您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“如何理解SpringMVC異常處理體系”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
在 SpringMVC 的異常體系中,處于最頂層的大 Boss 是 HandlerExceptionResolver,這是一個接口,里邊只有一個方法:
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver { @Nullable ModelAndView resolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex); }resolveException 方法就用來解析請求處理過程中所產生的異常,并最終返回一個 ModelAndView。
我們來看下 HandlerExceptionResolver 的實現類:
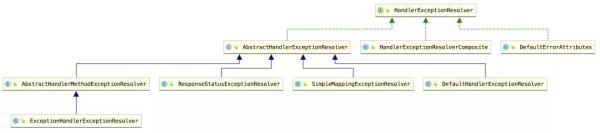
直接實現 HandlerExceptionResolver 接口的類有三個:
HandlerExceptionResolverComposite:這個一看又是一個組合,在最近的源碼分析中我們已經多次見到 xxxComposite 了,這里就不再贅述。
DefaultErrorAttributes:這個用來保存異常屬性。
AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver:這個的子類比較多:
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver:通過提前配置好的異常類和 View 之間的對應關系來解析異常。
AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver:處理使用 @ExceptionHandler 注解自定義的異常類型。
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver:按照不同類型來處理異常。
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver:處理含有 @ResponseStatus 注解的異常。
在 SpringMVC 中,大致的異常解析器就是這些,接下來我們來逐個學習這些異常解析器。
AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver 是真正干活的異常解析器的父類,我們就先從他的 resolveException 方法開始看起。
@Override @Nullable public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { if (shouldApplyTo(request, handler)) { prepareResponse(ex, response); ModelAndView result = doResolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (result != null) { logException(ex, request); } return result; } else { return null; } }鴻蒙官方戰略合作共建——HarmonyOS技術社區
首先調用 shouldApplyTo 方法判斷當前解析器是否可以處理傳入的處理器所拋出的異常,如果不支持,則直接返回 null,這個異常將交給下一個 HandlerExceptionResolver 去處理。
調用 prepareResponse 方法處理 response。
調用 doResolveException 方法實際處理異常,這是一個模版方法,具體的實現在子類中。
調用 logException 方法記錄異常日志信息。
記錄異常日志沒啥好說的,doResolveException 則是一個空的模版方法,所以這里對我們來說主要就是兩個方法:shouldApplyTo 和 prepareResponse,我們分別來看。
protected boolean shouldApplyTo(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable Object handler) { if (handler != null) { if (this.mappedHandlers != null && this.mappedHandlers.contains(handler)) { return true; } if (this.mappedHandlerClasses != null) { for (Class<?> handlerClass : this.mappedHandlerClasses) { if (handlerClass.isInstance(handler)) { return true; } } } } return !hasHandlerMappings(); }這里涉及到了兩個對象:mappedHandlers 和 mappedHandlerClasses:
mappedHandlers:存儲的是處理器對象(Controller 或者 Controller 中的方法)
mappedHandlerClasses:存儲的是處理器的 Class。
我們在配置異常解析器的時候可以配置這兩個對象,進而實現該異常處理器只為某一個處理器服務,但是一般來說沒這種需求,所以大家僅做了解即可。
如果開發者一開始配置了 mappedHandlers 或者 mappedHandlerClasses,則用這兩個和處理器去比較,否則就直接返回 true,表示支持該異常處理。
prepareResponse 方法比較簡單,主要是處理一下響應頭的緩存字段。
protected void prepareResponse(Exception ex, HttpServletResponse response) { if (this.preventResponseCaching) { preventCaching(response); } } protected void preventCaching(HttpServletResponse response) { response.addHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL, "no-store"); }這是 AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver 的大致內容,可以看到還是非常 easy 的,接下來我們來看它的實現類。
2.1 AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver
AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver 主要是重寫了 shouldApplyTo 方法和 doResolveException 方法,一個一個來看。
@Override protected boolean shouldApplyTo(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable Object handler) { if (handler == null) { return super.shouldApplyTo(request, null); } else if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler; handler = handlerMethod.getBean(); return super.shouldApplyTo(request, handler); } else if (hasGlobalExceptionHandlers() && hasHandlerMappings()) { return super.shouldApplyTo(request, handler); } else { return false; } }這塊感覺沒啥好說的,判斷邏輯基本上都還是調用父類的 shouldApplyTo 方法去處理。
doResolveException
@Override @Nullable protected final ModelAndView doResolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (handler instanceof HandlerMethod ? (HandlerMethod) handler : null); return doResolveHandlerMethodException(request, response, handlerMethod, ex); } @Nullable protected abstract ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception ex);doResolveException 是具體的異常處理方法,但是它里邊卻沒有實質性操作,具體的事情交給 doResolveHandlerMethodException 方法去做了,而該方法是一個抽象方法,具體的實現在子類中。
2.1.1 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver 只有一個子類就是 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,來看下它的 doResolveHandlerMethodException 方法:
@Override @Nullable protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) { ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception); if (exceptionHandlerMethod == null) { return null; } if (this.argumentResolvers != null) { exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers); } if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) { exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers); } ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); ArrayList<Throwable> exceptions = new ArrayList<>(); try { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod); } // Expose causes as provided arguments as well Throwable exToExpose = exception; while (exToExpose != null) { exceptions.add(exToExpose); Throwable cause = exToExpose.getCause(); exToExpose = (cause != exToExpose ? cause : null); } Object[] arguments = new Object[exceptions.size() + 1]; exceptions.toArray(arguments); // efficient arraycopy call in ArrayList arguments[arguments.length - 1] = handlerMethod; exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, arguments); } catch (Throwable invocationEx) { // Any other than the original exception (or a cause) is unintended here, // probably an accident (e.g. failed assertion or the like). if (!exceptions.contains(invocationEx) && logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Failure in @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod, invocationEx); } // Continue with default processing of the original exception... return null; } if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) { return new ModelAndView(); } else { ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel(); HttpStatus status = mavContainer.getStatus(); ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, status); mav.setViewName(mavContainer.getViewName()); if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) { mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView()); } if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) { Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes(); RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes); } return mav; } }這個方法雖然比較長,但是很好理解:
鴻蒙官方戰略合作共建——HarmonyOS技術社區
首先查找到帶有 @ExceptionHandler 注解的方法,封裝成一個 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 對象(關于 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 對象,松哥在之前的文章中已經介紹過了,具體參見:Spring Boot 定義接口的方法是否可以聲明為 private?)。
如果找到了對應的方法,則為 exceptionHandlerMethod 配置參數解析器、視圖解析器等,關于這些解析器,參考松哥之前的文章:SpringBoot 中如何自定義參數解析器?、深入分析 SpringMVC 參數解析器、Spring Boot 中如何統一 API 接口響應格式?。
接下來定義一個 exceptions 數組,如果發生的異常存在異常鏈,則將整個異常鏈存入 exceptions 數組中。
exceptions 數組再加上 handlerMethod,共同組成方法參數,調用 exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle 完成自定義異常方法的執行,執行結果被保存再 mavContainer 中。
如果請求到此結束,則直接構造一個 ModelAndView 返回。
否則從 mavContainer 中取出各項信息,構建新的 ModelAndView 返回。同時,如果存在重定向參數,也將之保存下來(關于重定向參數,參見:SpringMVC 中的參數還能這么傳遞?漲姿勢了!)。
這就是 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 的大致工作流程,可以看到,還是非常 easy 的。
2.2 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
這個看名字就知道是一個默認的異常處理器,用來處理一些常見的異常類型,我們來看一下它的 doResolveException 方法:
@Override @Nullable protected ModelAndView doResolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { try { if (ex instanceof HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) { return handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported( (HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) { return handleHttpMediaTypeNotSupported( (HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) { return handleHttpMediaTypeNotAcceptable( (HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof MissingPathVariableException) { return handleMissingPathVariable( (MissingPathVariableException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestParameterException) { return handleMissingServletRequestParameter( (MissingServletRequestParameterException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof ServletRequestBindingException) { return handleServletRequestBindingException( (ServletRequestBindingException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof ConversionNotSupportedException) { return handleConversionNotSupported( (ConversionNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof TypeMismatchException) { return handleTypeMismatch( (TypeMismatchException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotReadableException) { return handleHttpMessageNotReadable( (HttpMessageNotReadableException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotWritableException) { return handleHttpMessageNotWritable( (HttpMessageNotWritableException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) { return handleMethodArgumentNotValidException( (MethodArgumentNotValidException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestPartException) { return handleMissingServletRequestPartException( (MissingServletRequestPartException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof BindException) { return handleBindException((BindException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof NoHandlerFoundException) { return handleNoHandlerFoundException( (NoHandlerFoundException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof AsyncRequestTimeoutException) { return handleAsyncRequestTimeoutException( (AsyncRequestTimeoutException) ex, request, response, handler); } } catch (Exception handlerEx) { } return null; }可以看到,這里實際上就是根據不同的異常類型,然后調用不同的類去處理該異常。這里相關的處理都比較容易,以 HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException 為例,異常處理就是對 response 對象做一些配置,如下:
protected ModelAndView handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException ex, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler) throws IOException { String[] supportedMethods = ex.getSupportedMethods(); if (supportedMethods != null) { response.setHeader("Allow", StringUtils.arrayToDelimitedString(supportedMethods, ", ")); } response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, ex.getMessage()); return new ModelAndView(); }配置響應頭,然后 sendError,最后返回一個空的 ModelAndView 對象。
其實這里哥哥異常處理方法都大同小異,松哥就不再贅述啦。
2.3 ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
這個用來處理 ResponseStatusException 類型的異常,或者使用了 @ResponseStatus 注解標記的普通異常類。我們來看下它的 doResolveException 方法:
@Override @Nullable protected ModelAndView doResolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { try { if (ex instanceof ResponseStatusException) { return resolveResponseStatusException((ResponseStatusException) ex, request, response, handler); } ResponseStatus status = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(ex.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class); if (status != null) { return resolveResponseStatus(status, request, response, handler, ex); } if (ex.getCause() instanceof Exception) { return doResolveException(request, response, handler, (Exception) ex.getCause()); } } catch (Exception resolveEx) { } return null; }可以看到,首先判斷異常類型是不是 ResponseStatusException,如果是,則直接調用 resolveResponseStatusException 方法進行異常信息處理,如果不是,則去查找到異常類上的 @ResponseStatus 注解,并從中查找出相關的異常信息,然后調用 resolveResponseStatus 方法進行處理。
可以看到,ResponseStatusExceptionResolver 處理的異常類型有兩種:
直接繼承自 ResponseStatusException 的異常類,這種異常類可以直接從里邊提取出來想要的信息。
通過 @ResponseStatus 注解的普通異常類,這種情況下異常信息從 @ResponseStatus 注解中提取出來。
這個比較簡單,沒啥好說的。
2.4 SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver 則是根據不同的異常顯示不同的 error 頁面。可能有的小伙伴還沒用過 SimpleMappingExceptionResolver,所以松哥這里先簡單說一下用法。
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver 的配置非常簡單,直接提供一個 SimpleMappingExceptionResolver 的實例即可,如下:
@Bean SimpleMappingExceptionResolver simpleMappingExceptionResolver() { SimpleMappingExceptionResolver resolver = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver(); Properties mappings = new Properties(); mappings.put("java.lang.ArithmeticException", "11"); mappings.put("java.lang.NullPointerException", "22"); resolver.setExceptionMappings(mappings); Properties statusCodes = new Properties(); statusCodes.put("11", "500"); statusCodes.put("22", "500"); resolver.setStatusCodes(statusCodes); return resolver; }在 mappings 中配置異常和 view 之間的對應關系,要寫異常類的全路徑,后面的 11、22 則表示視圖名稱;statusCodes 中配置了視圖和響應狀態碼之間的映射關系。配置完成后,如果我們的項目在運行時拋出了 ArithmeticException 異常,則會展示出 11 視圖,如果我們的項目在運行時拋出了 NullPointerException 異常,則會展示出 22 視圖。
這是用法,了解了用法之后我們再來看源碼,就容易理解了,我們直接來看 doResolveException 方法:
@Override @Nullable protected ModelAndView doResolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { String viewName = determineViewName(ex, request); if (viewName != null) { Integer statusCode = determineStatusCode(request, viewName); if (statusCode != null) { applyStatusCodeIfPossible(request, response, statusCode); } return getModelAndView(viewName, ex, request); } else { return null; } }鴻蒙官方戰略合作共建——HarmonyOS技術社區
首先調用 determineViewName 方法確定視圖的名稱。
接下來調用 determineStatusCode 查看視圖是否有對應的 statusCode。
調用 applyStatusCodeIfPossible 方法將 statusCode 設置到 response 上,這個方法很簡單,不多說。
調用 getModelAndView 方法構造一個 ModelAndView 對象返回,在構造時,同時設置異常參數,異常的信息的 key 默認就是 exception。
在上面這個過程中,有兩個比較長的方法,松哥這里需要和大家額外多說兩句。
這個就是根據異常類型找到視圖名,我們來看下具體的查找方式:
@Nullable protected String determineViewName(Exception ex, HttpServletRequest request) { String viewName = null; if (this.excludedExceptions != null) { for (Class<?> excludedEx : this.excludedExceptions) { if (excludedEx.equals(ex.getClass())) { return null; } } } if (this.exceptionMappings != null) { viewName = findMatchingViewName(this.exceptionMappings, ex); } if (viewName == null && this.defaultErrorView != null) { viewName = this.defaultErrorView; } return viewName; }鴻蒙官方戰略合作共建——HarmonyOS技術社區
如果當前異常包含在 excludedExceptions 中,則直接返回 null(意思是當前異常被忽略處理了,直接按照默認方式來)。
如果 exceptionMappings 不為 null,則直接調用 findMatchingViewName 方法查找異常對應的視圖名(exceptionMappings 變量就是前面我們配置的映射關系),具體的查找方式就是遍歷我們前面配置的映射表。
如果沒找到對應的 viewName,并且用戶配置了 defaultErrorView,則將 defaultErrorView 賦值給 viewName,并將 viewName 返回。
@Nullable protected Integer determineStatusCode(HttpServletRequest request, String viewName) { if (this.statusCodes.containsKey(viewName)) { return this.statusCodes.get(viewName); } return this.defaultStatusCode; }這個就比較容易,直接去 statusCodes 中查看是否有視圖對應的狀態碼,如果有則直接返回,如果沒有,就返回一個默認的。
3.HandlerExceptionResolverComposite
最后,還有一個 HandlerExceptionResolverComposite 需要和大家介紹下,這是一個組合的異常處理器,用來代理哪些真正干活的異常處理器。
@Override @Nullable public ModelAndView resolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { if (this.resolvers != null) { for (HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver : this.resolvers) { ModelAndView mav = handlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (mav != null) { return mav; } } } return null; }它的 resolveException 方法就比較簡單了,這種寫法我們已經見到過很多次了,不再贅述。
“如何理解SpringMVC異常處理體系”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。