您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“Vue3怎么操作dom”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
<template>
<div>
<div ref="sectionRef"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue'
const sectionRef = ref()
</script>
通過對div元素添加了ref屬性,為了獲取到這個元素,我們聲明了一個與ref屬性名稱相同的變量sectionRef,然后我們通過 sectionRef.value 的形式即可獲取該div元素。
單一dom元素或者個數較少的場景
<template>
<div>
<p>通過ref直接拿到dom</p>
<div ref="sectionRef"></div>
<button @click="higherAction">變高</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue'
const sectionRef = ref()
let height = 100;
const higherAction = () => {
height += 50;
sectionRef.value.style = `height: ${height}px`;
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo1-container {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
.ref-section {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
transition: all .5s ease-in-out;
}
.btn {
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
background-color: gray;
color: #fff;
margin-top: 100px;
}
}
</style>
<template>
<div>
<div ref="listRef">
<div @click="higherAction(index)" v-for="(item, index) in state.list" :key="index">
<span>{{item}}</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'
const listRef = ref()
通過對父元素添加了ref屬性,并聲明了一個與ref屬性名稱相同的變量listRef,此時通過listRef.value會獲得包含子元素的dom對象
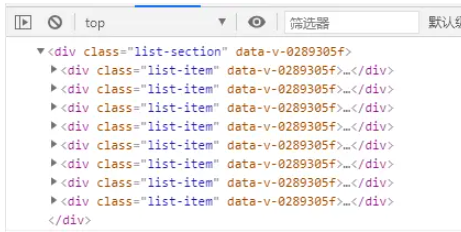
此時可以通過listRef.value.children[index]的形式獲取子元素dom
通過v-for循環生成的固定數量元素的場景
<template>
<div>
<p>通過父容器遍歷拿到dom</p>
<div ref="listRef">
<div @click="higherAction(index)" v-for="(item, index) in state.list" :key="index">
<span>{{item}}</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'
const listRef = ref()
const state = reactive({
list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
})
const higherAction = (index: number) => {
let height = listRef.value.children[index].style.height ? listRef.value.children[index].style.height : '20px';
height = Number(height.replace('px', ''));
listRef.value.children[index].style = `height: ${height + 20}px`;
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo2-container {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
.list-section {
width: 200px;
.list-item {
width: 200px;
height: 20px;
background-color: pink;
color: #333;
transition: all .5s ease-in-out;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
}
}
</style>
<template>
<div>
<div>
<div :ref="setRefAction" @click="higherAction(index)" v-for="(item, index) in state.list" :key="index">
<span>{{item}}</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
const state = reactive({
list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
refList: [] as Array<any>
})
const setRefAction = (el: any) => {
state.refList.push(el);
}
</script>
通過:ref循環調用setRefAction方法,該方法會默認接收一個el參數,這個參數就是我們需要獲取的div元素
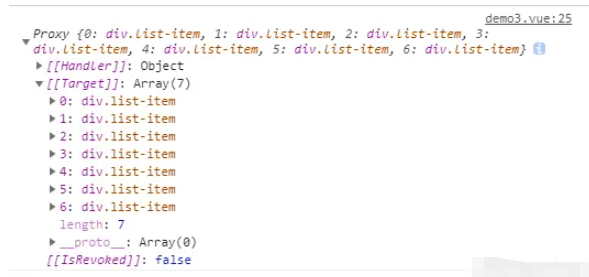
此時可以通過state.refList[index]的形式獲取子元素dom
通過v-for循環生成的不固定數量或者多種元素的場景
<template>
<div>
<p>通過:ref將dom引用放到數組中</p>
<div>
<div :ref="setRefAction" @click="higherAction(index)" v-for="(item, index) in state.list" :key="index">
<span>{{item}}</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
const state = reactive({
list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
refList: [] as Array<any>
})
const higherAction = (index: number) => {
let height = state.refList[index].style.height ? state.refList[index].style.height : '20px';
height = Number(height.replace('px', ''));
state.refList[index].style = `height: ${height + 20}px`;
console.log(state.refList[index]);
}
const setRefAction = (el: any) => {
state.refList.push(el);
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo2-container {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
.list-section {
width: 200px;
.list-item {
width: 200px;
height: 20px;
background-color: pink;
color: #333;
transition: all .5s ease-in-out;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
}
}
</style>
<template>
<div ref="cellRef" @click="cellAction">
<span>{{item}}</span>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue';
const props = defineProps({
item: Number
})
const emit = defineEmits(['cellTap']);
const cellRef = ref();
const cellAction = () => {
emit('cellTap', cellRef.value);
}
</script>
通過對子組件添加了ref屬性,并聲明了一個與ref屬性名稱相同的變量cellRef,此時可以通過emit將cellRef.value作為一個dom引用傳遞出去
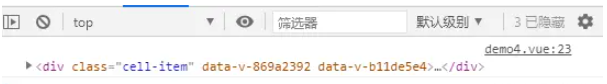
多個頁面都可能有操作組件dom的場景
<template>
<div ref="cellRef" @click="cellAction">
<span>{{item}}</span>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue';
const props = defineProps({
item: Number
})
const emit = defineEmits(['cellTap']);
const cellRef = ref();
const cellAction = () => {
emit('cellTap', cellRef.value);
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.cell-item {
width: 200px;
height: 20px;
background-color: pink;
color: #333;
transition: all .5s ease-in-out;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
</style><template>
<div>
<p>通過子組件emit傳遞ref</p>
<div>
<Cell :item="item" @cellTap="cellTapHandler" v-for="(item, index) in state.list" :key="index">
</Cell>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
import Cell from '@/components/Cell.vue'
const state = reactive({
list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
refList: [] as Array<any>
})
const cellTapHandler = (el: any) => {
let height = el.style.height ? el.style.height : '20px';
height = Number(height.replace('px', ''));
el.style = `height: ${height + 20}px`;
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo2-container {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
.list-section {
width: 200px;
}
}
</style>
“Vue3怎么操作dom”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。