您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了python線程間通信是如何實現的,具有一定借鑒價值,需要的朋友可以參考下。希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后大有收獲。下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
線程間通信的幾種實現方式
首先,要短信線程間通信的模型有兩種:共享內存和消息傳遞,以下方式都是基本這兩種模型來實現的。我們來基本一道面試常見的題目來分析:
題目:有兩個線程A、B,A線程向一個集合里面依次添加元素"abc"字符串,一共添加十次,當添加到第五次的時候,希望B線程能夠收到A線程的通知,然后B線程執行相關的業務操作。
方式一:使用volatile關鍵字
基于 volatile 關鍵字來實現線程間相互通信是使用共享內存的思想,大致意思就是多個線程同時監聽一個變量,當這個變量發生變化的時候 ,線程能夠感知并執行相應的業務。這也是最簡單的一種實現方式。
public class TestSync {
// 定義一個共享變量來實現通信,它需要是volatile修飾,否則線程不能及時感知
static volatile boolean notice = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 實現線程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("線程A向list中添加一個元素,此時list中的元素個數為:"+list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
notice = true;
}
});
// 實現線程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (notice) {
System.out.println("線程B收到通知,開始執行自己的業務...");
break;
}
}
});
// 需要先啟動線程B
threadB.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 再啟動線程A
threadA.start();
}
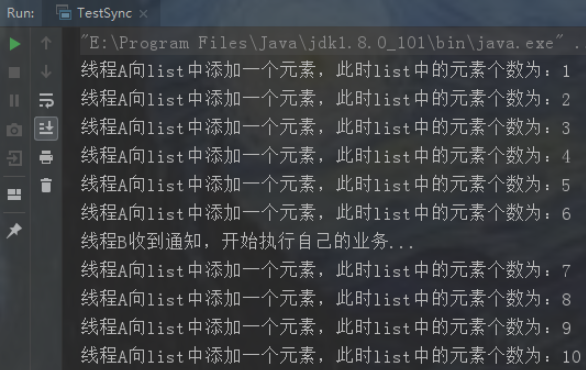
}運行結果為:
方式二:使用Object類的wait()和notify()方法
眾所周知,Object類提供了線程間通信的方法:wait()、notify()、notifyaAl(),它們是多線程通信的基礎,而這種實現方式的思想自然是線程間通信。
注意: wait和 notify必須配合synchronized使用,wait方法釋放鎖,notify方法不釋放鎖。
public class TestSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定義一個鎖對象
Object lock = new Object();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 實現線程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("線程A向list中添加一個元素,此時list中的元素個數為:"+
list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
lock.notify();// 喚醒B線程
}
}
});
// 實現線程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (list.size() != 5) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("線程B收到通知,開始執行自己的業務...");
}
}
});
// 需要先啟動線程B
threadB.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 再啟動線程A
threadA.start();
}
}運行結果為:

由打印結果截圖可知,在線程A發出notify()喚醒通知之后,依然是走完了自己線程的業務之后,線程B才開始執行,這也正好說明了,notify()方法不釋放鎖,而wait()方法釋放鎖。
方式三:使用JUC工具類 CountDownLatch
jdk1.5之后在java.util.concurrent包下提供了很多并發編程相關的工具類,簡化了我們的并發編程代碼的書寫,***CountDownLatch***基于AQS框架,相當于也是維護了一個線程間共享變量state。
public class TestSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 實現線程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("線程A向list中添加一個元素,此時list中的元素個數為:"+list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
});
// 實現線程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (list.size() != 5) {
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("線程B收到通知,開始執行自己的業務...");
break;
}
});
// 需要先啟動線程B
threadB.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 再啟動線程A
threadA.start();
}
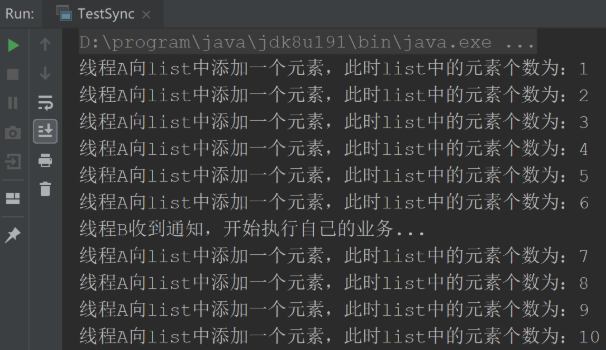
}運行結果為:
方法四:使用ReentrantLock結合Condition
public class TestSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 實現線程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("線程A向list中添加一個元素,此時list中的元素個數為:"+list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
condition.signal();
}
lock.unlock();
});
// 實現線程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
if (list.size() != 5) {
try {
condition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("線程B收到通知,開始執行自己的業務...");
lock.unlock();
});
threadB.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
threadA.start();
}
}運行結果為:
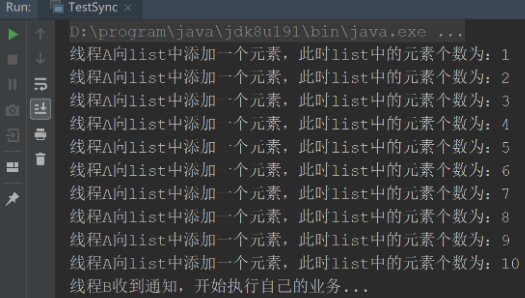
顯然這種方式使用起來并不是很好,代碼編寫復雜,而且線程B在被A喚醒之后由于沒有獲取鎖還是不能立即執行,也就是說,A在喚醒操作之后,并不釋放鎖。這種方法跟 Object 的 wait() 和 notify() 一樣。
方式五:基于LockSupport實現線程間的阻塞和喚醒
LockSupport 是一種非常靈活的實現線程間阻塞和喚醒的工具,使用它不用關注是等待線程先進行還是喚醒線程先運行,但是得知道線程的名字。
public class TestSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 實現線程B
final Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
if (list.size() != 5) {
LockSupport.park();
}
System.out.println("線程B收到通知,開始執行自己的業務...");
});
// 實現線程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("線程A向list中添加一個元素,此時list中的元素個數為:"+list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
LockSupport.unpark(threadB);
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
}
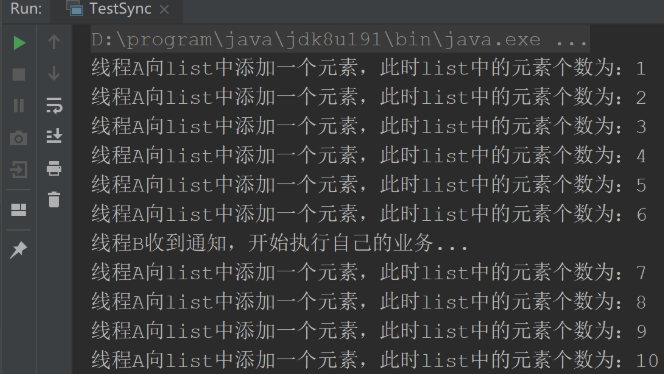
}運行結果:
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享python線程間通信是如何實現的內容對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,遇到問題就找億速云,詳細的解決方法等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。