您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天小編給大家分享一下基于Vue怎么實現移動端圖片裁剪組件功能的相關知識點,內容詳細,邏輯清晰,相信大部分人都還太了解這方面的知識,所以分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后有所收獲,下面我們一起來了解一下吧。
先看看效果:


一、組件的初始化參數
1、圖片img(url或者base64 data-url)
2、截圖的寬clipperImgWidth
3、截圖的高clipperImgHeight
props: {
img: String, //url或dataUrl
clipperImgWidth: {
type: Number,
default: 500
},
clipperImgHeight: {
type: Number,
default: 200
}
}二、布局
在Z軸方向看主要是由4層組成。第1層是一個占滿整個容器的canvas(稱cCanvas);第2層是一個有透明度的遮罩層;第3層是裁剪的區域(示例圖中的白色方框),里面包含一個與裁剪區域大小相等的canvas(稱pCanvas);第4層是一個透明層gesture-mask,用作綁定touchstart,touchmove,touchend事件。其中兩個canvas都會加載同一張圖片,只是起始坐標不一樣。為什么需要兩個canvas?因為想做出當手指離開屏幕時,裁剪區域外的部分表面會有一個遮罩層的效果,這樣能突出裁剪區域的內容。
<div class="cut-container" ref="cut">
<canvas ref="canvas"></canvas>
<!-- 裁剪部分 -->
<div class="cut-part">
<div class="pCanvas-container">
<canvas ref="pCanvas"></canvas>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 底部操作欄 -->
<div class="action-bar">
<button class="btn-cancel" @click="_cancel">取消</button>
<button class="btn-ok" @click="_cut">確認</button>
</div>
<!-- 背景遮罩 -->
<div class="mask" :class="{opacity: maskShow}"></div>
<!-- 手勢操作層 -->
<div class="gesture-mask" ref="gesture"></div>
</div>三、初始化canvas
canvas繪制的圖片在hdpi顯示屏上會出現模糊,具體原因這里不作分析,可以參考下這里。我這里的做法是讓canvas的width與height為其css width/height的devicePixelRatio倍,以及調用canvas api時所傳入的參數都要乘以window.devicePixelRatio。最后還要記錄一下兩個canvas坐標原點的x, y差值(originXDiff與originYDiff)。如下
_ratio(size) {
return parseInt(window.devicePixelRatio * size);
},
_initCanvas() {
let $canvas = this.$refs.canvas,
$pCanvas = this.$refs.pCanvas,
clipperClientRect = this.$refs.clipper.getBoundingClientRect(),
clipperWidth = parseInt(this.clipperImgWidth / window.devicePixelRatio),
clipperHeight = parseInt(this.clipperImgHeight / window.devicePixelRatio);
this.ctx = $canvas.getContext('2d');
this.pCtx = $pCanvas.getContext('2d');
//判斷clipperWidth與clipperHeight有沒有超過容器值
if (clipperWidth < 0 || clipperWidth > clipperClientRect.width) {
clipperWidth = 250
}
if (clipperHeight < 0 || clipperHeight > clipperClientRect.height) {
clipperHeight = 100
}
//因為canvas在手機上會被放大,因此里面的內容會模糊,這里根據手機的devicePixelRatio來放大canvas,然后再通過設置css來收縮,因此關于canvas的所有值或坐標都要乘以devicePixelRatio
$canvas.style.width = clipperClientRect.width + 'px';
$canvas.style.height = clipperClientRect.height + 'px';
$canvas.width = this._ratio(clipperClientRect.width);
$canvas.height = this._ratio(clipperClientRect.height);
$pCanvas.style.width = clipperWidth + 'px';
$pCanvas.style.height = clipperHeight + 'px';
$pCanvas.width = this._ratio(clipperWidth);
$pCanvas.height = this._ratio(clipperHeight);
//計算兩個canvas原點的x y差值
let cClientRect = $canvas.getBoundingClientRect(),
pClientRect = $pCanvas.getBoundingClientRect();
this.originXDiff = pClientRect.left - cClientRect.left;
this.originYDiff = pClientRect.top - cClientRect.top;
this.cWidth = cClientRect.width;
this.cHeight = cClientRect.height;
}四、加載圖片
加載圖片比較簡單,首先是創建一個Image對象并監聽器onload事件(因為加載的圖片有可能是跨域的,因此要設置其crossOrigin屬性為Anonymous,然后服務器上要設置Access-Control-Allow-Origin響應頭)。加載的圖片如果寬高大于容器的寬高,要對其進行縮小處理。最后垂直水平居中顯示()(這里注意的是要保存圖片繪制前的寬高值,因為日后縮放圖片是以該值為基礎再乘以縮放倍率,這里取imgStartWidth,imgStartHeight)如下
_loadImg() {
if (this.imgLoading || this.loadImgQueue.length === 0) {
return;
}
let img = this.loadImgQueue.shift();
if (!img) {
return;
}
let $img = new Image(),
onLoad = e => {
$img.removeEventListener('load', onLoad, false);
this.$img = $img;
this.imgLoaded = true;
this.imgLoading = false;
this._initImg($img.width, $img.height);
this.$emit('loadSuccess', e);
this.$emit('loadComplete', e);
this._loadImg();
},
onError = e => {
$img.removeEventListener('error', onError, false);
this.$img = $img = null;
this.imgLoading = false;
this.$emit('loadError', e);
this.$emit('loadComplete', e);
this._loadImg();
};
this.$emit('beforeLoad');
this.imgLoading = true;
this.imgLoaded = false;
$img.src = this.img;
$img.crossOrigin = 'Anonymous'; //因為canvas toDataUrl不能操作未經允許的跨域圖片,這需要服務器設置Access-Control-Allow-Origin頭
$img.addEventListener('load', onLoad, false);
$img.addEventListener('error', onError, false);
}
_initImg(w, h) {
let eW = null,
eH = null,
maxW = this.cWidth,
maxH = this.cHeight - this.actionBarHeight;
//如果圖片的寬高都少于容器的寬高,則不做處理
if (w <= maxW && h <= maxH) {
eW = w;
eH = h;
} else if (w > maxW && h <= maxH) {
eW = maxW;
eH = parseInt(h / w * maxW);
} else if (w <= maxW && h > maxH) {
eW = parseInt(w / h * maxH);
eH = maxH;
} else {
//判斷是橫圖還是豎圖
if (h > w) {
eW = parseInt(w / h * maxH);
eH = maxH;
} else {
eW = maxW;
eH = parseInt(h / w * maxW);
}
}
if (eW <= maxW && eH <= maxH) {
//記錄其初始化的寬高,日后的縮放功能以此值為基礎
this.imgStartWidth = eW;
this.imgStartHeight = eH;
this._drawImage((maxW - eW) / 2, (maxH - eH) / 2, eW, eH);
} else {
this._initImg(eW, eH);
}
}五、繪制圖片
下面的_drawImage有四個參數,分別是圖片對應cCanvas的x,y坐標以及圖片目前的寬高w,h。函數首先會清空兩個canvas的內容,方法是重新設置canvas的寬高。然后更新組件實例中對應的值,最后再調用兩個canvas的drawImage去繪制圖片。對于pCanvas來說,其繪制的圖片坐標值為x,y減去對應的originXDiff與originYDiff(其實相當于切換坐標系顯示而已,因此只需要減去兩個坐標系原點的x,y差值即可)。看看代碼
_drawImage(x, y, w, h) {
this._clearCanvas();
this.imgX = parseInt(x);
this.imgY = parseInt(y);
this.imgCurrentWidth = parseInt(w);
this.imgCurrentHeight = parseInt(h);
//更新canvas
this.ctx.drawImage(this.$img, this._ratio(x), this._ratio(y), this._ratio(w), this._ratio(h));
//更新pCanvas,只需要減去兩個canvas坐標原點對應的差值即可
this.pCtx.drawImage(this.$img, this._ratio(x - this.originXDiff), this._ratio(y - this.originYDiff), this._ratio(w), this._ratio(h));
},
_clearCanvas() {
let $canvas = this.$refs.canvas,
$pCanvas = this.$refs.pCanvas;
$canvas.width = $canvas.width;
$canvas.height = $canvas.height;
$pCanvas.width = $pCanvas.width;
$pCanvas.height = $pCanvas.height;
}六、移動圖片
移動圖片實現非常簡單,首先給gesture-mask綁定touchstart,touchmove,touchend事件,下面分別介紹這三個事件的內容
首先定義四個變量scx, scy(手指的起始坐標),iX,iY(圖片目前的坐標,相對于cCanvas)。
1、touchstart
方法很簡單,就是獲取touches[0]的pageX,pageY來更新scx與scy以及更新iX與iY
2、touchmove
獲取touches[0]的pageX,聲明變量f1x存放,移動后的x坐標等于iX + f1x - scx,y坐標同理,最后調用_drawImage來更新圖片。
看看代碼吧
_initEvent() {
let $gesture = this.$refs.gesture,
scx = 0,
scy = 0;
let iX = this.imgX,
iY = this.imgY;
$gesture.addEventListener('touchstart', e => {
if (!this.imgLoaded) {
return;
}
let finger = e.touches[0];
scx = finger.pageX;
scy = finger.pageY;
iX = this.imgX;
iY = this.imgY;
}, false);
$gesture.addEventListener('touchmove', e => {
e.preventDefault();
if (!this.imgLoaded) {
return;
}
let f1x = e.touches[0].pageX,
f1y = e.touches[0].pageY;
this._drawImage(iX + f1x - scx, iY + f1y - scy, this.imgCurrentWidth, this.imgCurrentHeight);
}, false);
}七、縮放圖片(這里不作特別說明的坐標都是相對于cCanvas坐標系)
繪制縮放后的圖片無非需要4個參數,縮放后圖片左上角的坐標以及寬高。求寬高相對好辦,寬高等于imgStartWidth * 縮放比率與imgstartHeight * 縮放倍率(imgStartWidth ,imgstartHeight 上文第四節有提到)。接下來就是求縮放倍率的問題了,首先在touchstart事件上求取兩手指間的距離d1;然后在touchmove事件上繼續求取兩手指間的距離d2,當前縮放倍率= 初始縮放倍率 + (d2-d1) / 步長(例如每60px算0.1),touchend事件上讓初始縮放倍率=當前縮放倍率。
至于如何求取縮放后圖片左上角的坐標值,在草稿紙上畫來畫去,畫了很久......終于有點眉目。首先要找到一個縮放中心(這里做法是取雙指的中點坐標,但是這個坐標必須要位于圖片上,如果不在圖片上,則取圖片上離該中點坐標最近的點),然后存在下面這個等式
(縮放中心x坐標 - 縮放后圖片左上角x坐標)/ 縮放后圖片的寬度 = (縮放中心x坐標 - 縮放前圖片左上角x坐標)/ 縮放前圖片的寬度;(y坐標同理)
接下來看看下面這個例子(在visio找了很久都沒有畫坐標系的功能,所以只能手工畫了)
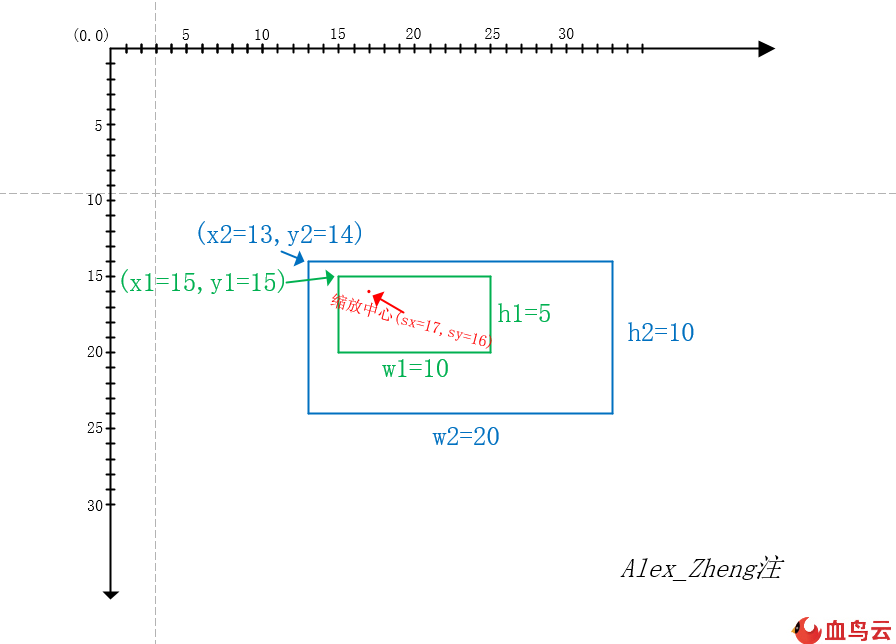
綠色框是一張10*5的圖片,藍色框是寬高放大兩倍后的圖片20*10,根據上面的公式推算的x2 = sx - w2(sx - x1) / w1,y2 = sy - h3(sy - y1) / h2。
堅持...繼續看看代碼吧
_initEvent() {
let $gesture = this.$refs.gesture,
cClientRect = this.$refs.canvas.getBoundingClientRect(),
scx = 0, //對于單手操作是移動的起點坐標,對于縮放是圖片距離兩手指的中點最近的圖標。
scy = 0,
fingers = {}; //記錄當前有多少只手指在觸控屏幕
//one finger
let iX = this.imgX,
iY = this.imgY;
//two finger
let figureDistance = 0,
pinchScale = this.imgScale;
$gesture.addEventListener('touchstart', e => {
if (!this.imgLoaded) {
return;
}
if (e.touches.length === 1) {
let finger = e.touches[0];
scx = finger.pageX;
scy = finger.pageY;
iX = this.imgX;
iY = this.imgY;
fingers[finger.identifier] = finger;
} else if (e.touches.length === 2) {
let finger1 = e.touches[0],
finger2 = e.touches[1],
f1x = finger1.pageX - cClientRect.left,
f1y = finger1.pageY - cClientRect.top,
f2x = finger2.pageX - cClientRect.left,
f2y = finger2.pageY - cClientRect.top;
scx = parseInt((f1x + f2x) / 2);
scy = parseInt((f1y + f2y) / 2);
figureDistance = this._pointDistance(f1x, f1y, f2x, f2y);
fingers[finger1.identifier] = finger1;
fingers[finger2.identifier] = finger2;
//判斷變換中點是否在圖片中,如果不是則去離圖片最近的點
if (scx < this.imgX) {
scx = this.imgX;
}
if (scx > this.imgX + this.imgCurrentWidth) {
scx = this.imgX + this.imgCurrentHeight;
}
if (scy < this.imgY) {
scy = this.imgY;
}
if (scy > this.imgY + this.imgCurrentHeight) {
scy = this.imgY + this.imgCurrentHeight;
}
}
}, false);
$gesture.addEventListener('touchmove', e => {
e.preventDefault();
if (!this.imgLoaded) {
return;
}
this.maskShowTimer && clearTimeout(this.maskShowTimer);
this.maskShow = false;
if (e.touches.length === 1) {
let f1x = e.touches[0].pageX,
f1y = e.touches[0].pageY;
this._drawImage(iX + f1x - scx, iY + f1y - scy, this.imgCurrentWidth, this.imgCurrentHeight);
} else if (e.touches.length === 2) {
let finger1 = e.touches[0],
finger2 = e.touches[1],
f1x = finger1.pageX - cClientRect.left,
f1y = finger1.pageY - cClientRect.top,
f2x = finger2.pageX - cClientRect.left,
f2y = finger2.pageY - cClientRect.top,
newFigureDistance = this._pointDistance(f1x, f1y, f2x, f2y),
scale = this.imgScale + parseFloat(((newFigureDistance - figureDistance) / this.imgScaleStep).toFixed(1));
fingers[finger1.identifier] = finger1;
fingers[finger2.identifier] = finger2;
if (scale !== pinchScale) {
//目前縮放的最小比例是1,最大是5
if (scale < this.imgMinScale) {
scale = this.imgMinScale;
} else if (scale > this.imgMaxScale) {
scale = this.imgMaxScale;
}
pinchScale = scale;
this._scale(scx, scy, scale);
}
}
}, false);
$gesture.addEventListener('touchend', e => {
if (!this.imgLoaded) {
return;
}
this.imgScale = pinchScale;
//從finger刪除已經離開的手指
let touches = Array.prototype.slice.call(e.changedTouches, 0);
touches.forEach(item => {
delete fingers[item.identifier];
});
//迭代fingers,如果存在finger則更新scx,scy,iX,iY,因為可能縮放后立即單指拖動
let i,
fingerArr = [];
for(i in fingers) {
if (fingers.hasOwnProperty(i)) {
fingerArr.push(fingers[i]);
}
}
if (fingerArr.length > 0) {
scx = fingerArr[0].pageX;
scy = fingerArr[0].pageY;
iX = this.imgX;
iY = this.imgY;
} else {
this.maskShowTimer = setTimeout(() => {
this.maskShow = true;
}, 300);
}
//做邊界值檢測
let x = this.imgX,
y = this.imgY,
pClientRect = this.$refs.pCanvas.getBoundingClientRect();
if (x > pClientRect.left + pClientRect.width) {
x = pClientRect.left
} else if (x + this.imgCurrentWidth < pClientRect.left) {
x = pClientRect.left + pClientRect.width - this.imgCurrentWidth;
}
if (y > pClientRect.top + pClientRect.height) {
y = pClientRect.top;
} else if (y + this.imgCurrentHeight < pClientRect.top) {
y = pClientRect.top + pClientRect.height - this.imgCurrentHeight;
}
if (this.imgX !== x || this.imgY !== y) {
this._drawImage(x, y, this.imgCurrentWidth, this.imgCurrentHeight);
}
});
},
_scale(x, y, scale) {
let newPicWidth = parseInt(this.imgStartWidth * scale),
newPicHeight = parseInt(this.imgStartHeight * scale),
newIX = parseInt(x - newPicWidth * (x - this.imgX) / this.imgCurrentWidth),
newIY = parseInt(y - newPicHeight * (y - this.imgY) / this.imgCurrentHeight);
this._drawImage(newIX, newIY, newPicWidth, newPicHeight);
},
_pointDistance(x1, y1, x2, y2) {
return parseInt(Math.sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2)));
}說明一下fingers是干嘛的,是用來記錄當前有多少只手指在屏幕上觸摸。可能會出現這種情況,雙指縮放后,其中一只手指移出顯示屏,而另外一個手指在顯示屏上移動。針對這種情況,要在touchend事件上根據e.changedTouches來移除fingers里已經離開顯示屏的finger,如果此時fingers里只剩下一個finger,則更新scx,scy,iX,iY為移動圖片做初始化準備。
八、裁剪圖片
這里很簡單,就調用pCanvas的toDataURL方法就可以了
_clipper() {
let imgData = null;
try {
imgData = this.$refs.pCanvas.toDataURL();
} catch (e) {
console.error('請在response header加上Access-Control-Allow-Origin,否則canvas無法裁剪未經許可的跨域圖片');
}
this.$emit('sure', imgData);
}以上就是“基于Vue怎么實現移動端圖片裁剪組件功能”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家閱讀完這篇文章都有很大的收獲,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識,如果還想學習更多的知識,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。