您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章給大家分享的是有關如何進行更加優雅地Docker部署項目,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家學習,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲,話不多說,跟著小編一起來看看吧。
如果你需要經常性需要多處部署同樣的項目,如果你曾經也遇到過"明明在我電腦運行得好好的"問題,如果聽說過 Docker 但還沒用過,如果你不確定你到底需不需要 Docker ,那么,希望你花時間閱讀一下這篇文章!
因為 Docker 將幫助你輕松運行自己不熟悉語言編寫的開源項目,幫助你更加優雅地部署自己的項目,省去重復下載并配置環境的繁瑣過程...
現在讓我們先睹為快,預覽一下基于 Docker 部署項目的實際效果,希望能讓你對 Docker 有個初步的印象!
Docker 部署的 nginx 作為反向代理服務器,支持 https 訪問以及泛域名解析.
體驗地址: https://snowdreams1006.cn/
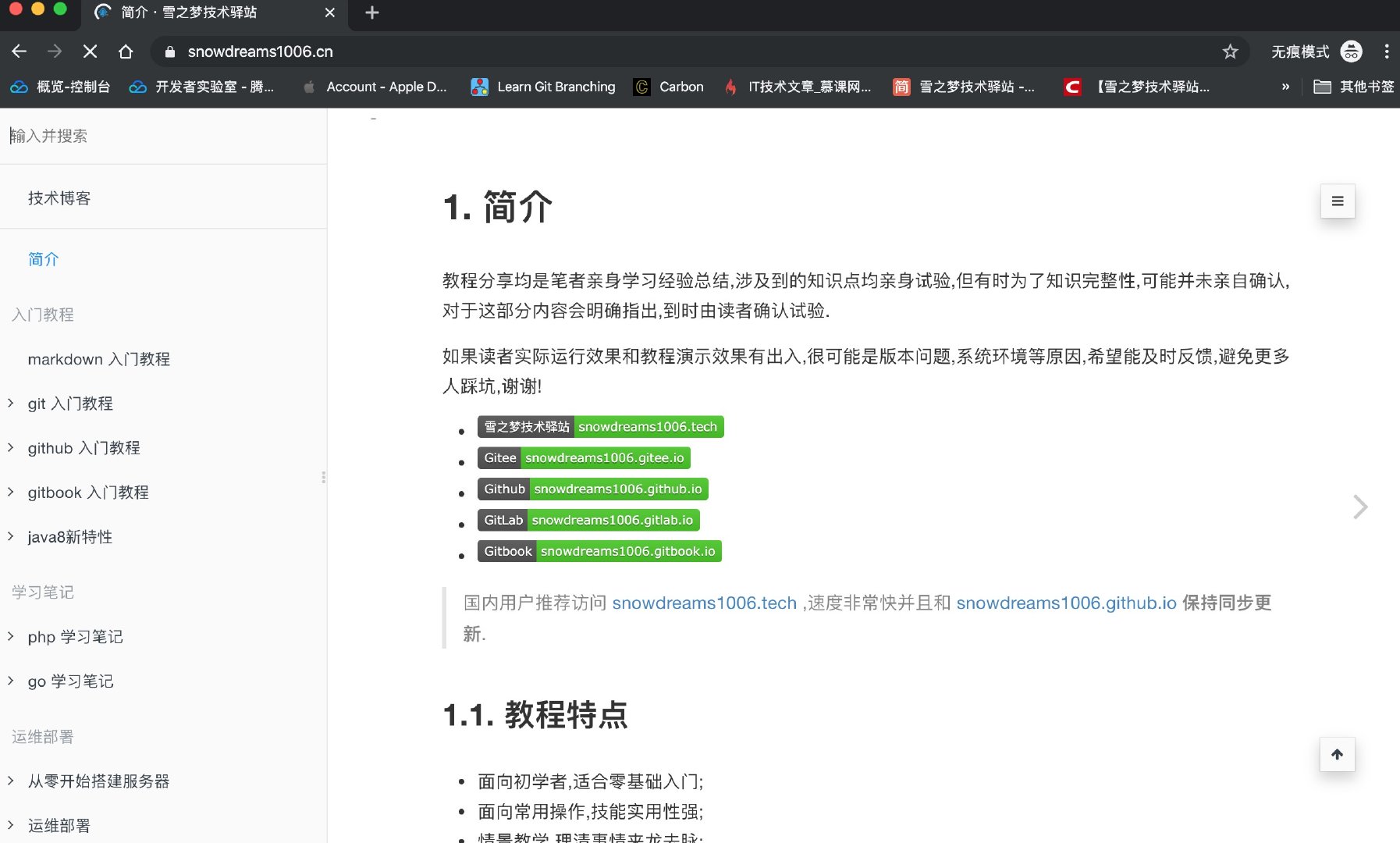
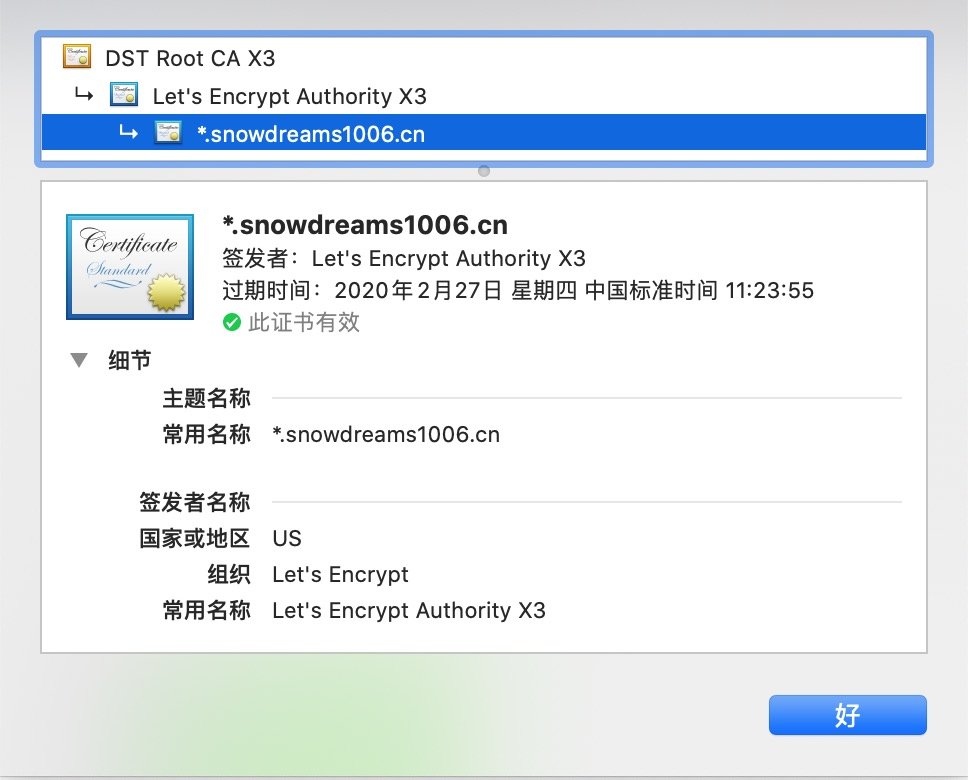
Docker 部署的 letsencrypt 免費制作泛域名證書并整合反向代理服務 nginx 實現 https 訪問.
> 體驗地址: https://www.snowdreams1006.cn/
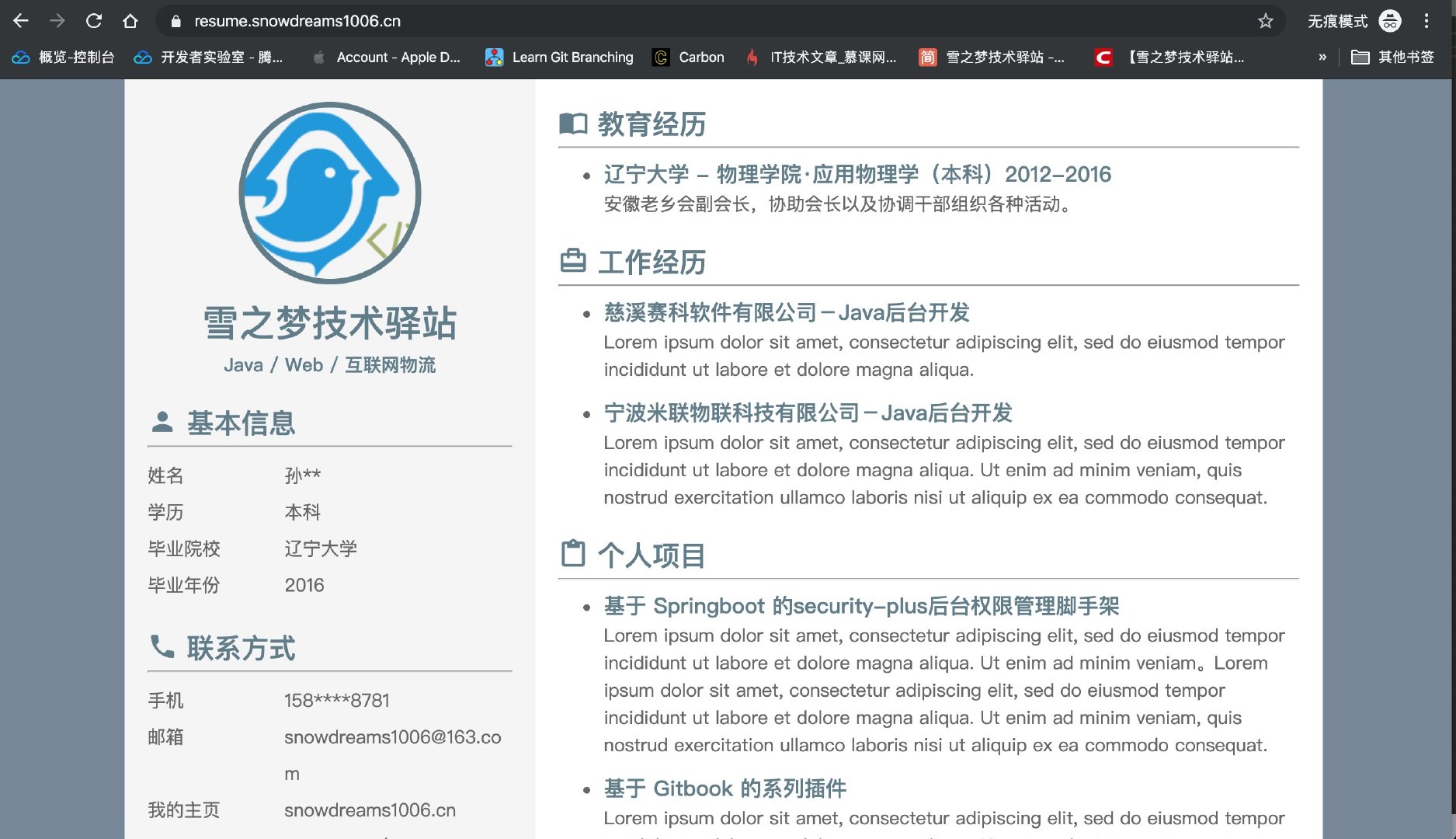
Docker 部署的 nginx 作為靜態服務器,部署靜態網站用于演示靜態博客功能.
體驗地址: https://resume.snowdreams1006.cn/
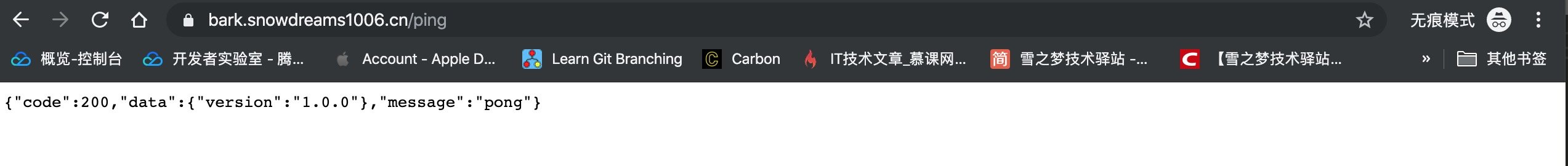
Docker 部署的 bark 作為后端服務器,部署開源項目用于充當消息推送服務器.
體驗地址: https://bark.snowdreams1006.cn/ping
Docker 部署的 webhook 作為后端服務器,部署開源項目用于接收 Webhook 事件回調.
體驗地址: https://webhook.snowdreams1006.cn/hooks/github
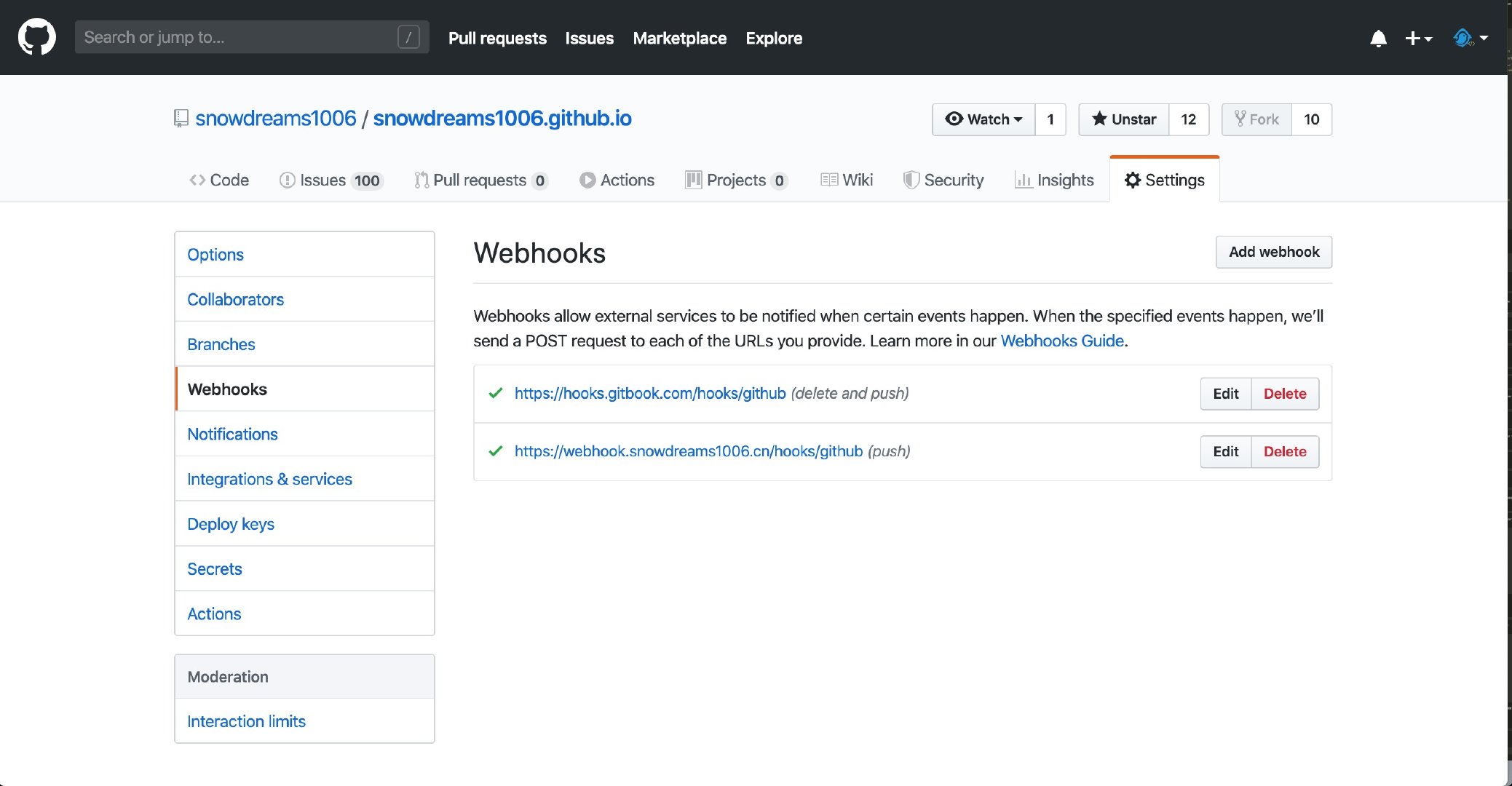
Docker 部署的 blog 作為靜態服務器,基于 Github Action 或 Webhook 實現博客內容自動更新并推送消息.
Github倉庫內容更新后觸發Github Action自動構建并部署遠程服務器靜態博客,同時發送的Webhook事件給webhook鉤子容器,緊接著調用bark消息推送容器,實現消息推送到微信消息以及 app 通知.
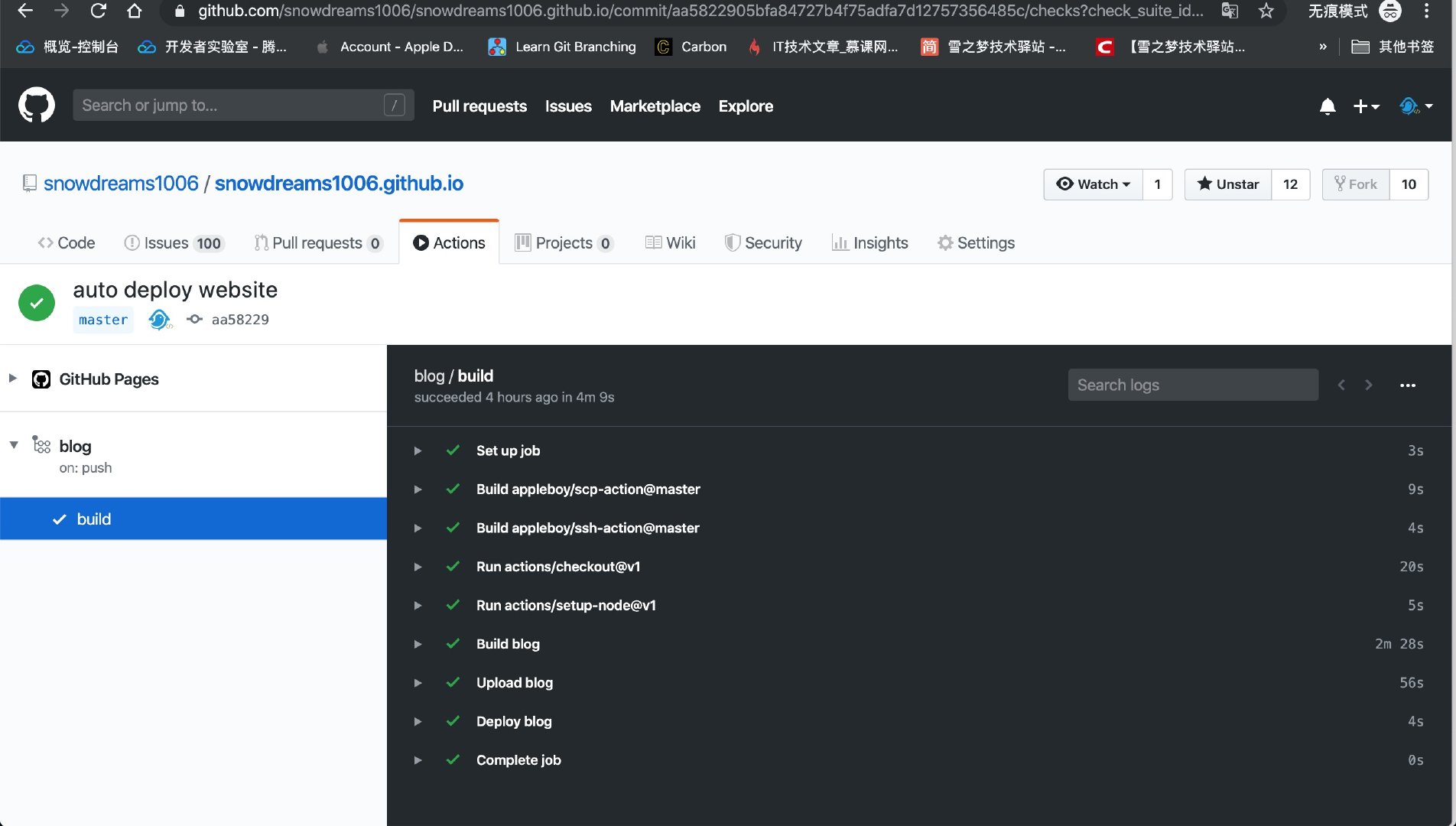
Github倉庫更新后自動運行Github Action源碼構建靜態博客并上傳到遠程服務器,blog容器會立即重啟完成內容更新.
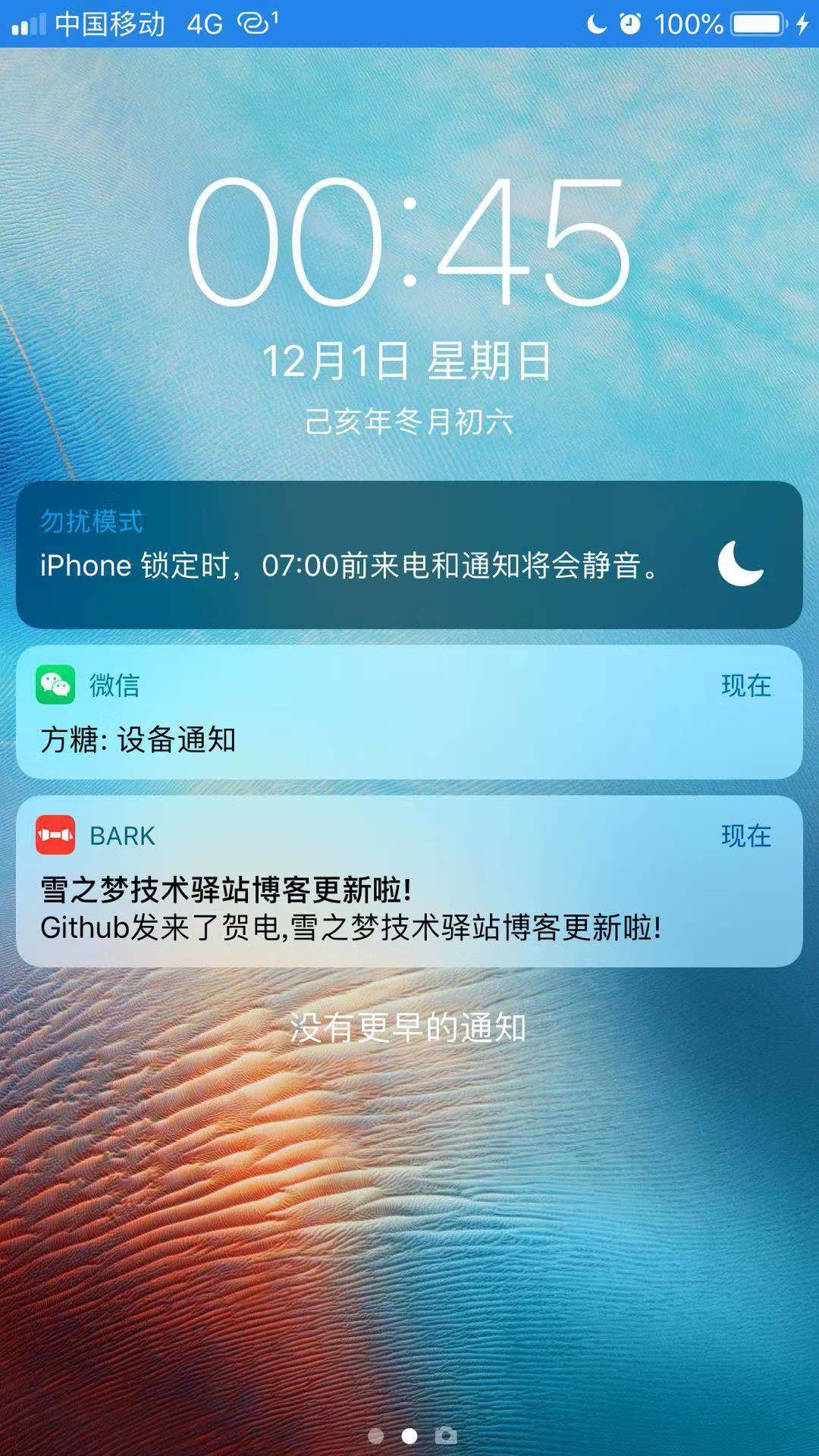
Github倉庫更新后發送Webhooks到遠程服務器,webhook容器接收到請求后轉發給bark容器,進而推送給手機.
無論是熟悉的開源項目還是陌生的開源項目,Docker 讓這些不一樣變得一樣,統一的管理方式使得使用成本大大降低,更加優雅地部署項目,真的不止是說說而已!

目前在 Linux 系統上安裝 Docker,對系統版本有以下要求:
CentOS : 7
Debian : 7.7(Wheezy LTS)、8.0(Jessie LTS)、9(Stretch)
Fedora : 24、25
Ubuntu : 16.04(Xenial LTS)、14.04(Trusty LTS)、17.04(Zesty)
一方面上述前提條件基本上新服務器都會滿足,另一方面筆者對此并未深入實驗,請讀者自行驗證,下面主要以 Centos7.6 為例講解如何安裝 Docker .
對于新手來說,盡管安裝 Docker 非常簡單,但是總是不可避免地會遇到一些意外情況,或許是安裝出錯需要重新安裝或者是不確定遠程服務器是否已經安裝,所以開始安裝前還是先看一下到底有沒有安裝過 Docker 吧!
調用 docker 命令
首先連接到遠程服務器后運行 docker 命令,如果像下面那樣輸出一大堆用法介紹,那么證明 Docker 已經成功安裝過,并且可能已經配置好相關環境了.
你現在唯一要做的就是學習一下 Docker 的基本用法,因為不用自己安裝 Docker 環境,基本上也可以不必往下看了.
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND
A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/root/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the daemon (overrides DOCKER_HOST env var and default context set with "docker context use")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level ("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal") (default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default "/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default "/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
builder Manage builds
config Manage Docker configs
container Manage containers
context Manage contexts
engine Manage the docker engine
image Manage images
network Manage networks
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.如果你輸入 docker 提示 command not found ,說明服務器很可能并沒有安裝 Docker 環境,下面就教你如何一步一步安裝 Docker 環境!
DockerStep 1 : 移除舊版本
sudo yum remove docker \ docker-client \ docker-client-latest \ docker-common \ docker-latest \ docker-latest-logrotate \ docker-logrotate \ docker-engine
這一步是可選的,是因為最新版
Docker的名稱已經發生了變化,為了保證安裝的是最新版的Docker-CE,所以首先卸載可能已經安裝過的舊版本.
Step 2 : 安裝必要系統依賴
sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
安裝一些必要依賴,跟著官方教程說明走就好了,即使系統已存在該環境也可以再次運行,放心復制粘貼吧!
Step 3 : 添加軟件源信息
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Step 4 : 更新 yum 緩存
sudo yum makecache fast
Step 5 : 安裝 docker-ce
sudo yum -y install docker-ce
如果上述安裝過程中沒有出現任何報錯,那么現在已經安裝好基本的 Docker 環境!
Docker查看狀態
sudo systemctl status docker
初次安裝成功后默認是不會自動啟動
Docker服務的,此時查看運行狀態的輸出結果不會包括Active: active (running)而是Active: inactive (dead).
首次啟動
sudo systemctl start docker
安裝后默認是沒有啟動
Docker服務的,因此安裝后需要先啟動Docker服務,再次查看運行狀態sudo systemctl status docker應該會出現正在運行Active: active (running).
重新啟動
sudo systemctl restart docker
如果
Docker服務已停止可以重新啟動,如果已經啟動也可以重新啟動.
停止服務
sudo systemctl stop docker
如果正在運行的
Docker存在問題需要停止維修,那么可以先停止Docker服務,待維修結束后可以運行sudo systemctl start docker再次啟動服務.
檢查自啟
systemctl list-unit-files | grep enabled | grep docker
檢查
Docker服務是否會開機自啟,如果存在結果則表示會開機自啟,如果沒有結果則表示不會開機自啟.
開機自啟
sudo systemctl enable docker
Docker服務是非常重要的進程服務,一般需要開機自啟,保證意外關機后能自行恢復服務,推薦開機自啟.
禁止自啟
sudo systemctl disable docker
如果不小心設置了開機自啟而你真的不打算開機自啟的話,那么可以禁用開機自啟功能,下次電腦重啟后不會自動啟動
Docker服務.
查看版本
docker version
查看當前安裝的 Docker 版本信息,可以看出來主要分為兩部分: Client: Docker Engine - Community 和 Server: Docker Engine - Community .
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker version Client: Docker Engine - Community Version: 19.03.5 API version: 1.40 Go version: go1.12.12 Git commit: 633a0ea Built: Wed Nov 13 07:25:41 2019 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Experimental: false Server: Docker Engine - Community Engine: Version: 19.03.5 API version: 1.40 (minimum version 1.12) Go version: go1.12.12 Git commit: 633a0ea Built: Wed Nov 13 07:24:18 2019 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Experimental: false containerd: Version: 1.2.10 GitCommit: b34a5c8af56e510852c35414db4c1f4fa6172339 runc: Version: 1.0.0-rc8+dev GitCommit: 3e425f80a8c931f88e6d94a8c831b9d5aa481657 docker-init: Version: 0.18.0 GitCommit: fec3683
現在并不必關心具體的版本信息,只要運行 docker version 命令后能夠輸出類似信息即可,接下來開始真正的表演!
Docker 服務已經安裝并啟動,接下來我們可以基于 Docker 部署應用了,當然現在離真正部署自己的應用還有不小距離,但是我們可以運行公開的應用啊!
學習任何新語言的第一件事就是運行 hello world ,學習 Docker 容器化部署也不例外,我們也運行 Docker 版本的 hello world !
當我們敲入 docker run hello-world 命令后,終端會輸出下列內容,只要輸出 Hello from Docker! 字樣就證明環境已經搭建完畢!
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker run hello-world Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/hello-world 1b930d010525: Pull complete Digest: sha256:4df8ca8a7e309c256d60d7971ea14c27672fc0d10c5f303856d7bc48f8cc17ff Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. To generate this message, Docker took the following steps: 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon. 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub. (amd64) 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the executable that produces the output you are currently reading. 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it to your terminal. To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with: $ docker run -it ubuntu bash Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID: https://hub.docker.com/ For more examples and ideas, visit: https://docs.docker.com/get-started/ [root@snowdreams1006 ~]#
如果你的網速比較慢,上述過程可能有一些耗時,但是如果你的網速一般而上述過程異常慢,很可能是因為你沒有配置鏡像!
因為 Docker 默認是先從國外下載項目到本地,然后再運行服務的,正如我們平時訪問 Github 一樣,那網速不是一般的慢!
Github 沒有鏡像加速地址并不能為我們加速訪問,但是 Docker 項目倉庫是有鏡像倉庫的,國內提供這種鏡像服務的有不少,基本上都需要注冊賬號獲取鏡像地址之類的.
這里提供一下網易的鏡像倉庫地址 http://hub-mirror.c.163.com 以及阿里云的個人鏡像倉庫地址 https://8upnmlh4.mirror.aliyuncs.com .
只要將鏡像地址配置給 Docker ,下一次再下載項目時速度應該就會得到明顯提升!
首選打開并編輯 /etc/docker/daemon.json 文件,如果沒有的話就新建該文件,內容如下:
{
"registry-mirrors": ["http://hub-mirror.c.163.com"]
}保存后重啟 Docker 服務,試一試運行 docker pull nginx 會不會很快呢?
假如發現意外想要重新安裝 Docker 服務或者就是想要卸載 Docker ,那么只需要簡單運行下列命令就能清除掉 Docker 環境!
sudo yum remove docker-ce sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
此時再次運行 docker 命令就會提示 command not found ,期待下一次相見會讓人煥然一新!
正如初次見面的那樣,當我們成功安裝 Docker 后控制臺輸出了一大堆關于用法的介紹,只不過當時年少輕狂并不在乎,驀然回首,竟發現如此有用!
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND
A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/root/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the daemon (overrides DOCKER_HOST env var and default context set with "docker context use")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level ("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal") (default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default "/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default "/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
builder Manage builds
config Manage Docker configs
container Manage containers
context Manage contexts
engine Manage the docker engine
image Manage images
network Manage networks
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.用法介紹的第一段就是自我介紹,用法是: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND ,即 docker + 可選選項 + 必選命令.
表示的含義就是 A self-sufficient runtime for containers 為容器提供一個自包含的運行環境!
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Docker 類似于生活中超級貨輪,運輸著統一規格的集裝箱,而集裝箱裝著各種各樣的貨物,開往不同的目的地.
容器則是集裝箱,貨輪為集裝箱提供了自包含的環境,集裝箱之間是相互獨立的,這也是對第一段話的簡單解釋.
下面我們繼續看第二段內容,主要解釋了有哪些配置項以及這些配置項背后表示的具體含義.
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/root/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the daemon (overrides DOCKER_HOST env var and default context set with "docker context use")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level ("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal") (default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default "/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default "/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit只要有一定英語基礎的人應該都能看懂其中的意思,如果對個人細節不是很清楚的話,可以復制粘貼到瀏覽器在線翻譯,這里就不全文解釋了.
不消息看到了最后一個 -v, --version 選項,表示的意思是打印版本信息并且退出.
看到這里我們就明白了,原來之前運行的 docker version 和這里的 --version 并不是一回事啊!
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker -v Docker version 19.03.5, build 633a0ea [root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker --version Docker version 19.03.5, build 633a0ea
單純從輸出結果來說,docker --version 更加簡潔,如果只是驗證環境安裝是否成功,還是運行docker --version 比較簡單明了.
第三部分是 Docker 支持的管理命令,現在不去深究細節,只要有印象就行,注意這里有個關于鏡像的命令 docker image
Management Commands: builder Manage builds config Manage Docker configs container Manage containers context Manage contexts engine Manage the docker engine image Manage images network Manage networks node Manage Swarm nodes plugin Manage plugins secret Manage Docker secrets service Manage services stack Manage Docker stacks swarm Manage Swarm system Manage Docker trust Manage trust on Docker images volume Manage volumes
因為自我介紹中關于用法是 docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND ,而中括號 [] 表示該內容是可選的,所以不加任何選項的基本用法就是 docker COMMAND ,因此其中關于 image 命令的完整用法就是: docker image .
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker image Usage: docker image COMMAND Manage images Commands: build Build an image from a Dockerfile history Show the history of an image import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image inspect Display detailed information on one or more images load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN ls List images prune Remove unused images pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry push Push an image or a repository to a registry rm Remove one or more images save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default) tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE Run 'docker image COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
別有洞天,管理命令中還有子命令,大概用法和之前介紹的內容大致相同,基本用法是: docker image COMMAND .
其中支持的命令中有 ls ,因此調用 ls 命令的最終完整命令就是: docker image ls .
# docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest fce289e99eb9 11 months ago 1.84kB
服務器已安裝的 image 中就包括我們熟悉的 hello-world ,至于什么是 REPOSITORY ,什么是 IMAGE 暫時也不用深究,只需要知道如何無文檔使用這些命令即可!
如果用心留意的話,可以看到 Run 'docker image COMMAND --help' for more information on a command. 這么一句話,看來我們有現成的幫助文檔供我們學習啊!
還是以 ls 命令為例,演示一下如何使用 docker image COMMAND --help 查看幫助文檔.
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker image ls --help Usage: docker image ls [OPTIONS] [REPOSITORY[:TAG]] List images Aliases: ls, images, list Options: -a, --all Show all images (default hides intermediate images) --digests Show digests -f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided --format string Pretty-print images using a Go template --no-trunc Don't truncate output -q, --quiet Only show numeric IDs
麻雀雖小五臟俱全,沒想到 ls 命令還有更加細粒度的用法說明,支持可選參數和 [REPOSITORY[:TAG]] ,除此之外還有 ls, images, list 別名!
如果 ls 有 images 和 list 別名,那么豈不是意味著 docker image ls 等價于 docker image images 和 docker image list ?
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker image list REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest fce289e99eb9 11 months ago 1.84kB [root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker image images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest fce289e99eb9 11 months ago 1.84kB
從上述輸出結果來看,三者的運行效果確實是一樣的,看來又發現了新大陸!
回到 docker 命令的主線,除了管理命令外還是普通命令,這部分命令也是經常性使用到的命令也是重點學習掌握的命令!
Commands: attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container build Build an image from a Dockerfile commit Create a new image from a container's changes cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem create Create a new container diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem events Get real time events from the server exec Run a command in a running container export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive history Show the history of an image images List images import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image info Display system-wide information inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects kill Kill one or more running containers load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN login Log in to a Docker registry logout Log out from a Docker registry logs Fetch the logs of a container pause Pause all processes within one or more containers port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container ps List containers pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry push Push an image or a repository to a registry rename Rename a container restart Restart one or more containers rm Remove one or more containers rmi Remove one or more images run Run a command in a new container save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default) search Search the Docker Hub for images start Start one or more stopped containers stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics stop Stop one or more running containers tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE top Display the running processes of a container unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers update Update configuration of one or more containers version Show the Docker version information wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
命令雖好但不可貪多,還是找到最簡單剛剛用過的 docker run 和 docker version 命令吧!
docker run : Run a command in a new container
表示在新的容器內運行命令,翻譯成生活語言就是在集裝箱內做著不可告人的神秘操作!
docker version : Show the Docker version information
顯示 Docker 版本信息,還記得 docker --version 嗎?
忘記了的話,往上翻翻看,--version 的描述是 Print version information and quit ,是一種更加簡單的版本信息.
無論是管理命令還是普通命令,直接輸入命令后都會有相應的用法說明以及幫助信息,同樣地追加 --help 即可!
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker run "docker run" requires at least 1 argument. See 'docker run --help'. Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...] Run a command in a new container
最后的才是亮點,在命令結尾處追加 --help 可以獲取更加詳細的幫助信息,這一點不僅適合一級命令 docker image --help 還適合二級子命令 docker image ls --help .
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
所以,遇到不懂的或者陌生的命令請一定要記住 --help 幫助命令,這是 docker 全部命令中最重要的一點!
Docker 是一種規范化的部署運維新方式,相對于傳統打包部署的來說,更加統一規范化,貨物是各種各樣的正如開發語言的多樣性一樣,但是集裝箱的出現卻顛覆了物流運輸,帶來了巨大的進步!
如果你是 Java 后臺開發,或多或少肯定有著自己獨立部署項目的經歷,先登錄服務器裝個 Java 環境再裝個 Tomcat 環境,最后在上傳自己的 War 包到 Tomcat 部署目錄,如此重復繁瑣的勞動還不一定能保證一次性成功!
因為有時你的代碼中很有可能有些絕對路徑,部署到服務器肯定會報錯,如果缺少了個人文件也會報錯等等,這時候就出現了經典的對話:明明在我的電腦運行地好好的啊!
Docker 的出現在一定程度上解決了這種問題,將應用打包到集裝箱,Docker 作為超級貨輪承載著集裝箱安全快速地運送到目的地,集裝箱內的環境是自給自足的封閉環境,所有的相關依賴一次性全部都給你.
無論是本機運輸這個封閉的集裝箱還是遠程服務器運輸這個集裝箱結果都是一樣的,再也不會出現環境不一致而導致的相互埋怨情況的發生了!
那么問題來了,如果給你一個集裝箱,你能安全快速運輸到目的地嗎?如果你手頭上已經有一批貨需要這種集裝箱服務,如何快速封裝成集裝箱呢?
對于第一個問題,本文已經給出答案,那就是 docker + docker COMMAND --help 查詢支持的命令以及查看命令的幫助文檔.
[root@snowdreams1006 ~]# docker
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND
A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default
"/root/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the
daemon (overrides DOCKER_HOST env var and
default context set with "docker context use")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level
("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal")
(default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default
"/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default
"/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default
"/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
builder Manage builds
config Manage Docker configs
container Manage containers
context Manage contexts
engine Manage the docker engine
image Manage images
network Manage networks
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.對于第二個問題,請先預習 docker 相關命令,感謝你的閱讀!
以上就是如何進行更加優雅地Docker部署項目,小編相信有部分知識點可能是我們日常工作會見到或用到的。希望你能通過這篇文章學到更多知識。更多詳情敬請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。