您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“Python Opencv數據增強的方法”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
常見的數據增強操作有:按比例放大或縮小圖片、旋轉、平移、水平翻轉、改變圖像通道等。
擴展縮放只是改變圖像的尺寸大小。OpenCV 提供的函數 cv2.resize()可以實現這個功能。圖像的尺寸可以自己手動設置,也可以指定縮放因子。可以選擇使用不同的插值方法。在縮放時我們推薦使用 cv2.INTER_AREA,在擴展時我們推薦使用 v2.INTER_CUBIC(慢) 和 v2.INTER_LINEAR。默認情況下所有改變圖像尺寸大小的操作使用的插值方法都是 cv2.INTER_LINEAR。
# 縮小 -- 寬和高都縮小為原來的scale倍 def zoom_down(img,scale): img = cv2.resize(img,None,fx= scale,fy= scale,interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC) return img # 放大 -- 寬和高都放大為原來的scale倍 def zoom_up(img,scale): img = cv2.resize(img,None,fx= scale,fy= scale,interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC) return img
resize庫中第二個參數是目標大小,例如如果我想把圖片resize成300*300大小的,可以這么寫:
img = cv2.resize(img,(300,300))
平移就是將對象換一個位置。如果你要沿(x,y)方向移動,移動的距離是(tx,ty),你可以以下面的方式構建移動矩陣:
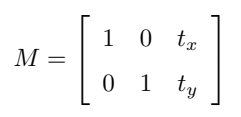
可以使用 Numpy 數組構建這個矩陣(數據類型是 np.float32),然后把它傳給函數cv2.warpAffine()。
mat_translation = np.float32([[1, 0, 20], [0, 1, 30]])
例如上面是的矩陣是將圖像往水平方向上移動20個像素點,豎直方向上移動30個像素點。
實例:
# 平移 -- 水平平移或豎直方向平移 def translation(img,tx,ty): height = img.shape[0] width = img.shape[1] mat_translation = np.float32([[1, 0, tx], [0, 1, ty]]) # 變換矩陣:設置平移變換所需的計算矩陣:2行3列 img = cv2.warpAffine(img, mat_translation, (width + tx, height + ty)) # 變換函數 return img
我這里封裝的tx和ty分別為水平和豎直方向需要移動的像素點數。
OpenCV 提供了一個函數:cv2.getRotationMatrix2D
# 旋轉 def rotation(img,angle,scale): rows = img.shape[0] cols = img.shape[1] # 這里的第一個參數為旋轉中心,第二個為旋轉角度,第三個為旋轉后的縮放因子 # 可以通過設置旋轉中心,縮放因子,以及窗口大小來防止旋轉后超出邊界的問題 M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cols / 2, rows / 2), angle, scale) # 向左旋轉angle度并縮放為原來的scale倍 img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (cols, rows)) # 第三個參數是輸出圖像的尺寸中心 return img
Opencv提供了cv2.flip()函數,可以第二個參數為1時為水平翻轉,為0時垂直翻轉。為了后面調用方便,我還是自己封裝了一下。
# 鏡像變換 def mirror(img,mode): img = cv2.flip(img, mode) # mode = 1 水平翻轉 mode = 0 垂直翻 return img
椒鹽噪聲為純黑或純白的像素點,隨機生成。
# 添加椒鹽噪聲 def spiced_salt_noise(img,prob): output = np.zeros(img.shape,np.uint8) thres = 1 - prob for i in range(img.shape[0]): for j in range(img.shape[1]): rdn = random.random() if rdn < prob: output[i][j] = 0 # 椒鹽噪聲由純黑和純白的像素點隨機組成 elif rdn > thres: output[i][j] = 255 else: output[i][j] = img[i][j] return output
與椒鹽噪聲不同,高斯噪聲是彩色的,方差越大時噪聲越大。
# 添加高斯噪聲 def gasuss_noise(image, mean = 0, var = 0.01): ''' 添加高斯噪聲 mean : 均值 var : 方差,方差越大越模糊 ''' image = np.array(image/255, dtype=float) noise = np.random.normal(mean, var ** 0.5, image.shape) out = image + noise if out.min() < 0: low_clip = -1. else: low_clip = 0. out = np.clip(out, low_clip, 1.0) out = np.uint8(out*255) return out
將圖片模糊或平滑有多種算法,例如高斯模糊、中值模糊、均值模糊等,我這里使用一個比較普通的cv2.blur()實現。同樣也是先封裝方便我后面調用。
# 模糊 def blur(img,scale): img = cv2.blur(img,(scale,scale)) # scale越大越模糊 return img
這里的scale其實就是濾波器的尺寸,一般取奇數,scale越大越模糊,
在opencv中,圖像的通道順序為BGR,也就是藍綠紅,可以改變成其他順序以得到不同的效果。
# 重新組合顏色通道 def change_channel(img): b = cv2.split(img)[0] g = cv2.split(img)[1] r = cv2.split(img)[2] brg = cv2.merge([b, r, g]) # 可以自己改變組合順序 return brg
我有以下幾張測試圖片:
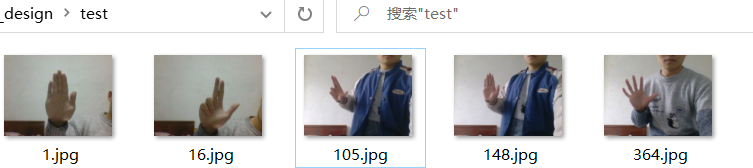
我希望隨機地對這些圖片進行一些變換,最終執行結果如下:
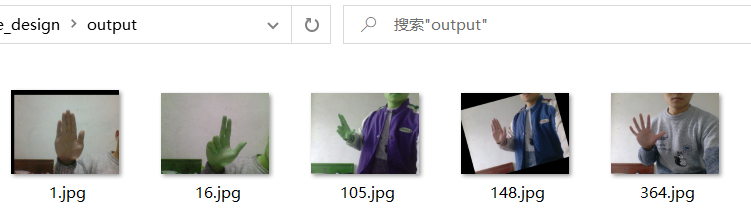
可以看到程序對我的圖片隨機進行了各種變換,我這里只是一次變換,讀者也可以嘗試對圖片同時進行多種變換。
本次程序如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2022/2/18 16:30
# @Author : 若谷
# @File : Data_Augumentation.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import numpy as np
import cv2
import random
import os
import sys
# 縮小 -- 寬和高都縮小為原來的scale倍
def zoom_down(img, scale):
img = cv2.resize(img, None, fx=scale, fy=scale, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
return img
# 放大 -- 寬和高都放大為原來的scale倍
def zoom_up(img, scale):
img = cv2.resize(img, None, fx=scale, fy=scale, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
return img
# 平移 -- 水平平移或豎直方向平移
def translation(img, tx, ty):
height = img.shape[0]
width = img.shape[1]
mat_translation = np.float32([[1, 0, tx], [0, 1, ty]]) # 變換矩陣:設置平移變換所需的計算矩陣:2行3列
img = cv2.warpAffine(img, mat_translation, (width + tx, height + ty)) # 變換函數
return img
# 旋轉
def rotation(img, angle, scale):
rows = img.shape[0]
cols = img.shape[1]
# 這里的第一個參數為旋轉中心,第二個為旋轉角度,第三個為旋轉后的縮放因子
# 可以通過設置旋轉中心,縮放因子,以及窗口大小來防止旋轉后超出邊界的問題
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cols / 2, rows / 2), angle, scale) # 向左旋轉angle度并縮放為原來的scale倍
img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (cols, rows)) # 第三個參數是輸出圖像的尺寸中心
return img
# 鏡像變換
def mirror(img, mode):
img = cv2.flip(img, mode) # mode = 1 水平翻轉 mode = 0 垂直翻
return img
# 添加椒鹽噪聲
def spiced_salt_noise(img, prob):
output = np.zeros(img.shape, np.uint8)
thres = 1 - prob
for i in range(img.shape[0]):
for j in range(img.shape[1]):
rdn = random.random()
if rdn < prob:
output[i][j] = 0 # 椒鹽噪聲由純黑和純白的像素點隨機組成
elif rdn > thres:
output[i][j] = 255
else:
output[i][j] = img[i][j]
return output
# 模糊
def blur(img, scale):
img = cv2.blur(img, (scale, scale)) # scale越大越模糊
return img
# 添加高斯噪聲
def gasuss_noise(image, mean=0, var=0.01):
'''
添加高斯噪聲
mean : 均值
var : 方差,方差越大越模糊
'''
image = np.array(image / 255, dtype=float)
noise = np.random.normal(mean, var ** 0.5, image.shape)
out = image + noise
if out.min() < 0:
low_clip = -1.
else:
low_clip = 0.
out = np.clip(out, low_clip, 1.0)
out = np.uint8(out * 255)
return out
# 重新組合顏色通道
def change_channel(img):
b = cv2.split(img)[0]
g = cv2.split(img)[1]
r = cv2.split(img)[2]
brg = cv2.merge([b, r, g]) # 可以自己改變組合順序
return brg
# 隨機進行以上操作
def Data_Augument():
for i in images_list:
img = cv2.imread(image_dir+i) # 圖片路徑+圖片名字
cv2.imshow('img',img)
functions = [('zoom_down', [img, 0.8]), # 第一個參數為函數名,后面為函數調用時的參數
('zoom_up', [img, 1.2]),
('translation', [img, 20, 30]),
('rotation', [img, 15, 0.9]),
('mirror', [img, 1]),
('spiced_salt_noise', [img, 0.01]),
('blur', [img, 5]),
('gasuss_noise', [img, 0, 0.01]),
('change_channel', [img])]
choice = random.choice(functions) # 隨機選擇一個函數執行
this_module = sys.modules[__name__] # 當前文件
res = getattr(this_module, choice[0])(*choice[1])
cv2.imwrite(output_dir + i, res)
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_dir = './test/' # 源圖片路徑
images_list = os.listdir(image_dir)
nums = len(os.listdir(image_dir))
print('found %d pictures' % nums)
output_dir = './output/' # 圖像變換后的保存路徑
Data_Augument() # 執行
print('finished!')“Python Opencv數據增強的方法”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。