您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹C++中對象排序的示例分析,文中介紹的非常詳細,具有一定的參考價值,感興趣的小伙伴們一定要看完!
在排序中進行交換的前提主要是進行對象間的 比較、
而常見的排序是對一個數組排序,然后對每個數組內容進行比較與交換、
如果是對一個class進行排序,則需要進行關鍵字成員進行比較,需要重寫下面幾個操作符:
bool operator == (const class& t); // 返回ture則表示相等
bool operator != (const class& t); // 和==相等操作符返回值相反
bool operator <(const class& t); // 返回true則當前對象小于t對象
bool operator > (const class& t);
bool operator <=(const class& t);
bool operator >=(const class& t);
比如將學生成績單按數學成績由高到低排序,如果數學成績相同的學生再按英語成績的高低等級排序。
代碼如下所示:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student {
int number; // 學號
int mathScore; // 數學成績
int enScore; // 英語成績
public:
Student() {
}
Student(int number, int mathScore, int enScore) {
this->number = number;
this->mathScore = mathScore;
this->enScore = enScore;
}
void printString() {
cout<<"number:"<<number <<" mathScore:" << mathScore <<" enScore:"<< enScore << endl;
}
bool operator == (const Student& t) {
return mathScore == t.mathScore && enScore == t.enScore;
}
// 不等于則調用==操作符,取反即可
bool operator != (const Student& t) {
return !(*this == t);
}
bool operator <(const Student& t) {
return mathScore < t.mathScore || (mathScore == t.mathScore && enScore < t.enScore);
}
bool operator > (const Student& t) {
return mathScore > t.mathScore || (mathScore == t.mathScore && enScore > t.enScore);
}
bool operator <=(const Student& t) {
return !(*this > t);
}
bool operator >=(const Student& t) {
return !(*this < t);
}
};測試代碼如下所示(使用上章我們寫的冒泡排序):
Student arr[8] = {
Student(1,65,77),
Student(2,44,65),
Student(3,75,65),
Student(4,65,77),
Student(5,98,97),
Student(6,86,96),
Student(7,92,63),
Student(8,32,78)
};
bubbleSort(arr, 8); // 使用冒泡排序 升序
cout<<"ascend: "<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
arr[i].printString();
}
cout<<endl;
bubbleSort(arr, 8, false); // 使用冒泡排序 降序
cout<<endl<<"descend: "<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
arr[i].printString();
}運行打印:
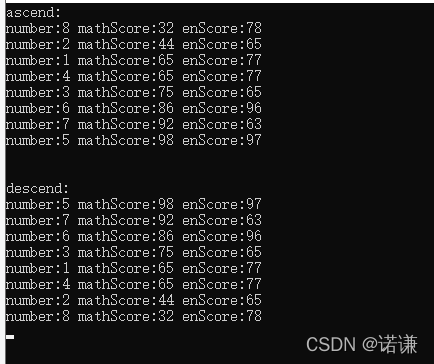
以上是“C++中對象排序的示例分析”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!希望分享的內容對大家有幫助,更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。