您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“Rugged::Repository提供的方法有哪些”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“Rugged::Repository提供的方法有哪些”文章吧。
1.概念
a.rugged是基于ruby語言開發的libgit2訪問庫, 提供了很好的速度和可移植性并且擁有ruby語言優美的特性.
b.libgit2是一套git核心方法的純c實現,被設計兼具速度和可移植性.
2.安裝
前提:首先當然按照ruby環境以及gem ruby包管理器(此處不介紹,可google),環境ubuntu
安裝命令如下:
$>gem install rugged
可能問題:包的依賴問題,亦可據錯誤google之
3.文檔
$>gem server
可打開gem內置的web服務器,可以瀏覽所有安裝的軟件和它們的說明文檔,打開http://localhost:8808
4.rugged庫內部模塊和常用類
主要有一個module Rugged,其中擁有Rugged::Repository,Rugged::Commit,Rugged::Branch,
Rugged::BranchCollections,Rugged::Object,Rugged:Tag,Rugged::Config,Rugged::Remote,
Rugged::Index,Rugged::SettingsRugged::Reference,Rugged::Patch,Rugged::Tree,Rugged::Diff,
Rugged::Error,Rugged::Credentials等相關模塊和類,后面會一一介紹.
5.簡單上手一試
require 'rugged'
#導入rugged模塊
repo = Rugged::Repository.new('/home/lry/workspace/ruby_test/git_test/.git')
#從參數給定的git路徑打開git repository,返回Rugged::Repository對象
puts Rugged::Repository.discover("/home/lry/workspace/ruby_test/git_test/.git")
# => "/home/lry/workspace/ruby_test/git_test/.git"
puts repo.exists?('e6a40e934434e11d1e8dad08cb95a49e9d5b2aec')
#判斷給定的sha1 oid表示的對象是否存在于repository中,sha1可通過在git status查看
# => true
puts repo.bare?
# => false
puts repo.empty?
#由于我的工作目錄中存在已提交文件,所以一下為空
# => false
puts repo.head_detached?
# => false
puts repo.path
# => "/home/lry/workspace/ruby_test/git_test/.git/"
puts repo.workdir
# => "/home/lry/workspace/ruby_test/git_test/"
# The HEAD of the repository.
puts ref = repo.head
# => #<Rugged::Reference:0x00000002520218>
puts ref.name
# => "refs/heads/master"
ref.target
# => #<Rugged::Commit:0x00000002520150>
object = repo.read('e6a40e934434e11d1e8dad08cb95a49e9d5b2aec')
# => #<Rugged::Commit:0x00000002520150>
puts object.len
# => 171
puts object.data
# => "tree 203809dc435dd4e78d203cbf766a17581d77b2fa
author ###
committer ###
add readme"
puts object.type
# => :commit6.Rugged的類結構組織
首先說明一下git, git存儲每一個文件,而不是像svn一樣紀錄版本之間的差別。
Repository包含很多Reference,Reference可以是是Reference或者Branch或者Tag或者AnnotationTag,Reference指向一個target,Reference類型type為:symbolic或者:direct, 如果type為:direct類型,則
target為Commit,否則為其他Reference。
Reference如refs/heads/master, refs/remotes/origin/master, refs/heads/zql/master, refs/tags/v1.0
Branch如refs/heads/master, refs/heads/zql/master,refs/remotes/origin/master
Tag如refs/tags/v1.0
AnnotationTag指加了message的tag
Commit即提交,一個提交即代表一個版本,每個Commit包含了該版本的所有文件,如下圖所示
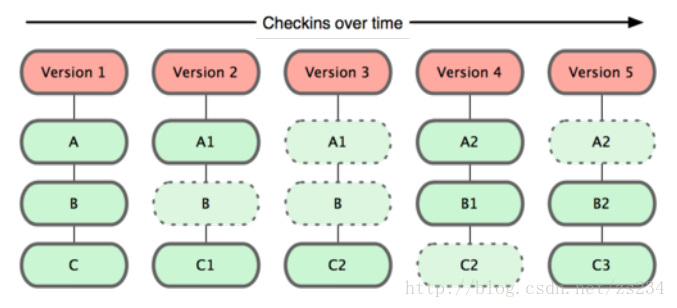
a) Version 1包含文件A,B,C
b) 修改了文件A,C; 進化為Version 2, 包含文件A1,B,C1
c) 修改了文件C1;進化為Version 3,包含文件A1, B, C2
d) 修改了文件A1,B;進化為Version 4,包含文件A2,B1,C2
e) 修改了文件B1,C2; 進化為Version 5, 包含文件A2,B2, C3
上述代表了git的文件變遷歷史。進一步說明,Commit指向一個Tree,Tree項目有Trees和Blobs以及Commits,Commit指向的Tree為根樹,Tree代表一個目錄,當然根樹代表頂級目錄,路徑為"";Blob代表文件;Commit代表子模塊。 每個目錄下也可以擁有子目錄和文件以及子模塊;如下圖所示:
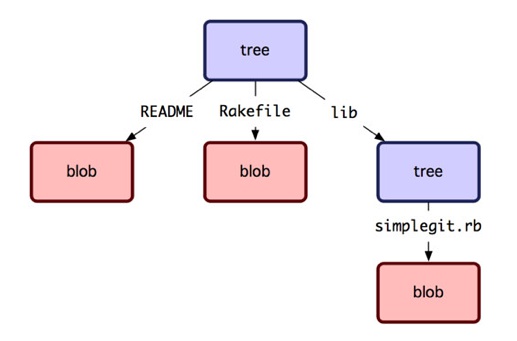
每個Commit的parents指向其父提交,也即是其上一個提交(當然也可以有多個,如merge),如上述Version 5的父提交時Version 4。下圖是Commit的組織方式:
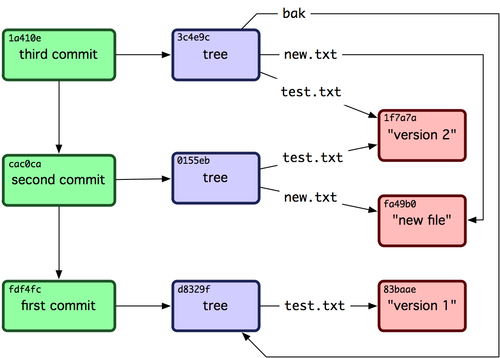
值得注意的是,文件(目錄)信息和內容是分開存儲的,文件信息包含文件的oid,通過oid再去倉庫通過idx去pack查找文件內容。
7.相關模塊和類詳解
1).當然,最重要的類就是Rugged::Repository了,使用它我們可以操作磁盤上的git repository.
a.初始化方法
bare(path[, alternates]) → repository
打開一個bare git repository,參數path為的.git的路徑(包括.git).返回Rugged::Repository表示該repository的對象
init_at(path, is_bare = false) → repository
示例:Rugged::Repository.init_at('~/repository', :bare)
#=> #<Rugged::Repository:0x108849488>若不存在則初始化repository,否則重新初始化,參數path為.git的上一級路徑(不包括.git),參數is_bare表示是否以bare初始化repository,默認為false.返回Rugged::Repository表示該repository的對象
new(path, options = {}) → repository
示例:Rugged::Repository.new('~/test/.git')
#=> #<Rugged::Repository:0x108849488>
Rugged::Repository.new(path, :alternates => ['./other/repo/.git/objects'])打開一個repository,參數path為.git的路徑或者其上一級路徑,options表示可選參數,接.git中子目錄的路徑.返回Rugged::Repository表示該repository的對象. 如果需要創建一個repository,請使用Rugged::init_at代替.
clone_at(url, local_path[, options]) → repository
示例:Repository.clone_at("https://github.com/libgit2/rugged.git", "./some/dir",
{ transfer_progress: lambda { |total_objects, indexed_objects, received_objects,
local_objects, total_deltas, indexed_deltas, received_bytes|
# ...}
})從遠程地址得到一個git的拷貝.url為項目倉庫的地址,local_path為本地拷貝的目錄.返回Rugged::Repository表示該repository的對象.
options有如下Hash選項:
:bare
Iftrue, the clone will be created as a bare repository. Defaults tofalse.
:checkout_branch
The name of a branch to checkout. Defaults to the remote’sHEAD.
:remote
The name to give to the “origin” remote. Defaults to"origin".
:ignore_cert_errors
If set totrue, errors while validating the remote’s host certificate will be ignored.
:credentials
The credentials to use for the clone operation. Can be either an instance of one of the Rugged::Credentials types, or a proc returning one of the former. The proc will be called with theurl, theusernamefrom the url (if applicable) and a list of applicable credential types.
:progress
A callback that will be executed with the textual progress received from the remote. This is the text send over the progress side-band (ie. the “counting objects” output).
:transfer_progress
A callback that will be executed to report clone progress information. It will be passed the amount oftotal_objects,indexed_objects,received_objects,local_objects,total_deltas,indexed_deltas, andreceived_bytes.
:update_tips
A callback that will be executed each time a reference was updated locally. It will be passed therefname,old_oidandnew_oid.
b.基本方法
discover(path = nil, across_fs = true) → repository
由path傳遞的路徑向上搜索.git文件夾,然后打開并生成一個Rugged::Repository對象,如果path為nil,則以當前路徑為起始點
hash_data(str, type) → oid
Repository.hash_data('hello world', :commit) #=> "de5ba987198bcf2518885f0fc1350e5172cded78"
Repository.hash_data('hello_world', :tag) #=> "9d09060c850defbc7711d08b57def0d14e742f4e"返回str的hash值.將str作為原始數據加上type相應的頭部進行散列.返回該結果的hash值字符串
hash_file(path, type) → oid
返回path指向的文件的hash值.返回sha1值的字符串
create_branch(name, sha_or_ref = "HEAD")
在倉庫中創建分支,name指定分支名,sha_ora_ref目標分支,可以為oid,reference name或者Rugged::Object實例.返回Rugged::Branch對象
branches()
返回當前repository中的分支,返回Rugged::Branch的BranchCollection對象集合
checkout(target, options = {})切換到由target指定的branch, reference or commit.
checkout_head([options]) → nil
切換到HEAD
ref(ref_name)
示例:repo.ref 'refs/heads/master'
# => #<Rugged::Reference:2199125780 {name: "refs/heads/master",
target: "25b5d3b40c4eadda8098172b26c68cf151109799"}>查找ref_name制定的Rugged::Reference對象
ref_names(glob = nil) references()#得到倉庫中的所有Referece,ReferenceCollection表示 refs(glob = nil)
head → ref
獲取指向repository Head的Rugged::Reference對象
head = str
設置repository的Head
index → idx index = idx
獲取或設置repository的默認的index,idx為Rugged::Index對象
namespace → str namespace = new_namespace
設置或設置repository的活動命名空間
path → path
獲取完整的,標準的.git的路徑
workdir → path or nil workdir = path
獲取或設置repository的工作目錄
config → cfg config = cfg
獲取和設置配置.cfg為Rugged::Config對象
lookup(oid)
查找一個SHA1,返回繼承Rugged::Object四個類中的某一個類的對象
exists?(oid) → true or false
是否給定的SHA1 OID (represented as a 40-character string)存在于repository
include?(oid) → true or false
repo.include?("d8786bfc97485e8d7b19b21fb88c8ef1f199fc3f") #=> true是否給定的SHA1 OID (represented as a 40-character string)存在于repository
tags()
獲取repository的所有tag.返回Rugged::Tag的集合Rugged::TagCollection對象
remotes()
獲取repository的所有remotes. 返回Rugged::Remote的集合Rugged::RemoteCollection對象
push(remote_or_url, *args)
推送refspecs到remote_or_url.返回refspecs為鍵值,如果成功值為nil,失敗為錯誤消息
last_commit()
獲取最后一次commit, 返回Rugged::Commit對象
read(oid) → str
讀取oid對象標識的對象原始數據
read_header(oid) → hash
讀取repository的Head信息.返回一個Hash對象,可能的鍵值對如下
:type =>A Symbol denoting the object’s type.可能的值:tree,:blob,:commit或:tag.
:len =>上述對象的長度
rev_parse(spec)
通過revision字符串查找對象.返回繼承Rugged::Object四個類中的某一個類的對象
rev_parse_oid(spec)
通過revision字符串查找oid.返回匹配revision的oid
write(buffer, type) → oid
將buffer中的數據作為被給定類型type寫入repository’s object database.
type可取值為:tag,:commit,:treeor:blob.
返回新建對象的oid
blob_at(revision, path)
獲取指定路徑path的revision的blob.
revision - The String SHA1.
path - The String file path.
返回字符串
diff(left, right, opts = {})
diff_workdir(left, opts = {})指定兩個版本的diff
merge_base(oid1, oid2, ...) merge_base(ref1, ref2, ...) merge_base(commit1, commit2, ...)
找到合并的base
merge_commits(our_commit, their_commit, options = {}) → index合并操作.our_commitandtheir_commitcan either be Rugged::Commit objects, or OIDs resolving to the former. 返回合并后的Rugged::Index對象
each_id { |id| block }
each_id → Iterator對在repository中發現的每一個object ID執行塊迭代,id為40個字符的字符串
status { |file, status_data| block }
status(path) → status_data
示例:repo.status { |file, status_data| puts "#{file} has status: #{status_data.inspect}" }
repo.status('src/diff.c') #=> [:index_new, :worktree_new]獲取工作目錄中文件的狀態.
c.操作對象數據庫
read(oid)
示例:object = repo.read('a0ae5566e3c8a3bddffab21022056f0b5e03ef07')
# => #<Rugged::OdbObject:0x109a64780> 通過oid讀取Rugged::OdbObject對象
Rugged::OdbObject.data() Rugged::OdbObject.len() Rugged::OdbObject.type() Rugged::OdbObject.oid() 示例:object.len# => 237 object.data # => "tree 76f23f186076fc291742816721ea8c3e95567241\nparent 8e3c5c52b8f29da0adc7e8be8a037cbeaea6de6b\nauthor Vicent Mart\303\255 <tanoku@gmail.com> 1333859005 +0200\ncommitter Vicent Mart\303\255 <tanoku@gmail.com> 1333859005 +0200\n\nAdd `Repository#blob_at`\n" object.type# => :commit object.oid#=> "d8786bfc97485e8d7b19b21fb88c8ef1f199fc3f"
以上就是關于“Rugged::Repository提供的方法有哪些”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。