解析
transformFileSync(actualPath);
// 讀取我們準備好的md文件
const actual = fs
.readFileSync(path.join(fixtureDir, "actual.md"))
.toString();
// 讀取插件解析生成的md文件
const expected = fs
.readFileSync(path.join(fixtureDir, "api-doc.md"))
.toString();
// diff
const diff = diffChars(actual, expected);
diff.length > 1 && _print(diff);
expect(diff.length).toBe(1);
});通過在AST explorer的源碼分析,我們在Babel中可以通過遍歷ExportNamedDeclaration(命名導出聲明);
在leadingComments數組中可以取出所有注釋文本的集合,在Babel處理時我們需要依次處理每一塊注釋后增加標記來避免重復處理;
在(path.node.declaration as t.TypeAlias).id.name中取屬性名稱;
將注釋文本通過doctrine模塊解析為對象后和屬性名合并對轉換Markdown所需要的所有數據~
type Comment =
| {
describe: string;
type: any;
options?: any;
default?: any;
}
| undefined;type ApiTable = {
attributeName: any;
attributeDescribe: any;
attributeType: any;
attributeOptions: any;
attributeDefault: any;
};pre:初始化存放apidoc容器,避免在存放時找不到容器;
visitor:解析源碼并獲取組織MD內容數據暫存到apidoc中;
post:取出所有的apidoc內容解析并輸出到本地文件中;
export default declare(
(api: BabelAPI, options: Record<string, any>, dirname: string) => {
api.assertVersion(7);
return {
name: "auto-attr-doc",
pre(this: PluginPass, file: BabelFile) {
this.set("api-doc", []);
},
visitor: {
ExportNamedDeclaration(
path: NodePath<t.ExportNamedDeclaration>,
state: PluginPass
) {
const apidoc = state.get("api-doc");
// 處理 path.node.leadingComments 中未處理的數據后塞到apidoc中
state.set("api-doc", apidoc);
},
},
post(this: PluginPass, file: BabelFile) {
const apidoc = this.get("api-doc");
const output = generateMD(apidoc);
const root = path.parse(file.opts.filename || "./").dir;
fs.writeFileSync(path.join(root, "api-doc.md"), output, {
encoding: "utf-8",
});
},
} as PluginObj<PluginPass>;
}
);leadingComments數組會在依次訪問ExportNamedDeclaration時不停增加,我們在處理掉當前索引的對象后增加一個處理過的標記skip,下次循環直接跳過;
通過parseComment函數解析后的對象可以通過tags數組獲取到所有的注釋項目,通過對應的title得到對應description內容;
在往apidoc存放數據時需要處理屬性名稱符合一定的規則,并將apidoc對象存放到原容器中;
{
ExportNamedDeclaration(
path: NodePath<t.ExportNamedDeclaration>,
state: PluginPass
) {
const apidoc = state.get("api-doc");
let _comment: Comment = undefined;
path.node.leadingComments?.forEach((comment) => {
if (!Reflect.has(comment, "skip")) {
const tags = parseComment(comment.value)?.tags;
_comment = {
describe:
tags?.find((v) => v.title === "cDescribe")?.description || "",
type: tags?.find((v) => v.title === "cType")?.description || "",
options:
tags?.find((v) => v.title === "cOptions")?.description || "",
default:
tags?.find((v) => v.title === "cDefault")?.description || "",
};
Reflect.set(comment, "skip", true);
}
});
apidoc.push({
attributeName: (path.node.declaration as t.TypeAlias).id.name.substr(1).toLocaleLowerCase(),
attributeDescribe: _comment!.describe,
attributeType: _comment!.type,
attributeOptions: _comment!.options,
attributeDefault: _comment!.default,
} as ApiTable);
state.set("api-doc", apidoc);
},
}const parseComment = (comment: string) => {
if (!comment) {
return;
}
return doctrine.parse(comment, {
unwrap: true,
});
};const generateMD = (apidoc: Array<ApiTable>) => {
let raw = `| 屬性名 | 說明 | 類型 | 可選值 | 默認值 |\n| ------ | ---- | ---- | ----- | ----- |\n`;
apidoc.forEach((item) => {
raw += `| ${item.attributeName} | ${item.attributeDescribe} | ${item.attributeType} | ${item.attributeOptions} | ${item.attributeDefault} |\n`;
});
return raw;
};
到此,相信大家對“Babel怎么實現自動生成Attribute文檔”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。