您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有關利用vue如何實現一個云標簽效果,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結了以下內容,希望大家根據這篇文章可以有所收獲。
標簽初始化
這里實現的核心主要是參考了前面的那篇解析3D標簽云的文章,作者給出了源碼,講解也比較通俗易懂。大體來說,整個代碼分三步:
貼上代碼:
<div id='app' >
<svg :width='width' :height='height' @mousemove='listener($event)'>
<a :href="tag.href" rel="external nofollow" v-for='tag in tags'>
<text :x='tag.x' :y='tag.y' :font-size='20 * (600/(600-tag.z))' :fill-opacity='((400+tag.z)/600)'>{{tag.text}}</text>
</a>
</svg>
</div>在模板中,借用指令v-for來渲染標簽,每個標簽上綁定了x,y,font-size(用來表現z軸),fill-opacity(都是與z坐標有關的表達式,用來表現z軸),及text;
data: {
width:700,//svg寬度
height:700,//svg高度
tagsNum:20,//標簽數量
RADIUS:200,//球的半徑
speedX:Math.PI/360,//球一幀繞x軸旋轉的角度
speedY:Math.PI/360,//球-幀繞y軸旋轉的角度
tags: []
}
computed:{
CX(){//球心x坐標
return this.width/2;
},
CY(){//球心y坐標
return this.height/2;
}
},做好了上面的基礎,下面我們來初始化標簽數據:
created(){//初始化標簽位置
let tags=[];
for(let i = 0; i < this.tagsNum; i++){
let tag = {};
let k = -1 + (2 * (i + 1) - 1) / this.tagsNum;
let a = Math.acos(k);
let b = a * Math.sqrt(this.tagsNum * Math.PI)//計算標簽相對于球心的角度
tag.text = i + 'tag';
tag.x = this.CX + this.RADIUS * Math.sin(a) * Math.cos(b);//根據標簽角度求出標簽的x,y,z坐標
tag.y = this.CY + this.RADIUS * Math.sin(a) * Math.sin(b);
tag.z = this.RADIUS * Math.cos(a);
tag.href = 'https://imgss.github.io';//給標簽添加鏈接
tags.push(tag);
}
this.tags = tags;//讓vue替我們完成視圖更新
},到了這里,我們就算了算坐標,vue完成了視圖更新的工作,這時基本上就可以得到一副靜態的圖像了:
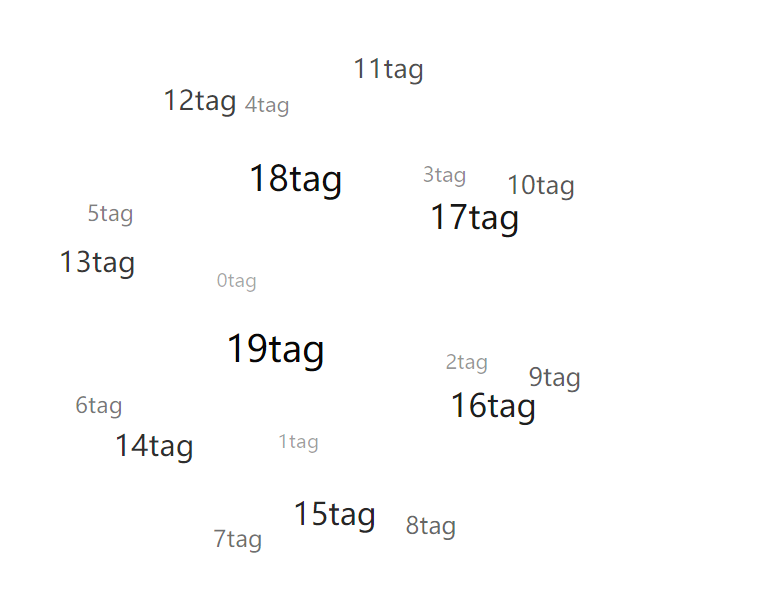
下面就是通過改變每一個tag的x,y的值來使球旋轉起來;實現方法是rotateX,rotateY函數:
rotateX(angleX){
var cos = Math.cos(angleX);
var sin = Math.sin(angleX);
for(let tag of this.tags){
var y1 = (tag.y- this.CY) * cos - tag.z * sin + this.CY;
var z1 = tag.z * cos + (tag.y- this.CY) * sin;
tag.y = y1;
tag.z = z1;
}
},
rotateY(angleY){
var cos = Math.cos(angleY);
var sin = Math.sin(angleY);
for(let tag of this.tags){
var x1 = (tag.x - this.CX) * cos - tag.z * sin + this.CX;
var z1 = tag.z * cos + (tag.x - this.CX) * sin;
tag.x = x1;
tag.z = z1;
}
},這兩個函數就是根據標簽原來的坐標和球旋轉的角度算出新的坐標,最后在mounted鉤子下面,寫一個animate函數,不斷調用這兩個函數,實現旋轉動畫
mounted(){//使球開始旋轉
setInterval(() => {
this.rotateX(this.speedX);
this.rotateY(this.speedY);
}, 17)
},全部代碼如下:
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
width:700,
height:700,
tagsNum:20,
RADIUS:200,
speedX:Math.PI/360,
speedY:Math.PI/360,
tags: []
},
computed:{
CX(){
return this.width/2;
},
CY(){
return this.height/2;
}
},
created(){//初始化標簽位置
let tags=[];
for(let i = 0; i < this.tagsNum; i++){
let tag = {};
let k = -1 + (2 * (i + 1) - 1) / this.tagsNum;
let a = Math.acos(k);
let b = a * Math.sqrt(this.tagsNum * Math.PI);
tag.text = i + 'tag';
tag.x = this.CX + this.RADIUS * Math.sin(a) * Math.cos(b);
tag.y = this.CY + this.RADIUS * Math.sin(a) * Math.sin(b);
tag.z = this.RADIUS * Math.cos(a);
tag.href = 'https://imgss.github.io';
tags.push(tag);
}
this.tags = tags;
},
mounted(){//使球開始旋轉
setInterval(() => {
this.rotateX(this.speedX);
this.rotateY(this.speedY);
}, 17)
},
methods: {
rotateX(angleX){
var cos = Math.cos(angleX);
var sin = Math.sin(angleX);
for(let tag of this.tags){
var y1 = (tag.y- this.CY) * cos - tag.z * sin + this.CY;
var z1 = tag.z * cos + (tag.y- this.CY) * sin;
tag.y = y1;
tag.z = z1;
}
},
rotateY(angleY){
var cos = Math.cos(angleY);
var sin = Math.sin(angleY);
for(let tag of this.tags){
var x1 = (tag.x - this.CX) * cos - tag.z * sin + this.CX;
var z1 = tag.z * cos + (tag.x-this.CX) * sin;
tag.x = x1;
tag.z = z1;
}
},
listener(event){//響應鼠標移動
var x = event.clientX - this.CX;
var y = event.clientY - this.CY;
this.speedX = x*0.0001>0 ? Math.min(this.RADIUS*0.00002, x*0.0001) : Math.max(-this.RADIUS*0.00002, x*0.0001);
this.speedY = y*0.0001>0 ? Math.min(this.RADIUS*0.00002, y*0.0001) : Math.max(-this.RADIUS*0.00002, y*0.0001);
}
}
})
</script>完整demo
vue
no vue
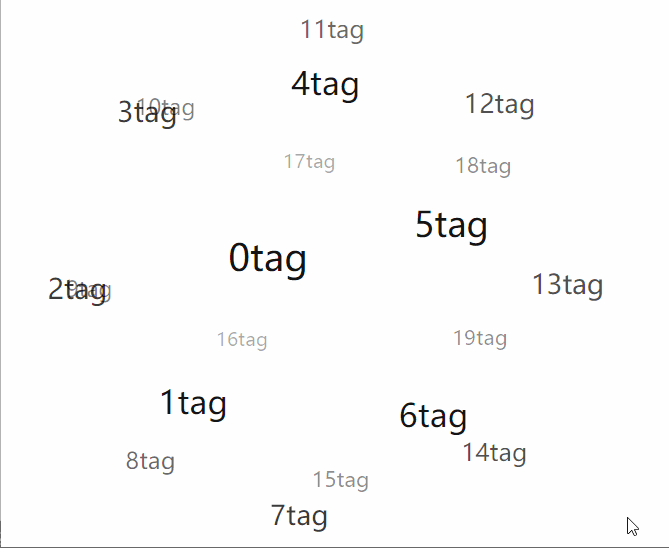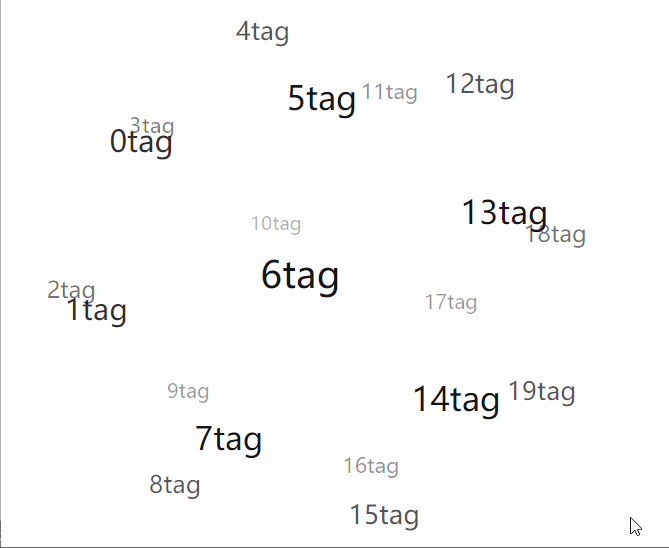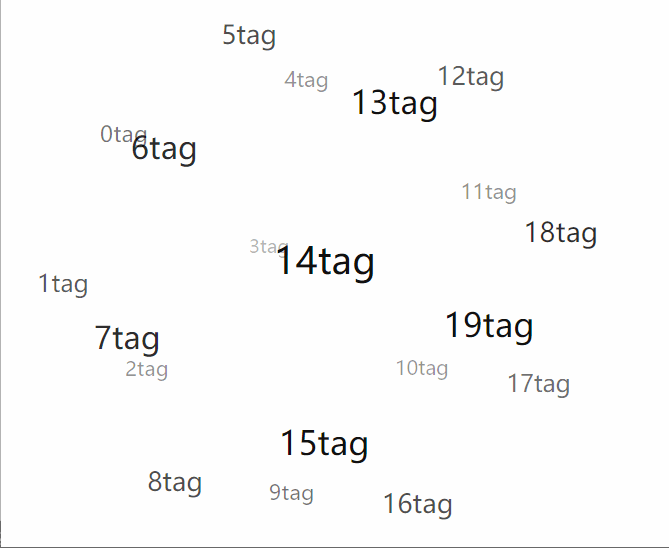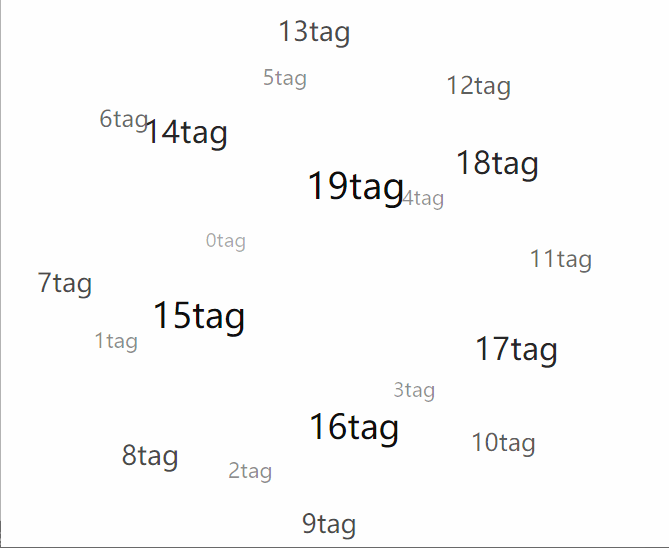
總結
vue的數據綁定可以減少我們對dom的操作,而將關注點放在邏輯上面,vue構造函數提供的幾個選項可以幫助我們更好的組織代碼
看完上述內容,你們對利用vue如何實現一個云標簽效果有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。