您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
對于剛入手thinkjs項目的新手來說,時常會犯的一個錯誤就是“混用”各種代碼邏輯,比如:我們經常在做后臺管理系統的時候用到的登錄框,
其實它原本是有一個路由專門存放自己的代碼邏輯,而在點擊提交按鈕的時候,要達到的效果便是賬號密碼正確的時候,正常跳轉頁面,而錯誤的時候給出提示;為了發現問題,就先把源代碼貼出來吧:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>用戶登錄</title>
</head>
<style>
*{ margin:0px; padding:0px; list-style:none;}
body,html{ height:100%;font:12px/1.5 \5FAE\8F6F\96C5\9ED1,tahoma,arial,sans-serif;}
html{ background:url(/static/img/bg.gif) repeat-x;}
body{ background:url(/static/img/ftbg.png) 0 bottom repeat-x;}
.main{ background:url(/static/img/mbg.png) no-repeat center bottom;position: absolute;width:100%;height:500px;top:50%;
margin-left:0;margin-top:-290px; z-index:99}
.loginbox{ width:410px; height:375px;background:url(/static/img/borderbg.png); position: absolute; left:50%; top:50%; margin-left:-200px; margin-top:-200px; border-radius:8px;-moz-border-radius: 8px; -webkit-border-radius:8px; z-index:999;}
.loginbg{ width:310px;padding:40px; margin:0 auto; margin-top:10px; background-color:#fff; border-radius:8px;-moz-border-radius: 8px; -webkit-border-radius:8px;}
.loginbox h4{ font-size:18px; font-weight:normal; color:#333; padding-bottom:15px; text-align:center;}
.loginbox input{ width:260px; height:46px; border:1px solid #dbdbdb; padding:0 5px; font-size:14px; color:#666;border-radius:5px rgba(0,0,0,0.5);-moz-border-radius: 5px; -webkit-border-radius:5px; padding-left:45px; line-height:46px;}
.loginbox ul li{ padding:15px 0; position:relative;}
.loginbox .user{ background:url(/static/img/lgicon.png) 0 0 no-repeat; display:inline-block; position:absolute; width:19px; height:20px; left:15px; top:27px;}
.loginbox .pwd{ background:url(/static/img/lgicon.png) 0 bottom no-repeat; display:inline-block; position:absolute; width:19px; height:22px; left:15px; top:27px;}
.loginbox input.lgbtn{ width:312px; background-color:#f86c6b; border:0px; color:#fff; font-size:18px; font-family:\5FAE\8F6F\96C5\9ED1;line-height:46px; text-align:center; cursor:pointer; text-indent:0px; padding:0px;}
.main h3{ margin-top:-40px; font-size:30px; text-align:center; color:#fff; font-weight:normal;}
.footer{ position:fixed; z-index:9; bottom:0px; text-align:center; color:#666; width:100%; padding-bottom:20px; font-size:14px;}
</style>
<body>
<div class="main">
<h3>用戶登錄</h3>
<div class="loginbox">
<div class="loginbg">
<h4>用戶登錄</h4>
<form id="fm" action="/index/login" method="post">
<ul>
<li><span class="user" ></span><input type="text" name="name" required="true" value=""></li>
<li><span class="pwd" ></span><input type="password" name="pwd" required="true" value=""><span id="msg">{{msg}}</span></li>
<li><input type="submit" value="登錄" class="lgbtn"/></li>
</ul>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!--<div class="footer">陜西鋼谷電子商務股份有限公司 版權所有2016</div>-->
</body>
</html>
頁面效果:
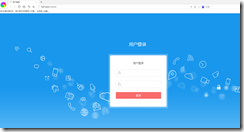
而正常的后臺處理邏輯也便是:
'use strict';
/**
* author: xxx
* create: 2017-02-05
* update: 2017-02-05
* desc: 登錄controller
*/
import Base from './base.js';
import cf from '../../common/config/config';
export default class extends Base {
indexAction() {//登錄頁面
//auto render template file index_index.html
return this.display();
};
/**
* 登錄方法
* @returns {*}
*/
async loginAction() {
let result = await this.model('admin').where({name: this.post().name, pwd: think.md5(this.post().pwd)}).select();
if (result&&result.length > 0) {
if(result[0].state==1){
let adminrole= await this.model('adminroles').where({id:result[0].rids}).select();
if(adminrole&&adminrole[0].state!=1){
this.assign('msg', '該用戶的身份已經被禁用或刪除,請聯系管理員!');
return this.display("index");//錯誤信息渲染至登錄頁面
}else{
let acresult = await this.model('adminaction').where({rid: result[0].rids}).field('action').select();//查詢該權限id的集合
result[0]['actions'] = acresult;//把集合賦予session
await this.session(cf.sessionKey, result[0]);
await this.model('adminlog').add({uid: result[0].id, createtime: new Date().getTime() / 1000, ip: this.ip()})//添加登錄日志
return this.redirect('/main');//跳轉main路由(主要是修改頁面顯示url)
}
}else{
this.assign('msg', '該用戶已經被停用或刪除,請聯系管理員!');
return this.display("index");//錯誤信息渲染至登錄頁面
}
} else {
this.assign('msg', '用戶名或密碼錯誤!');
return this.display("index");//錯誤信息渲染至登錄頁面
}
}
/**
* 退出方法
* @returns {promise|*|void|PreventPromise}
*/
async loginoutAction() {
await this.session();//清除session
return this.redirect('/');//跳轉登錄頁面
}
}
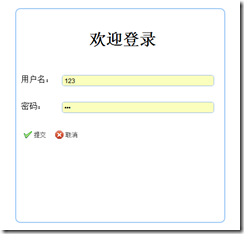
原本這樣處理下來的代碼算是最簡潔的方式。但是對于新手來說,因為在easyui官網上看到的demo比較多,于是在不太清楚各個之間的區別時,就容易出現“互相冗雜”在一起的現象,于是就出現了這樣的情況:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>用戶登錄</title>
<style>
.form-group {
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.form-group > label {
float: left;
width: 80px;
}
.form-group > input {
float: right;
}
h2 {
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
</style>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/js/jquery-easyui/themes/default/easyui.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/js/jquery-easyui/themes/icon.css">
<!--easyui js-->
<script src="/static/js/jquery-easyui/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/js/jquery-easyui/jquery.easyui.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/js/jquery-easyui/locale/easyui-lang-zh_CN.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div
id="login1" buttons="#dlg-buttons">
<h2>用戶登錄</h2>
<form id="ff1" method="post" url="/index/login">
<div class="form-group">
<label>用戶名:</label>
<input class="easyui-textbox" name="name" data-options="required:true">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>密碼:</label>
<input class="easyui-textbox" type="password" name="pwd"
data-options="required:true">
</div>
</form>
<div id="dlg-buttons">
<!--<a href="javascript:submitForm()" class="easyui-linkbutton" iconCls="icon-ok" plain="true">提交</a>-->
<a href="javascript:void(0)" class="easyui-linkbutton" onclick="submitForm()" iconCls="icon-ok"
plain="true">提交</a>
<a href="javascript:void(0)" class="easyui-linkbutton" onclick="clearForm()" iconCls="icon-cancel"
plain="true">取消</a>
</div>
<!--<b id="msg" ></b>-->
{{msg}}
</div>
</div>
<script>
function submitForm() {
jQuery.ajax({
url: "/index/login",
async: false,
method:"POST",
data:{
name:"123",
pwd:"123"
}
});
}
function clearForm() {
jQuery('#ff1').form('clear');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
后臺的處理邏輯:
'use strict';
import Base from './base.js';
export default class extends Base {
/**
* index action
* @return {Promise} []
*/
indexAction(){
//auto render template file index_index.html
return this.display();
}
async loginAction(){
// return this.redirect('/login');
console.log(this.post());
let name=this.post().name;
let pwd=this.post().pwd;
let model=this.model('user');
let data = await model.where({name:name,pwd:pwd}).find();
if(!think.isEmpty(data)){
console.log("http://////////");
return this.redirect('/login888');
// return this.json({'succ':true});
}else{
this.assign('msg','賬號或者密碼錯誤!');
return this.display('index');
// return this.json({'succ':false,'msg':'賬號或者密碼錯誤!'});
}
}
}
而這樣處理的結果卻是:
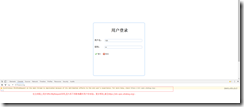
出現了瀏覽器自身報錯:此方法已被棄用。新手因為接觸thinkjs的并不是很多,所以時常會混淆其中,以為這樣很正確,其實在瀏覽器自身的js運行機制中,該方法是行不通的。因此建議初接觸thinkjs的小伙伴們,在寫頁面跳轉的邏輯,比如用到redirect或assign渲染時,前臺就不要使用ajax提交;而后臺用json返回時,就不要使用sumbit()提交。而這種非常隱蔽的問題,一般初學者也不會意識到問題存在哪里,因此還是需要小伙伴們多多看看相關的教程,增長自己的經驗。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。