您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“mysql5.6主從搭建的方法是什么”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
系統:centos6.6
主:192.168.142.129 mysql-5.6.30.tar.gz
從:192.168.142.130 192.168.142.131 mysql-5.6.30.tar.gz
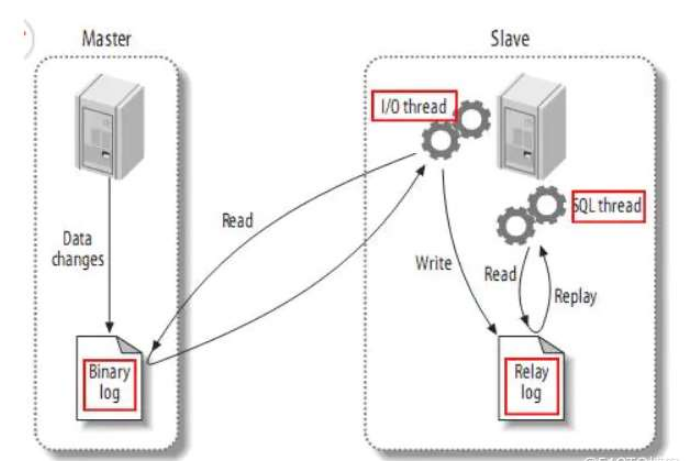
(1) master將改變記錄到二進制日志(binary log)中;
(2) slave將master的binary log events拷貝到它的中繼日志(relay log);slave的I/O線程從master的二進制日志中讀取事件并寫入中繼日志;
(3) slave重做中繼日志中的事件,將改變反映它自己的數據。slave的SQL線程從中繼日志讀取事件,并在本地重放其中的事件,使其與master中的數據一致。
mysql主從實現的步驟:
1、使用mysqldump 命令備份數據庫,
2、查看主節點二進制的位置點
3、創建備份用戶,并授權(replication client.replication slave)
4、從服務器修改server-id,必須與主mysql的server-id不同,開啟中繼日子,關閉二進制日子
5、從數據庫,倒入數據,并使用授權用戶,連接主mysql
6、start slave
SQL語言共分為以下幾大類:查詢語言DQL,控制語言DCL,操縱語言DML,定義語言DDL。事務控制TCL.
DQL(Data QUERY Languages)語句:即數據庫定義語句,用來查詢SELECT子句,FROM子句,WHERE子句組成的查詢塊,比如:select–from–where–grouop by–having–order by–limit
DDL(Data Definition Languages)語句:即數據庫定義語句,用來創建數據庫中的表、索引、視圖、存儲過程、觸發器等,常用的語句關鍵字有CREATE,ALTER,DROP,TRUNCATE,COMMENT,RENAME。增刪改表的結構
DML(Data Manipulation Language)語句:即數據操縱語句,用來查詢、添加、更新、刪除等,常用的語句關鍵字有:SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,MERGE,CALL,EXPLAIN PLAN,LOCK TABLE,包括通用性的增刪改查。增刪改表的數據
DCL(Data Control Language)語句:即數據控制語句,用于授權/撤銷數據庫及其字段的權限(DCL is short name of Data Control Language which includes commands such as GRANT and mostly concerned with rights, permissions and other controls of the database system.)。常用的語句關鍵字有:GRANT,REVOKE。
TCL(Transaction Control Language)語句:事務控制語句,用于控制事務,常用的語句關鍵字有:COMMIT,ROLLBACK,SAVEPOINT,SET TRANSACTION。
#!/bin/bash
yum -y install make gcc gcc-c++ openssl openssl-devel pcre-devel gd cmake ncurses ncurses-devel
id -u mysql
if [ `echo $?` -ne 0 ];
then
groupadd mysql
useradd -M -g mysql -s /sbin/nologin mysql
fi
if [ ! -d "/usr/local/mysql" ];
then
mkdir -p /usr/local/mysql
fi
mkdir -p /data/mysql
chown -R mysql:mysql /data/mysql
cd /home/soft/ #軟件存放目錄
tar zxvf mysql-5.6.30.tar.gz
cd mysql-5.6.30
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/mysql -DSYSCONFDIR=/etc -DMYSQL_DATADIR=/data/mysql/data -DINSTALL_MANDIR=/usr/share/man -DMYSQL_TCP_PORT=3306 -DMYSQL_UNIX_ADDR=/tmp/mysql.sock -DDEFAULT_CHARSET=utf8 -DEXTRA_CHARSETS=all -DDEFAULT_COLLATION=utf8_general_ci -DWITH_READLINE=1 -DWITH_SSL=system -DWITH_EMBEDDED_SERVER=1 -DENABLED_LOCAL_INFILE=1 -DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1
make && make install
chown -R mysql:mysql .
chmod +x scripts/mysql_install_db
./scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/data/mysql
cp ./support-files/mysql.server /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld
chmod 755 /etc/init.d/mysqld
chkconfig mysqld on
cat> /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld <<'EOF' #mysql啟動腳本
#!/bin/sh
# Copyright Abandoned 1996 TCX DataKonsult AB & Monty Program KB & Detron HB
# This file is public domain and comes with NO WARRANTY of any kind
# MySQL daemon start/stop script.
# Usually this is put in /etc/init.d (at least on machines SYSV R4 based
# systems) and linked to /etc/rc3.d/S99mysql and /etc/rc0.d/K01mysql.
# When this is done the mysql server will be started when the machine is
# started and shut down when the systems goes down.
# Comments to support chkconfig on RedHat Linux
# chkconfig: 2345 64 36
# description: A very fast and reliable SQL database engine.
# Comments to support LSB init script conventions
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: mysql
# Required-Start: $local_fs $network $remote_fs
# Should-Start: ypbind nscd ldap ntpd xntpd
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $network $remote_fs
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: start and stop MySQL
# Description: MySQL is a very fast and reliable SQL database engine.
### END INIT INFO
# If you install MySQL on some other places than /usr/local/mysql, then you
# have to do one of the following things for this script to work:
#
# - Run this script from within the MySQL installation directory
# - Create a /etc/my.cnf file with the following information:
# [mysqld]
# basedir=<path-to-mysql-installation-directory>
# - Add the above to any other configuration file (for example ~/.my.ini)
# and copy my_print_defaults to /usr/bin
# - Add the path to the mysql-installation-directory to the basedir variable
# below.
#
# If you want to affect other MySQL variables, you should make your changes
# in the /etc/my.cnf, ~/.my.cnf or other MySQL configuration files.
# If you change base dir, you must also change datadir. These may get
# overwritten by settings in the MySQL configuration files.
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
datadir=/data/mysql
# Default value, in seconds, afterwhich the script should timeout waiting
# for server start.
# Value here is overriden by value in my.cnf.
# 0 means don't wait at all
# Negative numbers mean to wait indefinitely
service_startup_timeout=900
# Lock directory for RedHat / SuSE.
lockdir='/var/lock/subsys'
lock_file_path="$lockdir/mysql"
# The following variables are only set for letting mysql.server find things.
# Set some defaults
mysqld_pid_file_path=
if test -z "$basedir"
then
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
bindir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
if test -z "$datadir"
then
datadir=/data/mysql/data
fi
sbindir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
libexecdir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
else
bindir="$basedir/bin"
if test -z "$datadir"
then
datadir="$basedir/data"
fi
sbindir="$basedir/sbin"
libexecdir="$basedir/libexec"
fi
# datadir_set is used to determine if datadir was set (and so should be
# *not* set inside of the --basedir= handler.)
datadir_set=
# Use LSB init script functions for printing messages, if possible
#
lsb_functions="/lib/lsb/init-functions"
if test -f $lsb_functions ; then
. $lsb_functions
else
log_success_msg()
{
echo " SUCCESS! $@"
}
log_failure_msg()
{
echo " ERROR! $@"
}
fi
PATH="/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin:$basedir/bin"
export PATH
mode=$1 # start or stop
[ $# -ge 1 ] && shift
other_args="$*" # uncommon, but needed when called from an RPM upgrade action
# Expected: "--skip-networking --skip-grant-tables"
# They are not checked here, intentionally, as it is the resposibility
# of the "spec" file author to give correct arguments only.
case `echo "testing\c"`,`echo -n testing` in
*c*,-n*) echo_n= echo_c= ;;
*c*,*) echo_n=-n echo_c= ;;
*) echo_n= echo_c='\c' ;;
esac
parse_server_arguments() {
for arg do
case "$arg" in
--basedir=*) basedir=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'`
bindir="$basedir/bin"
if test -z "$datadir_set"; then
datadir="$basedir/data"
fi
sbindir="$basedir/sbin"
libexecdir="$basedir/libexec"
;;
--datadir=*) datadir=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'`
datadir_set=1
;;
--pid-file=*) mysqld_pid_file_path=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'` ;;
--service-startup-timeout=*) service_startup_timeout=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'` ;;
esac
done
}
wait_for_pid () {
verb="$1" # created | removed
pid="$2" # process ID of the program operating on the pid-file
pid_file_path="$3" # path to the PID file.
i=0
avoid_race_condition="by checking again"
while test $i -ne $service_startup_timeout ; do
case "$verb" in
'created')
# wait for a PID-file to pop into existence.
test -s "$pid_file_path" && i='' && break
;;
'removed')
# wait for this PID-file to disappear
test ! -s "$pid_file_path" && i='' && break
;;
*)
echo "wait_for_pid () usage: wait_for_pid created|removed pid pid_file_path"
exit 1
;;
esac
# if server isn't running, then pid-file will never be updated
if test -n "$pid"; then
if kill -0 "$pid" 2>/dev/null; then
: # the server still runs
else
# The server may have exited between the last pid-file check and now.
if test -n "$avoid_race_condition"; then
avoid_race_condition=""
continue # Check again.
fi
# there's nothing that will affect the file.
log_failure_msg "The server quit without updating PID file ($pid_file_path)."
return 1 # not waiting any more.
fi
fi
echo $echo_n ".$echo_c"
i=`expr $i + 1`
sleep 1
done
if test -z "$i" ; then
log_success_msg
return 0
else
log_failure_msg
return 1
fi
}
# Get arguments from the my.cnf file,
# the only group, which is read from now on is [mysqld]
if test -x ./bin/my_print_defaults
then
print_defaults="./bin/my_print_defaults"
elif test -x $bindir/my_print_defaults
then
print_defaults="$bindir/my_print_defaults"
elif test -x $bindir/mysql_print_defaults
then
print_defaults="$bindir/mysql_print_defaults"
else
# Try to find basedir in /etc/my.cnf
conf=/etc/my.cnf
print_defaults=
if test -r $conf
then
subpat='^[^=]*basedir[^=]*=\(.*\)$'
dirs=`sed -e "/$subpat/!d" -e 's//\1/' $conf`
for d in $dirs
do
d=`echo $d | sed -e 's/[ ]//g'`
if test -x "$d/bin/my_print_defaults"
then
print_defaults="$d/bin/my_print_defaults"
break
fi
if test -x "$d/bin/mysql_print_defaults"
then
print_defaults="$d/bin/mysql_print_defaults"
break
fi
done
fi
# Hope it's in the PATH ... but I doubt it
test -z "$print_defaults" && print_defaults="my_print_defaults"
fi
#
# Read defaults file from 'basedir'. If there is no defaults file there
# check if it's in the old (depricated) place (datadir) and read it from there
#
extra_args=""
if test -r "$basedir/my.cnf"
then
extra_args="-e $basedir/my.cnf"
else
if test -r "$datadir/my.cnf"
then
extra_args="-e $datadir/my.cnf"
fi
fi
parse_server_arguments `$print_defaults $extra_args mysqld server mysql_server mysql.server`
#
# Set pid file if not given
#
if test -z "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
then
mysqld_pid_file_path=$datadir/`hostname`.pid
else
case "$mysqld_pid_file_path" in
/* ) ;;
* ) mysqld_pid_file_path="$datadir/$mysqld_pid_file_path" ;;
esac
fi
case "$mode" in
'start')
# Start daemon
# Safeguard (relative paths, core dumps..)
cd $basedir
echo $echo_n "Starting MySQL"
if test -x $bindir/mysqld_safe
then
# Give extra arguments to mysqld with the my.cnf file. This script
# may be overwritten at next upgrade.
$bindir/mysqld_safe --datadir="$datadir" --pid-file="$mysqld_pid_file_path" $other_args >/dev/null 2>&1 &
wait_for_pid created "$!" "$mysqld_pid_file_path"; return_value=$?
# Make lock for RedHat / SuSE
if test -w "$lockdir"
then
touch "$lock_file_path"
fi
exit $return_value
else
log_failure_msg "Couldn't find MySQL server ($bindir/mysqld_safe)"
fi
;;
'stop')
# Stop daemon. We use a signal here to avoid having to know the
# root password.
if test -s "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
then
mysqld_pid=`cat "$mysqld_pid_file_path"`
if (kill -0 $mysqld_pid 2>/dev/null)
then
echo $echo_n "Shutting down MySQL"
kill $mysqld_pid
# mysqld should remove the pid file when it exits, so wait for it.
wait_for_pid removed "$mysqld_pid" "$mysqld_pid_file_path"; return_value=$?
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL server process #$mysqld_pid is not running!"
rm "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
fi
# Delete lock for RedHat / SuSE
if test -f "$lock_file_path"
then
rm -f "$lock_file_path"
fi
exit $return_value
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL server PID file could not be found!"
fi
;;
'restart')
# Stop the service and regardless of whether it was
# running or not, start it again.
if $0 stop $other_args; then
$0 start $other_args
else
log_failure_msg "Failed to stop running server, so refusing to try to start."
exit 1
fi
;;
'reload'|'force-reload')
if test -s "$mysqld_pid_file_path" ; then
read mysqld_pid < "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
kill -HUP $mysqld_pid && log_success_msg "Reloading service MySQL"
touch "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL PID file could not be found!"
exit 1
fi
;;
'status')
# First, check to see if pid file exists
if test -s "$mysqld_pid_file_path" ; then
read mysqld_pid < "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
if kill -0 $mysqld_pid 2>/dev/null ; then
log_success_msg "MySQL running ($mysqld_pid)"
exit 0
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running, but PID file exists"
exit 1
fi
else
# Try to find appropriate mysqld process
mysqld_pid=`pidof $libexecdir/mysqld`
if test -z $mysqld_pid ; then
if test -f "$lock_file_path" ; then
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running, but lock file ($lock_file_path) exists"
exit 2
fi
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running"
exit 3
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL is running but PID file could not be found"
exit 4
fi
fi
;;
*)
# usage
basename=`basename "$0"`
echo "Usage: $basename {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|status} [ MySQL server options ]"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0
EOF
cat> /etc/my.cnf <<'EOF' #mysql配置文件
[client]
#password = your_password
port = 3306
socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
# Here follows entries for some specific programs
# The MySQL server
[mysqld]
port = 3306
socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
skip-external-locking
key_buffer_size = 384M
max_allowed_packet = 64M
table_open_cache = 512
sort_buffer_size = 2M
read_buffer_size = 2M
read_rnd_buffer_size = 8M
myisam_sort_buffer_size = 64M
thread_cache_size = 8
query_cache_size = 32M
# Try number of CPU's*2 for thread_concurrency
thread_concurrency = 8
basedir = /usr/local/mysql
datadir = /data/mysql
max_connections = 5000
long_query_time = 1
slow_query_log = 1
slow_query_log_file = /var/log/mysql/slow.log
# Don't listen on a TCP/IP port at all. This can be a security enhancement,
# if all processes that need to connect to mysqld run on the same host.
# All interaction with mysqld must be made via Unix sockets or named pipes.
# Note that using this option without enabling named pipes on Windows
# (via the "enable-named-pipe" option) will render mysqld useless!
lower_case_table_names = 1
# Replication Master Server (default)
# binary logging is required for replication
#log-bin=mysql-bin
skip-name-resolve
# required unique id between 1 and 2^32 - 1
# defaults to 1 if master-host is not set
# but will not function as a master if omitted
#server-id = 1
# binary logging - not required for slaves, but recommended
#log-bin=mysql-bin
#
# binary logging format - mixed recommended
#binlog_format=mixed
# Uncomment the following if you are using InnoDB tables
#innodb_data_home_dir = /data/mysql/data
#innodb_data_file_path = ibdata1:2000M;ibdata2:10M:autoextend
#innodb_log_group_home_dir = /data/mysql/data
# You can set .._buffer_pool_size up to 50 - 80 %
# of RAM but beware of setting memory usage too high
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 4096M
#innodb_additional_mem_pool_size = 20M
# Set .._log_file_size to 25 % of buffer pool size
innodb_log_file_size = 512M
#innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 0
#innodb_lock_wait_timeout = 50
[mysqldump]
quick
max_allowed_packet = 64M
[mysql]
no-auto-rehash
# Remove the next comment character if you are not familiar with SQL
#safe-updates
[myisamchk]
key_buffer_size = 256M
sort_buffer_size = 256M
read_buffer = 2M
write_buffer = 2M
[mysqlhotcopy]
interactive-timeout
EOF
ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqladmin /usr/bin
ln -s /usr/local/mysql/lib/mysql /usr/lib
ln -s /usr/local/mysql/include/mysql /usr/include/mysql
mkdir /var/lib/mysql
ln -s /tmp/mysql.sock /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/mysql/bin' >> /etc/profile
sleep 2
source /etc/profile
service mysqld start
sleep 5
cd /usr/local/mysql/bin && mysqladmin -uroot password 'mysql' #授權root用戶的password
source /etc/profile1、這里驗證主庫有數據的情況,然后授權有復制權限的用戶
mysql> create database db1; mysql> use db1 mysql> create table t1(id int, name varchar(12)); mysql> insert into t1 values(1, 'tom'), (2, 'jerry'), (3, 'jack'); mysql> grant replication slave,replication client on *.* to 'backuser'@'192.168.142.130' identified by 'mysqll'; mysql> grant replication slave,replication client on *.* to 'backuser'@'192.168.142.131' identified by 'mysql'; mysql> flush privileges;
2、修改各個數據庫的配置文件后重啟數據庫
vi /etc/my.cnf #主庫配置文件 server-id=1 log-bin=mysql-bin binlog-do-db=db1 binlog-ignore-db=mysql vi /etc/my.cnf #從庫配置文件 server-id=2 #從庫id不能和主庫一樣,其他從庫往后面排 log-bin=relay-bin replicate-do-db=db1 #同步db1庫 replicate-ignore-db=mysql #不會同步mysql庫 read_only #只讀 service mysqld restart
3、主庫鎖表備份,然后文件傳給從庫
mysql> flush tables with read lock; #主庫鎖表防止新的數據寫入 mysql> show master status; #查看主庫位置節點 新打開一個終端備份: mysqldump -u root -p --default-character-set=utf8 --opt -Q -R --skip-lock-tables db1 > /root/db1.sql scp /root/db1.sql root@192.168.142.130:/root scp /root/db1.sql root@192.168.142.130:/root
4、從庫導入數據,然后change到主庫的節點
mysql -u root -p mysql> create database db1; mysql> use db1 mysql> source /root/db1.sql mysql> change master to master_host='192.168.142.129',master_user='backuser',master_password='mysql',master_log_file='mysql-bin.000001',master_log_pos=120; mysql> start slave; mysql> show slave status\G
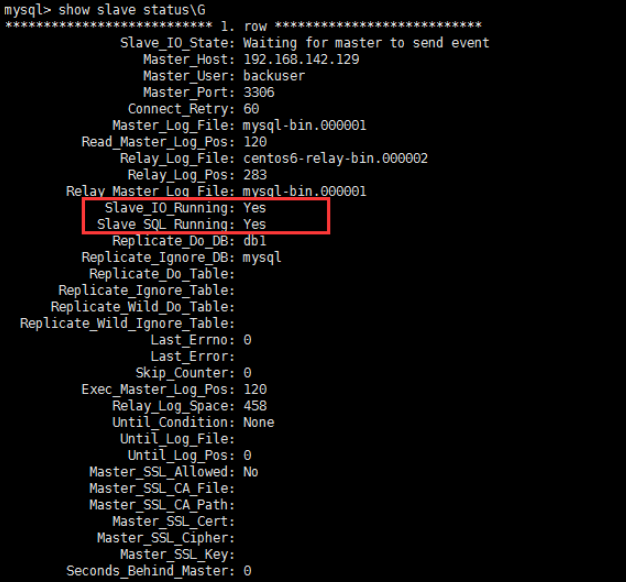
5、主庫解鎖
mysql> unlock tables;
以上配置對主從不同步,重新配置主從同樣適用。
1、造成不同步的原因
網絡的延遲主從兩臺機器的負載不一致max_allowed_packet設置不一致key自增鍵開始的鍵值跟自增步長設置不一致引起的主從不一致mysql異常宕機情況下,如果未設置sync_binlog=1或者innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1很有可能
出現binlog或者relaylog文件出現損壞,導致主從不一致mysql本身的bug引起的主從不同步版本不一致,特別是高版本是主,低版本為從的情況下,主數據庫上面支持的功能,從數據庫上面不支持該功能
2、解決辦法
(1)忽略錯誤后,繼續同步
該方法適用于主從庫數據相差不大,或者要求數據可以不完全統一的情況,數據要求不嚴格的情況
stop slave; set global sql_slave_skip_counter =1; start slave; show slave status\G
(2)重新做主從
參考上面配置主庫鎖表重新做主從。
“mysql5.6主從搭建的方法是什么”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。