溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章為大家展示了使用go語言怎么對BMP文件頭進行讀取,內容簡明扼要并且容易理解,絕對能使你眼前一亮,通過這篇文章的詳細介紹希望你能有所收獲。
WORD 兩個字節 16bit
DWORD 四個字節 32bit
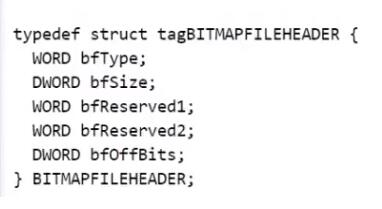
package main
import (
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
file, err := os.Open("tim.bmp")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
//type拆成兩個byte來讀
var headA, headB byte
//Read第二個參數字節序一般windows/linux大部分都是LittleEndian,蘋果系統用BigEndian
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &headA)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &headB)
//文件大小
var size uint32
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &size)
//預留字節
var reservedA, reservedB uint16
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &reservedA)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &reservedB)
//偏移字節
var offbits uint32
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &offbits)
fmt.Println(headA, headB, size, reservedA, reservedB, offbits)
}執行結果
66 77 196662 0 0 54
使用結構體方式
package main
import (
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"os"
)
type BitmapInfoHeader struct {
Size uint32
Width int32
Height int32
Places uint16
BitCount uint16
Compression uint32
SizeImage uint32
XperlsPerMeter int32
YperlsPerMeter int32
ClsrUsed uint32
ClrImportant uint32
}
func main() {
file, err := os.Open("tim.bmp")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
//type拆成兩個byte來讀
var headA, headB byte
//Read第二個參數字節序一般windows/linux大部分都是LittleEndian,蘋果系統用BigEndian
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &headA)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &headB)
//文件大小
var size uint32
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &size)
//預留字節
var reservedA, reservedB uint16
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &reservedA)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &reservedB)
//偏移字節
var offbits uint32
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &offbits)
fmt.Println(headA, headB, size, reservedA, reservedB, offbits)
infoHeader := new(BitmapInfoHeader)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, infoHeader)
fmt.Println(infoHeader)
}執行結果:
66 77 196662 0 0 54
&{40 256 256 1 24 0 196608 3100 3100 0 0}
補充:golang(Go語言) byte/[]byte 與 二進制形式字符串 互轉
效果
把某個字節或字節數組轉換成字符串01的形式,一個字節用8個”0”或”1”字符表示。
比如:
byte(3) –> “00000011”
[]byte{1,2,3} –> “[00000001 00000010 00000011]”
“[00000011 10000000]” –> []byte{0x3, 0x80}開源庫 biu
實際上我已經將其封裝到一個開源庫了(biu),其中的一個功能就能達到上述效果:
//byte/[]byte -> string
bs := []byte{1, 2, 3}
s := biu.BytesToBinaryString(bs)
fmt.Println(s) //[00000001 00000010 00000011]
fmt.Println(biu.ByteToBinaryString(byte(3))) //00000011
//string -> []byte
s := "[00000011 10000000]"
bs := biu.BinaryStringToBytes(s)
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", bs) //[]byte{0x3, 0x80}代碼實現
const (
zero = byte('0')
one = byte('1')
lsb = byte('[') // left square brackets
rsb = byte(']') // right square brackets
space = byte(' ')
)
var uint8arr [8]uint8
// ErrBadStringFormat represents a error of input string's format is illegal .
var ErrBadStringFormat = errors.New("bad string format")
// ErrEmptyString represents a error of empty input string.
var ErrEmptyString = errors.New("empty string")
func init() {
uint8arr[0] = 128
uint8arr[1] = 64
uint8arr[2] = 32
uint8arr[3] = 16
uint8arr[4] = 8
uint8arr[5] = 4
uint8arr[6] = 2
uint8arr[7] = 1
}
// append bytes of string in binary format.
func appendBinaryString(bs []byte, b byte) []byte {
var a byte
for i := 0; i < 8; i++ {
a = b
b <<= 1
b >>= 1
switch a {
case b:
bs = append(bs, zero)
default:
bs = append(bs, one)
}
b <<= 1
}
return bs
}
// ByteToBinaryString get the string in binary format of a byte or uint8.
func ByteToBinaryString(b byte) string {
buf := make([]byte, 0, 8)
buf = appendBinaryString(buf, b)
return string(buf)
}
// BytesToBinaryString get the string in binary format of a []byte or []int8.
func BytesToBinaryString(bs []byte) string {
l := len(bs)
bl := l*8 + l + 1
buf := make([]byte, 0, bl)
buf = append(buf, lsb)
for _, b := range bs {
buf = appendBinaryString(buf, b)
buf = append(buf, space)
}
buf[bl-1] = rsb
return string(buf)
}
// regex for delete useless string which is going to be in binary format.
var rbDel = regexp.MustCompile(`[^01]`)
// BinaryStringToBytes get the binary bytes according to the
// input string which is in binary format.
func BinaryStringToBytes(s string) (bs []byte) {
if len(s) == 0 {
panic(ErrEmptyString)
}
s = rbDel.ReplaceAllString(s, "")
l := len(s)
if l == 0 {
panic(ErrBadStringFormat)
}
mo := l % 8
l /= 8
if mo != 0 {
l++
}
bs = make([]byte, 0, l)
mo = 8 - mo
var n uint8
for i, b := range []byte(s) {
m := (i + mo) % 8
switch b {
case one:
n += uint8arr[m]
}
if m == 7 {
bs = append(bs, n)
n = 0
}
}
return
}上述內容就是使用go語言怎么對BMP文件頭進行讀取,你們學到知識或技能了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或者豐富自己的知識儲備,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。