您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天小編給大家分享一下OpenCV如何實現圖像去噪算法的相關知識點,內容詳細,邏輯清晰,相信大部分人都還太了解這方面的知識,所以分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后有所收獲,下面我們一起來了解一下吧。
Primal-dual algorithm是一種用于解決特殊類型的變分問題的算法(即找到一個函數來最小化一些泛函)。
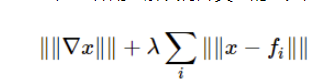
特別是由于圖像去噪可以看作是變分問題,因此可以使用原始對偶算法進行去噪,這正是該算法所實現的。
cv::denoise_TVL1 (const std::vector< Mat > &observations, Mat &result, double lambda=1.0, int niters=30)
| observations | 該數組應包含要恢復的圖像的一個或多個噪聲版本。 |
| result | 這里將存儲去噪圖像。 無需預先分配存儲空間,必要時會自動分配。 |
| lambda | 對應于上述公式中的 λ。 當它被放大時,平滑(模糊)的圖像比細節(但可能有更多噪點)的圖像更受歡迎。 粗略地說,隨著它變小,結果會更加模糊,但會去除更多的異常值。 |
| niters | 算法將運行的迭代次數。 當然,越多的迭代越好,但是這個說法很難量化細化,所以就使用默認值,如果結果不好就增加它。 |
使用非局部均值去噪算法,該方法基于一個簡單的原理:將像素的顏色替換為相似像素顏色的平均值。 但是與給定像素最相似的像素根本沒有理由靠近。 因此,掃描圖像的大部分以尋找真正類似于想要去噪的像素的所有像素是合法的。執行圖像去噪,并進行了多種計算優化。 噪聲預期為高斯白噪聲。
cv::cuda::fastNlMeansDenoising (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h, int search_window=21, int block_size=7, Stream &stream=Stream::Null()) cv::fastNlMeansDenoising (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h=3, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21) cv::fastNlMeansDenoising (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, const std::vector< float > &h, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21, int
針對彩色圖像的 fastNlMeansDenoising 函數。
cv::cuda::fastNlMeansDenoisingColored (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h_luminance, float photo_render, int search_window=21, int block_size=7, Stream &stream=Stream::Null()) cv::fastNlMeansDenoisingColored (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h=3, float hColor=3, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21)
針對圖像序列的 fastNlMeansDenoising 函數。
cv::fastNlMeansDenoisingColoredMulti (InputArrayOfArrays srcImgs, OutputArray dst, int imgToDenoiseIndex, int temporalWindowSize, float h=3, float hColor=3, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21) cv::fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti (InputArrayOfArrays srcImgs, OutputArray dst, int imgToDenoiseIndex, int temporalWindowSize, float h=3, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21) cv::fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti (InputArrayOfArrays srcImgs, OutputArray dst, int imgToDenoiseIndex, int temporalWindowSize, const std::vector< float > &h, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21, int normType=NORM_L2)
執行純非局部方法去噪,沒有任何簡化,因此速度不快。
cv::cuda::nonLocalMeans (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h, int search_window=21, int block_size=7, int borderMode=BORDER_DEFAULT, Stream &stream=Stream::Null())
opencv\modules\photo\src\denoise_tvl1.cpp
#include "precomp.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define ABSCLIP(val,threshold) MIN(MAX((val),-(threshold)),(threshold))
namespace cv{
class AddFloatToCharScaled{
public:
AddFloatToCharScaled(double scale):_scale(scale){}
inline double operator()(double a,uchar b){
return a+_scale*((double)b);
}
private:
double _scale;
};
using std::transform;
void denoise_TVL1(const std::vector<Mat>& observations,Mat& result, double lambda, int niters){
CV_Assert(observations.size()>0 && niters>0 && lambda>0);
const double L2 = 8.0, tau = 0.02, sigma = 1./(L2*tau), theta = 1.0;
double clambda = (double)lambda;
double s=0;
const int workdepth = CV_64F;
int i, x, y, rows=observations[0].rows, cols=observations[0].cols,count;
for(i=1;i<(int)observations.size();i++){
CV_Assert(observations[i].rows==rows && observations[i].cols==cols);
}
Mat X, P = Mat::zeros(rows, cols, CV_MAKETYPE(workdepth, 2));
observations[0].convertTo(X, workdepth, 1./255);
std::vector< Mat_<double> > Rs(observations.size());
for(count=0;count<(int)Rs.size();count++){
Rs[count]=Mat::zeros(rows,cols,workdepth);
}
for( i = 0; i < niters; i++ )
{
double currsigma = i == 0 ? 1 + sigma : sigma;
// P_ = P + sigma*nabla(X)
// P(x,y) = P_(x,y)/max(||P(x,y)||,1)
for( y = 0; y < rows; y++ )
{
const double* x_curr = X.ptr<double>(y);
const double* x_next = X.ptr<double>(std::min(y+1, rows-1));
Point2d* p_curr = P.ptr<Point2d>(y);
double dx, dy, m;
for( x = 0; x < cols-1; x++ )
{
dx = (x_curr[x+1] - x_curr[x])*currsigma + p_curr[x].x;
dy = (x_next[x] - x_curr[x])*currsigma + p_curr[x].y;
m = 1.0/std::max(std::sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy), 1.0);
p_curr[x].x = dx*m;
p_curr[x].y = dy*m;
}
dy = (x_next[x] - x_curr[x])*currsigma + p_curr[x].y;
m = 1.0/std::max(std::abs(dy), 1.0);
p_curr[x].x = 0.0;
p_curr[x].y = dy*m;
}
//Rs = clip(Rs + sigma*(X-imgs), -clambda, clambda)
for(count=0;count<(int)Rs.size();count++){
transform<MatIterator_<double>,MatConstIterator_<uchar>,MatIterator_<double>,AddFloatToCharScaled>(
Rs[count].begin(),Rs[count].end(),observations[count].begin<uchar>(),
Rs[count].begin(),AddFloatToCharScaled(-sigma/255.0));
Rs[count]+=sigma*X;
min(Rs[count],clambda,Rs[count]);
max(Rs[count],-clambda,Rs[count]);
}
for( y = 0; y < rows; y++ )
{
double* x_curr = X.ptr<double>(y);
const Point2d* p_curr = P.ptr<Point2d>(y);
const Point2d* p_prev = P.ptr<Point2d>(std::max(y - 1, 0));
// X1 = X + tau*(-nablaT(P))
x = 0;
s=0.0;
for(count=0;count<(int)Rs.size();count++){
s=s+Rs[count](y,x);
}
double x_new = x_curr[x] + tau*(p_curr[x].y - p_prev[x].y)-tau*s;
// X = X2 + theta*(X2 - X)
x_curr[x] = x_new + theta*(x_new - x_curr[x]);
for(x = 1; x < cols; x++ )
{
s=0.0;
for(count=0;count<(int)Rs.size();count++){
s+=Rs[count](y,x);
}
// X1 = X + tau*(-nablaT(P))
x_new = x_curr[x] + tau*(p_curr[x].x - p_curr[x-1].x + p_curr[x].y - p_prev[x].y)-tau*s;
// X = X2 + theta*(X2 - X)
x_curr[x] = x_new + theta*(x_new - x_curr[x]);
}
}
}
result.create(X.rows,X.cols,CV_8U);
X.convertTo(result, CV_8U, 255);
}
}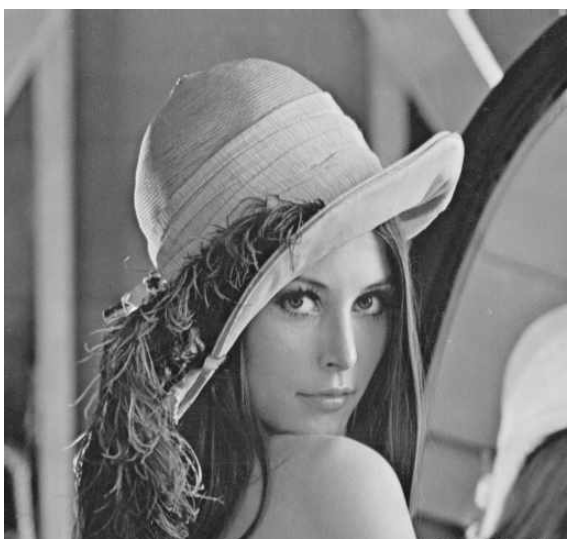
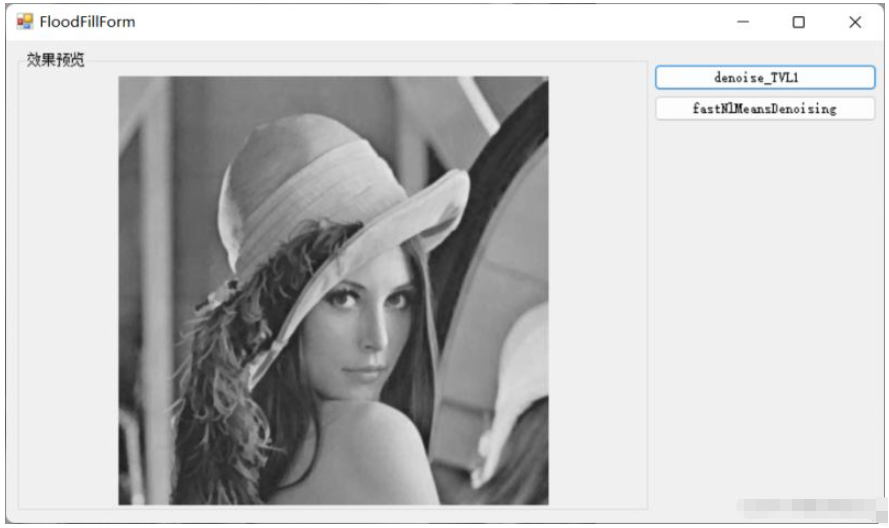
原圖
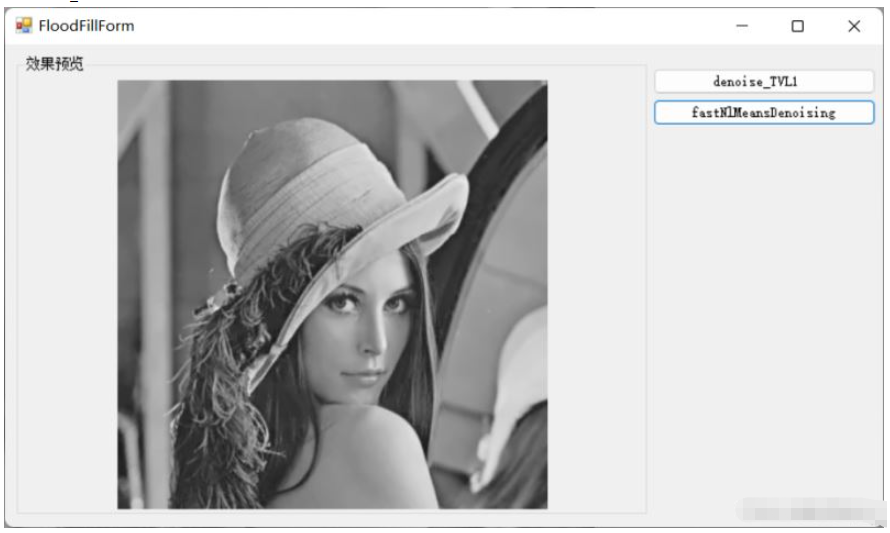
denoise_TVL1
以上就是“OpenCV如何實現圖像去噪算法”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家閱讀完這篇文章都有很大的收獲,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識,如果還想學習更多的知識,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。