您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Jackson庫中objectMapper的使用方法”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Jackson庫中objectMapper的使用方法”吧!
ObjectMapper類是Jackson庫的主要類。它提供一些功能將轉換成Java對象與SON結構互相轉換,在項目中遇到過,故記錄一下。
在 pom.xml 加入依賴
<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.8.3</version> </dependency>
創建一個實體類RiemannUser:
package com.test.objectMapper;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author riemann
* @date 2019/05/27 22:48
*/
public class RiemannUser implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int id;
private String message;
private Date sendDate;
private String nodeName;
private List<Integer> intList;
public RiemannUser() {
super();
}
public RiemannUser(int id, String message, Date sendDate) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.message = message;
this.sendDate = sendDate;
}
public static long getSerialVersionUID() {
return serialVersionUID;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public Date getSendDate() {
return sendDate;
}
public void setSendDate(Date sendDate) {
this.sendDate = sendDate;
}
public String getNodeName() {
return nodeName;
}
public void setNodeName(String nodeName) {
this.nodeName = nodeName;
}
public List<Integer> getIntList() {
return intList;
}
public void setIntList(List<Integer> intList) {
this.intList = intList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RiemannUser{" + "id=" + id + ", message='" + message + '\'' + ", sendDate=" + sendDate + ", nodeName='" + nodeName + '\'' + ", intList=" + intList + '}';
}
}先創建一個ObjectMapper,然后賦值一些屬性:
public static ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
static {
// 轉換為格式化的json
mapper.enable(SerializationFeature.INDENT_OUTPUT);
// 如果json中有新增的字段并且是實體類類中不存在的,不報錯
mapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
}1、對象與json字符串、byte數組
@Test
public void testObject() throws JsonGenerationException, JsonMappingException, IOException {
RiemannUser riemann = new RiemannUser(1,"Hello World", new Date());
mapper.writeValue(new File("D:/test.txt"), riemann);//寫到文件中
//mapper.writeValue(System.out, riemann); //寫到控制臺
String jsonStr = mapper.writeValueAsString(riemann);
System.out.println("對象轉json字符串: " + jsonStr);
byte[] byteArr = mapper.writeValueAsBytes(riemann);
System.out.println("對象轉為byte數組:" + byteArr);
RiemannUser riemannUser = mapper.readValue(jsonStr, RiemannUser.class);
System.out.println("json字符串轉為對象:" + riemannUser);
RiemannUser riemannUser2 = mapper.readValue(byteArr, RiemannUser.class);
System.out.println("byte數組轉為對象:" + riemannUser2);
}運行結果:
對象轉json字符串: {
"id" : 1,
"message" : "Hello World",
"sendDate" : 1558971056693,
"nodeName" : null,
"intList" : null
}
對象轉為byte數組:[B@31610302
json字符串轉為對象:RiemannUser{id=1, message='Hello World', sendDate=Mon May 27 23:30:56 CST 2019, nodeName='null', intList=null}
byte數組轉為對象:RiemannUser{id=1, message='Hello World', sendDate=Mon May 27 23:30:56 CST 2019, nodeName='null', intList=null}
2、list集合與json字符串
@Test
public void testList() throws JsonGenerationException, JsonMappingException, IOException {
List<RiemannUser> riemannList = new ArrayList<>();
riemannList.add(new RiemannUser(1,"a",new Date()));
riemannList.add(new RiemannUser(2,"b",new Date()));
riemannList.add(new RiemannUser(3,"c",new Date()));
String jsonStr = mapper.writeValueAsString(riemannList);
System.out.println("集合轉為字符串:" + jsonStr);
List<RiemannUser> riemannLists = mapper.readValue(jsonStr, List.class);
System.out.println("字符串轉集合:" + riemannLists);
}運行結果:
集合轉為字符串:[ {
"id" : 1,
"message" : "a",
"sendDate" : 1558971833351,
"nodeName" : null,
"intList" : null
}, {
"id" : 2,
"message" : "b",
"sendDate" : 1558971833351,
"nodeName" : null,
"intList" : null
}, {
"id" : 3,
"message" : "c",
"sendDate" : 1558971833351,
"nodeName" : null,
"intList" : null
} ]
字符串轉集合:[{id=1, message=a, sendDate=1558971833351, nodeName=null, intList=null}, {id=2, message=b, sendDate=1558971833351, nodeName=null, intList=null}, {id=3, message=c, sendDate=1558971833351, nodeName=null, intList=null}]
3、map與json字符串
@Test
public void testMap() {
Map<String, Object> testMap = new HashMap<>();
testMap.put("name", "riemann");
testMap.put("age", 27);
testMap.put("date", new Date());
testMap.put("user", new RiemannUser(1, "Hello World", new Date()));
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = mapper.writeValueAsString(testMap);
System.out.println("Map轉為字符串:" + jsonStr);
Map<String, Object> testMapDes = null;
try {
testMapDes = mapper.readValue(jsonStr, Map.class);
System.out.println("字符串轉Map:" + testMapDes);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Map轉為字符串:{
"date" : 1558972169132,
"name" : "riemann",
"user" : {
"id" : 1,
"message" : "Hello World",
"sendDate" : 1558972169134,
"nodeName" : null,
"intList" : null
},
"age" : 27
}
字符串轉Map:{date=1558972169132, name=riemann, user={id=1, message=Hello World, sendDate=1558972169134, nodeName=null, intList=null}, age=27}
4、修改轉換時的日期格式:
@Test
public void testOther() throws IOException {
// 修改時間格式
mapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
RiemannUser riemannUser = new RiemannUser(1,"Hello World",new Date());
riemannUser.setIntList(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
String jsonStr = mapper.writeValueAsString(riemannUser);
System.out.println("對象轉為字符串:" + jsonStr);
}運行結果:
對象轉為字符串:{
"id" : 1,
"message" : "Hello World",
"sendDate" : "2019-05-27 23:53:55",
"nodeName" : null,
"intList" : [ 1, 2, 3 ]
}
相信做過Java 開發對這個類應該不陌生,沒錯,這個類是jackson提供的,主要是用來把對象轉換成為一個json字符串返回到前端,
現在大部分數據交換都是以json來傳輸的,所以這個很重要,那你到底又對這個類有著有多少了解呢,下面我說一下我遇到的一些坑
首先,先把我要說的幾個坑需要設置的屬性貼出來先
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的時候序列對象的所有屬性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
//反序列化的時候如果多了其他屬性,不拋出異常
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
//如果是空對象的時候,不拋異常
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false);
//取消時間的轉化格式,默認是時間戳,可以取消,同時需要設置要表現的時間格式
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false);
objectMapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))簡單說一下這個類的基本用法,以下采用代碼塊加截圖的形式來說明和部分文字件數
package com.shiro.test;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的時候序列對象的所有屬性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
//取消時間的轉化格式,默認是時間戳,可以取消,同時需要設置要表現的時間格式
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false);
objectMapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
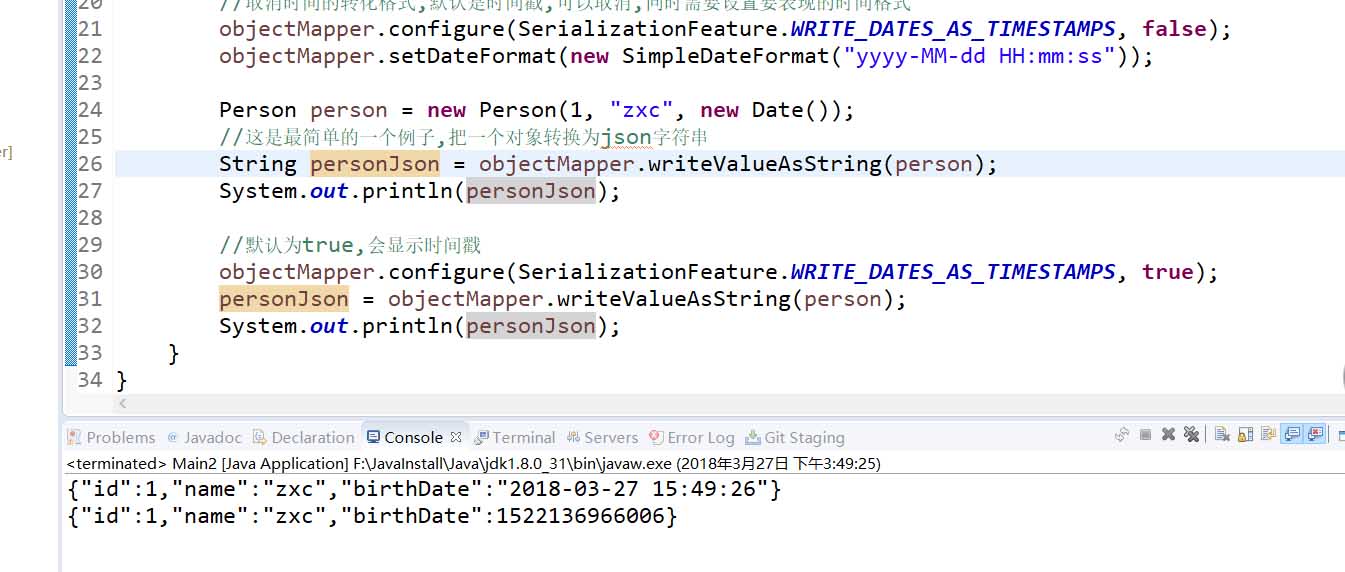
Person person = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
//這是最簡單的一個例子,把一個對象轉換為json字符串
String personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(personJson);
//默認為true,會顯示時間戳
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, true);
personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(personJson);
}
}輸出的信息如下
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false)的作用
package com.shiro.test;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
public class Main2 {
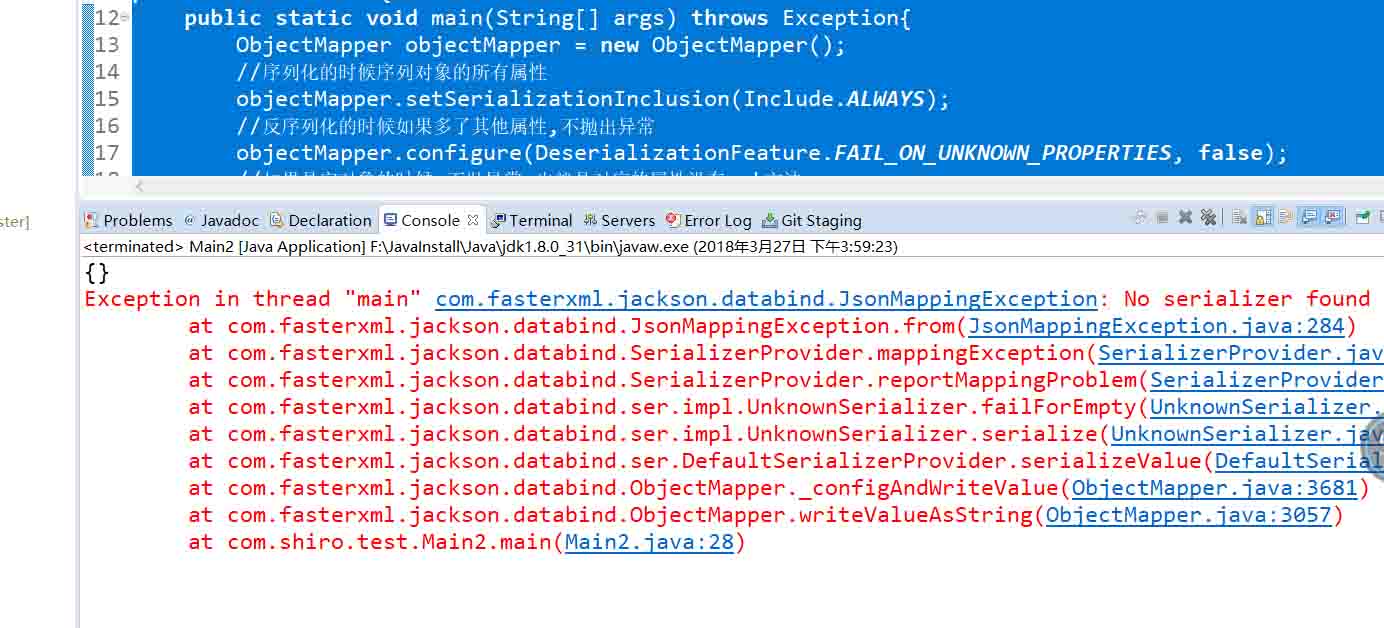
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的時候序列對象的所有屬性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
//如果是空對象的時候,不拋異常,也就是對應的屬性沒有get方法
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false);
Person person = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
String personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(personJson);
//默認是true,即會拋異常
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, true);
personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(personJson);
}
}對應的person類此時為
package com.shiro.test;
import java.util.Date;
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Date birthDate;
// public Integer getId() {
// return id;
// }
// public void setId(Integer id) {
// this.id = id;
// }
// public String getName() {
// return name;
// }
// public void setName(String name) {
// this.name = name;
// }
// public Date getBirthDate() {
// return birthDate;
// }
// public void setBirthDate(Date birthDate) {
// this.birthDate = birthDate;
// }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", birthDate=" + birthDate + "]";
}
public Person(Integer id, String name, Date birthDate) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.birthDate = birthDate;
}
public Person() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}結果如下
package com.shiro.test;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class Main2 {
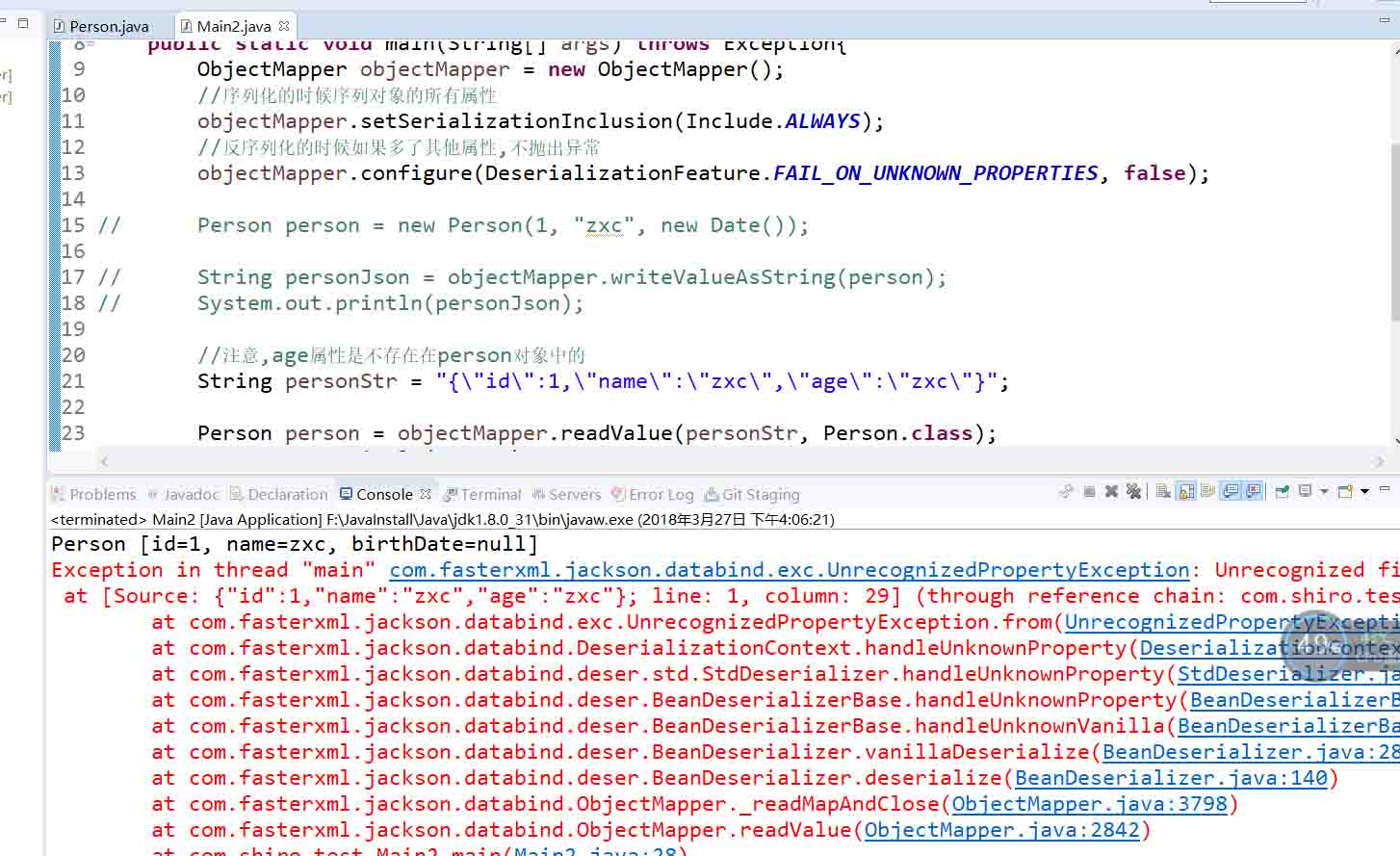
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的時候序列對象的所有屬性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
//反序列化的時候如果多了其他屬性,不拋出異常
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
// Person person = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
// String personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
// System.out.println(personJson);
//注意,age屬性是不存在在person對象中的
String personStr = "{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"zxc\",\"age\":\"zxc\"}";
Person person = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
//默認為true
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, true);
person = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}執行后的結果如下
這些便是這幾個屬性的作用所以,由于第一個比較簡單我就這樣說一下吧
Include.ALWAYS 是序列化對像所有屬性
Include.NON_NULL 只有不為null的字段才被序列化
Include.NON_EMPTY 如果為null或者 空字符串和空集合都不會被序列化
然后再說一下如何把一個對象集合轉換為一個 Java里面的數組
package com.shiro.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JavaType;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的時候序列對象的所有屬性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.NON_DEFAULT);
Person person1 = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
Person person2 = new Person(2, "ldh", new Date());
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<>();
persons.add(person1);
persons.add(person2);
//先轉換為json字符串
String personStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(persons);
//反序列化為List<user> 集合,1需要通過 TypeReference 來具體傳遞值
List<Person> persons2 = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, new TypeReference<List<Person>>() {});
for(Person person : persons2) {
System.out.println(person);
}
//2,通過 JavaType 來進行處理返回
JavaType javaType = objectMapper.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(List.class, Person.class);
List<Person> persons3 = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, javaType);
for(Person person : persons3) {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
}感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Jackson庫中objectMapper的使用方法”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Jackson庫中objectMapper的使用方法這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。