您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這期內容當中小編將會給大家帶來有關怎么在Android中實現雙進程守護,文章內容豐富且以專業的角度為大家分析和敘述,閱讀完這篇文章希望大家可以有所收獲。
雙進程守護
雙進程守護的思想就是,兩個進程共同運行,如果有其中一個進程被殺,那么另一個進程就會將被殺的進程重新拉起,相互保護,在一定的意義上,維持進程的不斷運行。
雙進程守護的兩個進程,一個進程用于我們所需的后臺操作,且叫它本地進程,另一個進程只負責監聽著本地進程的狀態,在本地進程被殺的時候拉起,于此同時本地進程也在監聽著這個進程,準備在它被殺時拉起,我們將這個進程稱為遠端進程。
由于在 Android 中,兩個進程之間無法直接交互,所以我們這里還要用到 AIDL (Android interface definition Language ),進行兩個進程間的交互。
代碼實現
先來看一下demo代碼結構,結構很簡單,我這里創建了一個 Activity 作為界面,以及兩個 Service ,一個是后臺操作的 本地Service,另一個是守護進程的 遠端Service,還有一個 AIDL文件用作進程間交互用。
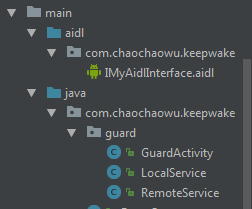
項目結構
Activity 的定義很簡單,就幾個按鈕,控制 Service 的狀態,我這邊定義了三個按鈕,一個是開啟后臺服務,另外兩個分別是關閉本地Service和遠端的Service。
/**
* @author chaochaowu
*/
public class GuardActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@BindView(R.id.button)
Button button;
@BindView(R.id.button2)
Button button2;
@BindView(R.id.button3)
Button button3;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
getSupportActionBar().hide();
setContentView(R.layout.activity_guard);
ButterKnife.bind(this);
}
@OnClick({R.id.button, R.id.button2, R.id.button3})
public void onViewClicked(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.button:
startService(new Intent(this, LocalService.class));
break;
case R.id.button2:
stopService(new Intent(this, LocalService.class));
break;
case R.id.button3:
stopService(new Intent(this, RemoteService.class));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}可以看一下界面。
主界面
AIDL文件可以根據業務需要添加接口。
/**
* @author chaochaowu
*/
interface IMyAidlInterface {
String getServiceName();
}重點是在兩個 Service 上。
在定義Service時,需要在 AndroidManifest 中聲明一下 遠端Service 的 process 屬性,保證 本地Service 和 遠端Service 兩者跑在不同的進程上,如果跑在同一個進程上,該進程被殺,那就什么都沒了,就沒有了雙進程守護的說法了。
<service android:name=".guard.LocalService" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true" /> <service android:name=".guard.RemoteService" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true" android:process=":RemoteProcess"/>
先來看 LocalService 的代碼,重點關注 onStartCommand 方法 和 ServiceConnection 中重寫的方法。onStartCommand 方法是在 Service 啟動后被調用,在 LocalService 被啟動后,我們將 RemoteService 進行了啟動,并將 LocalService 和 RemoteService 兩者綁定了起來(因為遠端Service 對于用戶來說是不可見的,相對于我們實際工作的進程也是獨立的,它的作用僅僅是守護線程,所以說 RemoteService 僅與 LocalService 有關系,應該只能由 LocalService 將它啟動)。
啟動并綁定之后,我們需要重寫 ServiceConnection 中的方法,監聽兩者之間的綁定關系,關鍵的是對兩者綁定關系斷開時的監聽。
當其中一個進程被殺掉時,兩者的綁定關系就會被斷開,觸發方法 onServiceDisconnected ,所以,我們要在斷開時,進行進程拉起的操作,重寫 onServiceDisconnected 方法,在方法中將另外一個 Service 重新啟動,并將兩者重新綁定。
/**
* @author chaochaowu
*/
public class LocalService extends Service {
private MyBinder mBinder;
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
IMyAidlInterface iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
Log.i("LocalService", "connected with " + iMyAidlInterface.getServiceName());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Toast.makeText(LocalService.this,"鏈接斷開,重新啟動 RemoteService",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
startService(new Intent(LocalService.this,RemoteService.class));
bindService(new Intent(LocalService.this,RemoteService.class),connection, Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);
}
};
public LocalService() {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Toast.makeText(this,"LocalService 啟動",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
startService(new Intent(LocalService.this,RemoteService.class));
bindService(new Intent(this,RemoteService.class),connection, Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
mBinder = new MyBinder();
return mBinder;
}
private class MyBinder extends IMyAidlInterface.Stub{
@Override
public String getServiceName() throws RemoteException {
return LocalService.class.getName();
}
}
}在另外一個 RemoteService 中也一樣,在與 LocalService 斷開鏈接的時候,由于監聽到綁定的斷開,說明 RemoteService 還存活著,LocalService 被殺進程,所以要將 LocalService 進行拉起,并重新綁定。方法寫在 onServiceDisconnected 中。
/**
* @author chaochaowu
*/
public class RemoteService extends Service {
private MyBinder mBinder;
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
IMyAidlInterface iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
Log.i("RemoteService", "connected with " + iMyAidlInterface.getServiceName());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Toast.makeText(RemoteService.this,"鏈接斷開,重新啟動 LocalService",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
startService(new Intent(RemoteService.this,LocalService.class));
bindService(new Intent(RemoteService.this,LocalService.class),connection, Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);
}
};
public RemoteService() {
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Toast.makeText(this,"RemoteService 啟動",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
bindService(new Intent(this,LocalService.class),connection,Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
mBinder = new MyBinder();
return mBinder;
}
private class MyBinder extends IMyAidlInterface.Stub{
@Override
public String getServiceName() throws RemoteException {
return RemoteService.class.getName();
}
}
}Android是一種基于Linux內核的自由及開放源代碼的操作系統,主要使用于移動設備,如智能手機和平板電腦,由美國Google公司和開放手機聯盟領導及開發。
上述就是小編為大家分享的怎么在Android中實現雙進程守護了,如果剛好有類似的疑惑,不妨參照上述分析進行理解。如果想知道更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。