您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有關如何理解Elasticsearch Document Get API,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結了以下內容,希望大家根據這篇文章可以有所收獲。
小編將重點介紹ElasticSearch Doucment Get AP。
從《ElasticSearch Client詳解》可知,ElasticSearch Get Rest Hign level Get Api聲明如下:
public final GetResponse get(GetRequest getRequest, RequestOptions options) throws IOException
public final void getAsync(GetRequest getRequest, RequestOptions options, ActionListener<GetResponse> listener)
上述兩個API,一個同步調用,一個異步調用,同步調用方法直接組裝GetResponse 并返回,而異步方法通過回調ActionListener,并將執行結果(GetResponse )傳入回調方法。從中可以看出,Get API的核心是GetRequest 與RequestOptions,RequestOptions在上節中已詳細說明,接下來將重點關注GetRequest。
1、GetRequest
GetRequest完整的類繼承層次如下:
其核心屬性如圖所示:
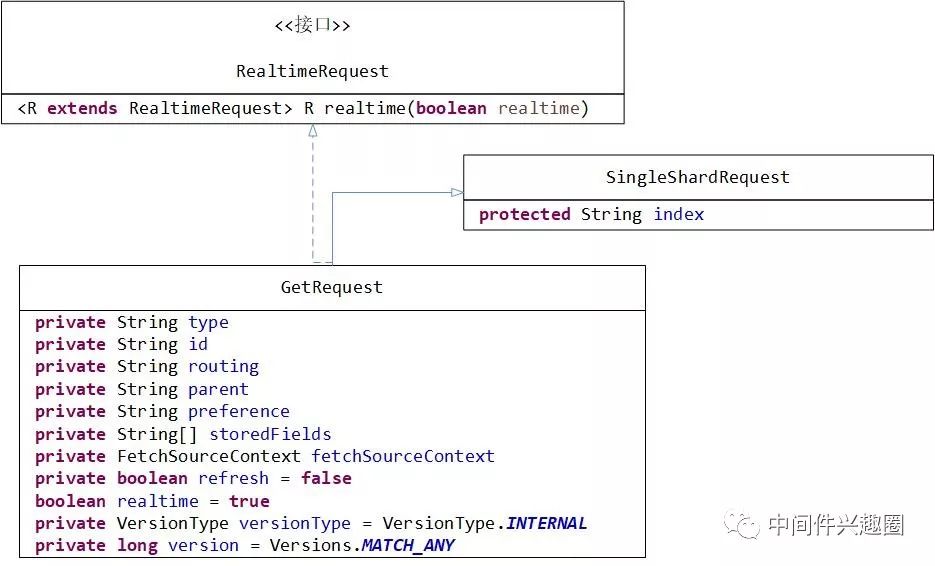 下面我們一一來介紹一下GetRequest的核心屬性。
下面我們一一來介紹一下GetRequest的核心屬性。
protected String index:索引庫,對應關系型數據庫的Database。
private String type:類型,對應關系型數據庫的表。
private String id:文檔ID,對應關系型數據庫表中一行的主鍵ID。
private String routing:路由值。
private String parent:
private String preference:get請求選取執行節點的偏好,傾向性,在下文會詳細介紹。
private String[] storedFields:顯示的指定需要返回的字段,默認會返回_source中所有字段。
private FetchSourceContext fetchSourceContext:指定需要返回字段的上下文,是storedFields的補充與完善,支持通配符,下文會詳細分析。
private boolean refresh = false:是否刷新。
boolean realtime = true:是否實時執行,默認為true。
private VersionType versionType = VersionType.INTERNAL:版本類型,已在《Elasticsearch Document Get API詳解、原理與示例》中詳細介紹
private long version = Versions.MATCH_ANY:數據版本,關于數據的版本管理,已在《Elasticsearch Document Get API詳解、原理與示例》中詳細介紹。
2、Get API Demo
1、示例一:
public static void testGet() {
RestHighLevelClient client = EsClient.getClient();
try {
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("twitter", "_doc", "1");
GetResponse result = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(result);
} catch(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
EsClient.close(client);
}
}返回值:
{
"_index":"twitter",
"_type":"_doc",
"_id":"1",
"_version":3,
"found":true,
"_source":{
"post_date":"2009-11-16T14:12:12",
"message":"trying out Elasticsearch",
"user":"dingw"
}
}2、示例二:基于storeFields進行source字段過濾
public static void testGet_storeFields() {
RestHighLevelClient client = EsClient.getClient();
try {
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("twitter", "_doc", "1");
request.storedFields("user");
GetResponse result = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(result);
} catch(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
EsClient.close(client);
}
}返回值:
{
"_index":"twitter",
"_type":"_doc",
"_id":"1",
"_version":3,
"found":true
}不符合預期,這是為什么呢?將在下文給出答案。
3、示例三:使用fetchSourceContext進行字段的過濾
public static void testGet_fetchSourceContext() {
RestHighLevelClient client = EsClient.getClient();
try {
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("twitter", "_doc", "1");
= new String[]{"message", "*date"};
FetchSourceContext fsc = new FetchSourceContext(true, includes, null);
request.fetchSourceContext(fsc);
GetResponse result = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(result);
} catch(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
EsClient.close(client);
}
}返回結果:
{
"_index":"twitter",
"_type":"_doc",
"_id":"1",
"_version":3,
"found":true,
"_source":{
"post_date":"2009-11-16T14:12:12",
"message":"trying out Elasticsearch"
}
}符合預期,只獲取_source中的message與以date結尾的屬性。
3、Get API 內部工作機制分析
3.1 實時性(Realtime)
默認情況下,get API是實時的,并且不會受到索引刷新頻率的影響。如果一個文檔被更新了(update),但是還沒有刷新,那么get API將會發出一個刷新調用,以使文檔可見。這也會使其他文檔在上一次刷新可見后發生變化。如果不使用實時獲取,可以將realtime設置false。
3.2 source字段過濾
按需返回所需字段,例如SQL語句select * 返回所有字段,可以通過select a.id,a.name返回所需字段。Elasticsearch提供了如下兩種方式對_source字段進行過濾:
3.2.1 Stored Fields
get操作允許通過傳遞storedFields參數來指定一組需要獲取儲存的字段。如果所請求的字段沒有被存儲,它們將被忽略。請考慮以下映射:
PUT twitter
{
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"properties": {
"counter": {
"type": "integer",
"store": false
},
"tags": {
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
}
}
}
}
}注意映射在定義時,store字段,如果設置為false,就算指定storedFields=["counter"],也不會返回結果,也就時上述【示例2】沒有返回 _source的原因。
3.2.2 FetchSourceContext
fetchSourceContext顧名思義,就是fetch source的上下文環境,提供更加完善的過濾邏輯,主要特性為支持include、exclude和支持通篇符過濾。
FetchSourceContext的構造函數:
public FetchSourceContext(boolean fetchSource, String[] includes, String[] excludes) {
this.fetchSource = fetchSource;
this.includes = includes == null ? Strings.EMPTY_ARRAY : includes;
this.excludes = excludes == null ? Strings.EMPTY_ARRAY : excludes;
}可以從兩個維度includes(包含)、excludes(排除)。還支持帶"*"的通配符,例如includes = ["msg*"]表示以msg開頭的屬性。通配符的解析邏輯:org.elasticsearch.common.regex#simpleMatchToAutomaton:
public static Automaton simpleMatchToAutomaton(String pattern) {
List<Automaton> automata = new ArrayList<>();
int previous = 0;
for (int i = pattern.indexOf('*'); i != -1; i = pattern.indexOf('*', i + 1)) {
automata.add(Automata.makeString(pattern.substring(previous, i)));
automata.add(Automata.makeAnyString());
previous = i + 1;
}
automata.add(Automata.makeString(pattern.substring(previous)));
return Operations.concatenate(automata);
}3.3 路由機制
如果路由字段不是ID,請使用routing屬性,更好的轉發請求,否則會全部轉發到所有的復制組,然后匯聚并返回。
3.4 傾向性(優先級、Preference)
Preference參數控制get請求對同一個復制組內多個副本的選擇,默認情況下,該操作是在碎片副本之間進行隨機分配的。一言以蔽之,preference的作用是同一個復制組中的路由規則。
其可選值:
_primary
操作將只在主分片上執行。
_local
如果可能的話,操作將更傾向于在本地分配的碎片上執行。當請求發到一個Node上,如果該Node上有對應的副本,則在該節點上執行,不會再將請求轉發到其他節點。
自定義字符串值
同一個自定義值,將會固定使用同一個分片(路由),該值通常會和會話信息綁定在一起,例如用戶名,sessionId等,在應用層面對各
分片節點進行分流。
3.5 刷新機制
refersh如果設置為true,以便在get操作之前刷新相關分片,并使其可搜索,會刷新整個分片節點,此參數不建議使用,因為get操作默認是實時的,無性能損耗。
其他分布式特性、版本等是ElasticSearch的通用特性,就不再重復講解了。
本節首先羅列了文檔Get API,并對GetRequest進行了詳細分析,接著通過3個 示例展示Get API的使用,最后重點分析GET API 內部的實現機制(實時性、source過濾、路由、復制組內分片節點傾向性、刷新機制等)。
看完上述內容,你們對如何理解Elasticsearch Document Get API有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。