您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家介紹leetcode中怎么利用多線程實現按序打印,內容非常詳細,感興趣的小伙伴們可以參考借鑒,希望對大家能有所幫助。
我們提供了一個類:
public class Foo {
public void first() { print("first"); }
public void second() { print("second"); }
public void third() { print("third"); }
}
三個不同的線程 A、B、C 將會共用一個 Foo 實例。一個將會調用 first() 方法
一個將會調用 second() 方法
還有一個將會調用 third() 方法
請設計修改程序,以確保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被執行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被執行。
示例 1:
輸入: [1,2,3]
輸出: "firstsecondthird"
解釋:
有三個線程會被異步啟動。
輸入 [1,2,3] 表示線程 A 將會調用 first() 方法,線程 B 將會調用 second() 方法,線程 C 將會調用 third() 方法。
正確的輸出是 "firstsecondthird"。
示例 2:輸入: [1,3,2]
輸出: "firstsecondthird"
解釋:
輸入 [1,3,2] 表示線程 A 將會調用 first() 方法,線程 B 將會調用 third() 方法,線程 C 將會調用 second() 方法。
正確的輸出是 "firstsecondthird"。
提示:
盡管輸入中的數字似乎暗示了順序,但是我們并不保證線程在操作系統中的調度順序。
你看到的輸入格式主要是為了確保測試的全面性。
package com.lau.multithread.sortprint;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 按序打印-實現方案1-鎖
*
我們提供了一個類:
public class Foo {
public void first() { print("first"); }
public void second() { print("second"); }
public void third() { print("third"); }
}
三個不同的線程 A、B、C 將會共用一個 Foo 實例。
一個將會調用 first() 方法
一個將會調用 second() 方法
還有一個將會調用 third() 方法
請設計修改程序,以確保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被執行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被執行。
*
*
*/
class Foo {
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
final Condition firstCondition = lock.newCondition();
final Condition secondCondition = lock.newCondition();
final Condition thirdCondition = lock.newCondition();
private volatile int flag = 0;
public void first() {
try {
lock.lock();
while(this.flag != 0) {
firstCondition.await();
}
print("first");
flag = 1;
secondCondition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void second() {
try {
lock.lock();
while(this.flag != 1) {
secondCondition.await();
}
print("second");
flag = 2;
thirdCondition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void third() {
try {
lock.lock();
while(this.flag != 2) {
thirdCondition.await();
}
print("third");
flag = 0;
firstCondition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void print(String target) {
System.out.print(target);
}
}
public class PrintInOrderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Foo foo = new Foo();
Map<Integer, Runnable> map = new HashMap<Integer, Runnable>() {
{
put(1, () -> foo.first());
put(2, () -> foo.second());
put(3, () -> foo.third());
}
};
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
threadPool.submit(map.get(Integer.valueOf(args[i])));
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}package com.lau.multithread.sortprint;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 按序打印-實現方案2-傳統方式
*
我們提供了一個類:
public class Foo {
public void first() { print("first"); }
public void second() { print("second"); }
public void third() { print("third"); }
}
三個不同的線程 A、B、C 將會共用一個 Foo 實例。
一個將會調用 first() 方法
一個將會調用 second() 方法
還有一個將會調用 third() 方法
請設計修改程序,以確保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被執行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被執行。
*
*
*/
class Foo2 {
private volatile int flag = 0;
public synchronized void first() {
try {
while(this.flag != 0) {
this.wait();
}
print("first");
flag = 1;
this.notifyAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public synchronized void second() {
try {
while(this.flag != 1) {
this.wait();
}
print("second");
flag = 2;
this.notifyAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public synchronized void third() {
try {
while(this.flag != 2) {
this.wait();
}
print("third");
flag = 0;
this.notifyAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void print(String target) {
System.out.print(target);
}
}
public class PrintInOrderDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Foo2 foo = new Foo2();
Map<Integer, Runnable> map = new HashMap<Integer, Runnable>() {
{
put(1, () -> foo.first());
put(2, () -> foo.second());
put(3, () -> foo.third());
}
};
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
threadPool.submit(map.get(Integer.valueOf(args[i])));
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}package com.lau.multithread.sortprint;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
/**
* 按序打印-實現方案3-信號量
*
我們提供了一個類:
public class Foo {
public void first() { print("first"); }
public void second() { print("second"); }
public void third() { print("third"); }
}
三個不同的線程 A、B、C 將會共用一個 Foo 實例。
一個將會調用 first() 方法
一個將會調用 second() 方法
還有一個將會調用 third() 方法
請設計修改程序,以確保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被執行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被執行。
*
*
*/
class Foo3 {
private final Semaphore firstSp = new Semaphore(1);
private final Semaphore secondSp = new Semaphore(0);
private final Semaphore thirdSp = new Semaphore(0);
public void first() {
try {
firstSp.acquire();
print("first");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
secondSp.release();
}
}
public void second() {
try {
secondSp.acquire();
print("second");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
thirdSp.release();
}
}
public void third() {
try {
thirdSp.acquire();
print("third");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
firstSp.release();
}
}
private void print(String target) {
System.out.print(target);
}
}
public class PrintInOrderDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Foo3 foo = new Foo3();
Map<Integer, Runnable> map = new HashMap<Integer, Runnable>() {
{
put(1, () -> foo.first());
put(2, () -> foo.second());
put(3, () -> foo.third());
}
};
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
threadPool.submit(map.get(Integer.valueOf(args[i])));
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}打印設置:
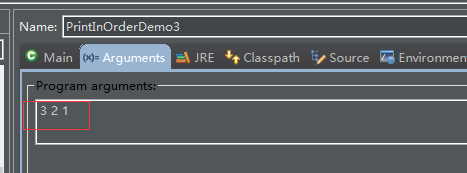
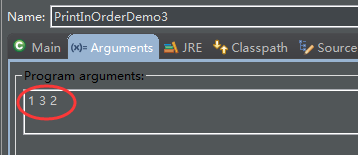
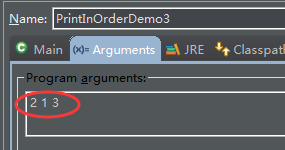
輸出:
firstsecondthird
關于leetcode中怎么利用多線程實現按序打印就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。