您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要為大家展示了“iOS中程序異常Crash友好化處理的示例分析”,內容簡而易懂,條理清晰,希望能夠幫助大家解決疑惑,下面讓小編帶領大家一起研究并學習一下“iOS中程序異常Crash友好化處理的示例分析”這篇文章吧。
實現效果如圖:
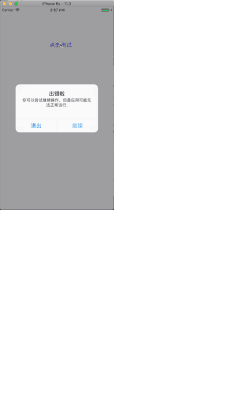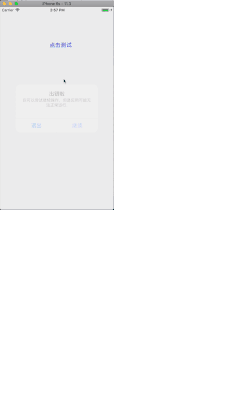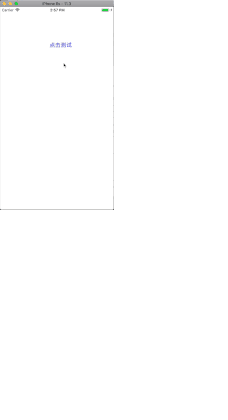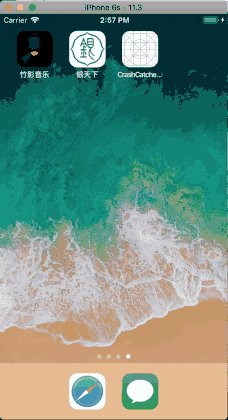
效果實現:
用法:
1.將截圖的中CatchedHelper文件夾拖到你的項目工程中。
2.在AppDelegate.m中找到以下方法并如下添加代碼:
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
[UncaughtExceptionHandler installUncaughtExceptionHandler:YES showAlert:YES];
return YES;
}以上代碼就可以實現稍微友好一點的crash攔截處理。
代碼解釋:
UncaughtExceptionHandler.h主要代碼:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface UncaughtExceptionHandler : NSObject /*! * 異常的處理方法 * * @param install 是否開啟捕獲異常 * @param showAlert 是否在發生異常時彈出alertView */ + (void)installUncaughtExceptionHandler:(BOOL)install showAlert:(BOOL)showAlert; @end
UncaughtExceptionHandler.m文件主要的代碼如下:
1.發送異常信號
/*
* 異常的處理方法
*
* @param install 是否開啟捕獲異常
* @param showAlert 是否在發生異常時彈出alertView
*/
+ (void)installUncaughtExceptionHandler:(BOOL)install showAlert:(BOOL)showAlert {
if (install && showAlert) {
[[self alloc] alertView:showAlert];
}
NSSetUncaughtExceptionHandler(install ? HandleException : NULL);
signal(SIGABRT, install ? SignalHandler : SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGILL, install ? SignalHandler : SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGSEGV, install ? SignalHandler : SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGFPE, install ? SignalHandler : SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGBUS, install ? SignalHandler : SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGPIPE, install ? SignalHandler : SIG_DFL);
}產生上述的signal的時候就會調用我們定義的SignalHandler來處理異常。
ps: NSSetUncaughtExceptionHandler就是iOS SDK中提供的一個現成的函數,用來捕獲異常的方法,使用方便。但它不能捕獲拋出的signal,所以定義了SignalHandler方法。
2.處理異常
void HandleException(NSException *exception) {
int32_t exceptionCount = OSAtomicIncrement32(&UncaughtExceptionCount);
// 如果太多不用處理
if (exceptionCount > UncaughtExceptionMaximum) {
return;
}
//獲取調用堆棧
NSArray *callStack = [exception callStackSymbols];
NSMutableDictionary *userInfo = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithDictionary:[exception userInfo]];
[userInfo setObject:callStack forKey:UncaughtExceptionHandlerAddressesKey];
//在主線程中,執行制定的方法, withObject是執行方法傳入的參數
[[[UncaughtExceptionHandler alloc] init]
performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(handleException:)
withObject:
[NSException exceptionWithName:[exception name]
reason:[exception reason]
userInfo:userInfo]
waitUntilDone:YES];
}該方法就是對應NSSetUncaughtExceptionHandler的處理,只要方法關聯到這個函數,那么發生相應錯誤時會自動調用該函數,調用時會傳入exception參數。獲取異常后會將捕獲的異常傳入最終調用處理的handleException函數。
3.無法捕獲的signal處理
//處理signal報錯
void SignalHandler(int signal) {
int32_t exceptionCount = OSAtomicIncrement32(&UncaughtExceptionCount);
// 如果太多不用處理
if (exceptionCount > UncaughtExceptionMaximum) {
return;
}
NSString* description = nil;
switch (signal) {
case SIGABRT:
description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Signal SIGABRT was raised!\n"];
break;
case SIGILL:
description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Signal SIGILL was raised!\n"];
break;
case SIGSEGV:
description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Signal SIGSEGV was raised!\n"];
break;
case SIGFPE:
description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Signal SIGFPE was raised!\n"];
break;
case SIGBUS:
description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Signal SIGBUS was raised!\n"];
break;
case SIGPIPE:
description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Signal SIGPIPE was raised!\n"];
break;
default:
description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Signal %d was raised!",signal];
}
NSMutableDictionary *userInfo = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
NSArray *callStack = [UncaughtExceptionHandler backtrace];
[userInfo setObject:callStack forKey:UncaughtExceptionHandlerAddressesKey];
[userInfo setObject:[NSNumber numberWithInt:signal] forKey:UncaughtExceptionHandlerSignalKey];
//在主線程中,執行指定的方法, withObject是執行方法傳入的參數
[[[UncaughtExceptionHandler alloc] init]
performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(handleException:)
withObject:
[NSException exceptionWithName:UncaughtExceptionHandlerSignalExceptionName
reason: description
userInfo: userInfo]
waitUntilDone:YES];
}以上方法是對于捕獲不到的signal信號進行處理,列出常見的異常類型。
4.堆棧調用
//獲取調用堆棧
+ (NSArray *)backtrace {
//指針列表
void* callstack[128];
//backtrace用來獲取當前線程的調用堆棧,獲取的信息存放在這里的callstack中
//128用來指定當前的buffer中可以保存多少個void*元素
//返回值是實際獲取的指針個數
int frames = backtrace(callstack, 128);
//backtrace_symbols將從backtrace函數獲取的信息轉化為一個字符串數組
//返回一個指向字符串數組的指針
//每個字符串包含了一個相對于callstack中對應元素的可打印信息,包括函數名、偏移地址、實際返回地址
char **strs = backtrace_symbols(callstack, frames);
int i;
NSMutableArray *backtrace = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:frames];
for (i = 0; i < frames; i++) {
[backtrace addObject:[NSString stringWithUTF8String:strs[i]]];
}
free(strs);
return backtrace;
}backtrace是Linux下用來追蹤函數調用堆棧以及定位段錯誤的函數。
5.使用UIAlerView進行友好化提示
- (void)handleException:(NSException *)exception {
[self validateAndSaveCriticalApplicationData:exception];
if (!showAlertView) {
return;
}
#pragma clang diagnostic push
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated-declarations"
UIAlertView *alert =
[[UIAlertView alloc]
initWithTitle:@"出錯啦"
message:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"你可以嘗試繼續操作,但是應用可能無法正常運行.\n"]
delegate:self
cancelButtonTitle:@"退出"
otherButtonTitles:@"繼續", nil];
[alert show];
#pragma clang diagnostic pop
CFRunLoopRef runLoop = CFRunLoopGetCurrent();
CFArrayRef allModes = CFRunLoopCopyAllModes(runLoop);
while (!self.dismissed) {
//點擊繼續
for (NSString *mode in (__bridge NSArray *)allModes) {
//快速切換Mode
CFRunLoopRunInMode((CFStringRef)mode, 0.001, false);
}
}
//點擊退出
CFRelease(allModes);
NSSetUncaughtExceptionHandler(NULL);
signal(SIGABRT, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGILL, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGSEGV, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGFPE, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGBUS, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_DFL);
if ([[exception name] isEqual:UncaughtExceptionHandlerSignalExceptionName]) {
kill(getpid(), [[[exception userInfo] objectForKey:UncaughtExceptionHandlerSignalKey] intValue]);
} else {
[exception raise];
}
}以上是“iOS中程序異常Crash友好化處理的示例分析”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。