您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
訪問路徑是指Oracle找到用戶需要的數據的方法,這些方法很少,包括:
聲名狼藉的全表掃描--人們不惜一切視圖避免的(曲解的)訪問路徑。
各種類型的索引掃描--這是人們感覺良好的訪問路徑(多數情況下是被曲解的)。
通過hash或者rowid的方式直接訪問,通常對于單數據行來說,是最快的。
并沒有一種訪問路徑是最好的,如果有,那么Oracle只需提供這一種訪問路徑就好了。
全表掃描
全掃描就是順序的讀取表中的所有數據塊。采用多塊讀的方式,從頭開始掃描表中的塊,直到高水位線。全掃描是處理大數據量行之有效的方法。需要牢記:全掃描并不邪惡,多數情況下全掃描是獲得結果的最快方法。
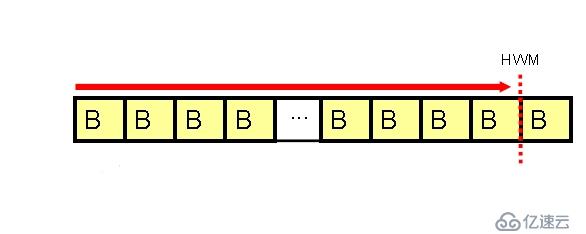
全掃描每次讀取的塊數由參數db_file_multiblock_read_count指定
SQL> show parameter db_file_mu NAME TYPE VALUE ------------------------------------ --------------------------------- ------------------------------ db_file_multiblock_read_count integer 128
2.rowid 訪問
rowid是一行數據的物理位置,訪問單行數據的速度是最快的。
SQL> select * from emp where rowid ='AAASZHAAEAAAACXAAN'; 7934 MILLER CLERK 7782 1982/01/23 00:00:00 1300 10
通過索引的方式訪問數據,其實也是通過索引,先找到這行數據的rowid,然后再通過rowid訪問數據。
SQL> set autotrace on traceonly SQL> select * from emp where empno=7934; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 2949544139 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 2 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | PK_EMP | 1 | | 0 (0)| 00:00:01 | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
rowid還可以進行范圍掃描。
SQL> select * from emp where rowid between 'AAASZHAAEAAAACXAAA' and 'AAASZHAAEAAAACXAAN'; 7369 SMITH CLERK 7902 1980/12/17 00:00:00 800 20 7499 ALLEN SALESMAN 7698 1981/02/20 00:00:00 1600 300 30 7521 WARD SALESMAN 7698 1981/02/22 00:00:00 1250 500 30 7566 JONES MANAGER 7839 1981/04/02 00:00:00 2975 20 7654 MARTIN SALESMAN 7698 1981/09/28 00:00:00 1250 1400 30 7698 BLAKE MANAGER 7839 1981/05/01 00:00:00 2850 30 7782 CLARK MANAGER 7839 1981/06/09 00:00:00 2450 10 7788 SCOTT ANALYST 7566 1987/04/19 00:00:00 3000 20 7839 KING PRESIDENT 1981/11/17 00:00:00 5000 10 7844 TURNER SALESMAN 7698 1981/09/08 00:00:00 1500 0 30 7876 ADAMS CLERK 7788 1987/05/23 00:00:00 1100 20 7900 JAMES CLERK 7698 1981/12/03 00:00:00 950 30 7902 FORD ANALYST 7566 1981/12/03 00:00:00 3000 20 7934 MILLER CLERK 7782 1982/01/23 00:00:00 1300 10 14 rows selected.
3. 索引掃描
索引掃描是最常見的數據訪問之一,例如
SQL> set autotrace on traceonly SQL> select * from emp where empno=7934; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 2949544139 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 2 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | PK_EMP | 1 | | 0 (0)| 00:00:01 | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
我們下面主要以b-tree索引為例
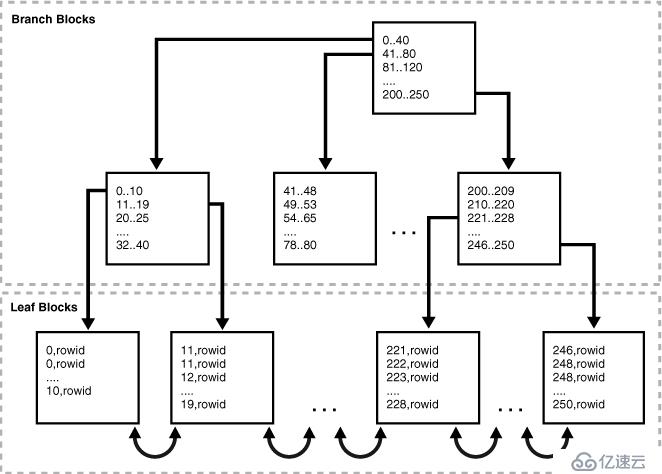
索引唯一性掃描
優化器知道索引列的值是唯一的,查詢結果只返回一行。這種索引的訪問速度最快,找到一行數據就不再繼續掃描索引,直接返回。
SQL> select * from emp where empno=7934; 7934 MILLER CLERK 7782 1982/01/23 00:00:00 1300 10 Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 2949544139 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 2 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | PK_EMP | 1 | | 0 (0)| 00:00:01 | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
實際上Oracle中并沒有非唯一索引,在非唯一索引中,Oracle將數據的rowid添加到索引鍵中使其唯一。
索引范圍掃描
SQL> set autot traceonly SQL> select empno from emp where empno<5000; no rows selected Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 1567865628 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 4 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | |* 1 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| PK_EMP | 1 | 4 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
有取的是,索引可以按照兩個方向去掃描索引
SQL> select empno from emp where empno<5000 order by empno;
no rows selected
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1567865628
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 4 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| PK_EMP | 1 | 4 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - access("EMPNO"<5000)
SQL> select empno from emp where empno<5000 order by empno desc;
no rows selected
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2474278666
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 4 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | INDEX RANGE SCAN DESCENDING| PK_EMP | 1 | 4 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------這個的好處是避免排序操作
如果你建立的是非唯一索引,即便你使用=查詢,也是范圍掃描
SQL> create index ind_emp_ename on emp(ename);
Index created.
SQL> select * from emp where ename='KING';
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2929622481
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 38 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 38 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IND_EMP_ENAME | 1 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("ENAME"='KING')索引全掃描
SQL> select empno from emp; 14 rows selected. Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 179099197 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 14 | 56 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | INDEX FULL SCAN | PK_EMP | 14 | 56 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
索引全掃描,并不是掃描全部的索引。它實際上只需掃描索引的葉子節點。但是為了找到葉子節點的位置,也會掃描部分的分支節點。
我們看如下查詢
SQL> select empno,ename from emp; 14 rows selected. Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 3956160932 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 14 | 140 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMP | 14 | 140 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 | --------------------------------------------------------------------------
查詢列ename并不在索引中,所以走的是全表掃描。但是如果我們將語句做如下修改。
SQL> select empno,ename from emp order by empno; 14 rows selected. Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 4170700152 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 14 | 140 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 14 | 140 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 2 | INDEX FULL SCAN | PK_EMP | 14 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Oracle為了避免排序操作,而使用了索引全掃描。因為索引是有序的數據,并且索引全掃描是按順序的單塊讀操作。
max和min
SQL> select max(empno) from emp; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 1707959928 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 4 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | SORT AGGREGATE | | 1 | 4 | | | | 2 | INDEX FULL SCAN (MIN/MAX)| PK_EMP | 1 | 4 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
該掃描使用了索引全掃描,但其實并非真正的全掃描,max和min限定詞使得Oracle知道何時停止,它只是掃描最高塊或者最低塊。
索引跳躍掃描
通常要使用索引,索引的前置列一定要出現在查詢條件中。
SQL> create table t(a int,b int ,c int,d int,e int,f int,g int); SQL> create index t_idx on t(a,b,c);
通常情況下只有如下的查詢才會使用索引
select * from t where a =:a; select * from t where a =:a and b =:b; select * from t where a =:a and b =:b and c =:c;
但是如下查詢不會使用索引(除了使用hint強制索引全掃描)
select * from t where b =:b; select * from t where c =:c; select * from t where b =:b and c =:c;
Oracle 9i后實現了跳躍索引掃描,條件如下:
謂詞中使用了索引中其他的列。
前置列值的DISTINCT_NUM比較少。
我們看看如下示例
SQL> create table t as
2 select mod(rownum,3) a,rownum b,rownum c,object_name d
3 from all_objects;
Table created.
SQL> create index t_idx on t(a,b,c);
Index created.
SQL> analyze table t compute statistics;
Table analyzed.
SQL> select * from t where b=1 and c=1;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2053318169
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 34 | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T | 1 | 34 | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX SKIP SCAN | T_IDX | 1 | | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("B"=1 AND "C"=1)
filter("B"=1 AND "C"=1)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
8 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
724 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
523 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
2 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1 rows processed因為a的值比較少,只有3個,Oracle把索引(a,b,c) 看成3個小索引 。
索引快速全掃描
索引快速全掃描與索引全掃描明顯的不同,它有如下特征
它讀取索引中的每個塊,包括所有分支塊。
它采用多塊讀,像全表掃描一樣。
它不按排序順序掃描索引。
我們先建立一個表,并插入大量數據。
SQL> create table big_table as select * from dba_objects; Table created. SQL> insert into big_table select * from big_table; 74577 rows created. SQL> insert into big_table select * from big_table; 223731 rows created. SQL> / 447462 rows created. SQL> commit; Commit complete. SQL> alter table big_table modify object_id not null; Table altered. SQL> create index idx_big_table_objid on big_table(object_id); Index created. SQL> analyze table big_table compute statistics; Table analyzed.
執行如下查詢
SQL> set autot traceonly SQL> select object_id from big_table; 894924 rows selected. Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 205523069 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 894K| 3495K| 544 (2)| 00:00:07 | | 1 | INDEX FAST FULL SCAN| IDX_BIG_TABLE_OBJID | 894K| 3495K| 544 (2)| 00:00:07 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Statistics ---------------------------------------------------------- 15 recursive calls 0 db block gets 61534 consistent gets 2 physical reads 0 redo size 15755358 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client 656794 bytes received via SQL*Net from client 59663 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client 0 sorts (memory) 0 sorts (disk) 894924 rows processed
查詢使用的是索引快速全掃描。
有心的人可以思考一下,如下查詢為啥沒有使用索引快速全掃描,而使用了索引全掃描。
SQL> select empno from emp; 14 rows selected. Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 179099197 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 14 | 56 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | INDEX FULL SCAN | PK_EMP | 14 | 56 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Statistics ---------------------------------------------------------- 0 recursive calls 0 db block gets 2 consistent gets 0 physical reads 0 redo size 686 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client 523 bytes received via SQL*Net from client 2 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client 0 sorts (memory) 0 sorts (disk) 14 rows processed
索引連接
索引連接(index join)是在表中存在多個索引時針對某個查詢所選中的索引路徑。
我們看如下例子
SQL> create table t1 as select * from dba_objects;
Table created.
SQL> create index t1_idx1 on t1(object_id);
Index created.
SQL> create index t1_idx2 on t1(owner,object_type);
Index created.
SQL> analyze table t1 compute statistics;
Table analyzed.
SQL> set autot traceonly
SQL> select object_id,owner,object_type from t1
2 where object_id between 100 and 2000
3 and owner='SYS';
1478 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2563395799
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 69 | 1173 | 18 (6)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | VIEW | index$_join$_001 | 69 | 1173 | 18 (6)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | HASH JOIN | | | | | |
|* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| T1_IDX1 | 69 | 1173 | 7 (15)| 00:00:01 |
|* 4 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| T1_IDX2 | 69 | 1173 | 12 (9)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter("OBJECT_ID"<=2000 AND "OWNER"='SYS' AND "OBJECT_ID">=100)
2 - access(ROWID=ROWID)
3 - access("OBJECT_ID">=100 AND "OBJECT_ID"<=2000)
4 - access("OWNER"='SYS')
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
215 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
32014 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
1601 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
100 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1478 rows processed優化器通過掃描T1_IDX1,T1_IDX2得到結果集,用兩個結果集的rowid進行join運算,得到返回集。
這樣避免掃描表。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。