您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
在一個類中,如果類沒有指針成員,一切方便,因為默認合成的析構函數會自動處理所有的內存。但是如果一個類帶了指針成員,那么需要我們自己來寫一個析構函數來管理內存。在<<c++ primer>> 中寫到,如果一個類需要我們自己寫析構函數,那么這個類,也會需要我們自己寫拷貝構造函數和拷貝賦值函數。
析構函數:
我們這里定義一個類HasPtr,這個類中包含一個int 類型的指針。然后定義一個析構函數,這個函數打印一句話。
HasPtr.h 類的頭文件
#pragma once
#ifndef __HASPTR__
#define __HASPTR__
class HasPtr
{
public:
HasPtr(int i,int *p);
//HasPtr& operator=(HasPtr&);
//HasPtr(const HasPtr&);
~HasPtr();
int get_ptr_value();
void set_ptr_value(int *p);
int get_val();
void set_val(int v);
private:
int val;
int *ptr;
};
#endif // !__HASPTR__
HasPtr.cpp 類的實現
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "HasPtr.h"
using namespace std;
HasPtr::HasPtr(int i, int *p)
{
val = i;
ptr = p;
}
int HasPtr::get_ptr_value()
{
return *ptr;
}
void HasPtr::set_ptr_value(int *p)
{
ptr = p;
}
int HasPtr::get_val()
{
return val;
}
void HasPtr::set_val(int v)
{
val = v;
}
HasPtr::~HasPtr()
{
cout << "destructor of HasPtr " << endl;
}
ClassWithPointer 類,包含main入口,HasPtr在stack上。
// ClassWithPointer.cpp : 定義控制臺應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "HasPtr.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int temp = 100;
HasPtr ptr(2,&temp);
cout << ptr.get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr.get_val() << endl;
system("PAUSE");
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
執行該入口方法,發現最后還是打印了析構函數這句話,OK,在main 方法中,stack上定義了一個HasPtr,在main方法退出前,析構函數自動調用了。
如果將HasPtr改為動態對象,也就是放在堆上呢?
ClassWithPointer 類,包含main入口,HasPtr在heap上。
// ClassWithPointer.cpp : 定義控制臺應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "HasPtr.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int temp = 100;
//HasPtr ptr(2,&temp);
HasPtr *ptr = new HasPtr(2,&temp);
cout << ptr->get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr->get_val() << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
執行一下,發現析構函數沒有調用。OK,我們在return 0前面添加一個delete ptr; 析構函數執行了。
所以,這里有兩個結論:
現在在析構函數中調用delete 語句來刪除指針成員。
頭文件不變,HasPtr.cpp 文件代碼如下:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "HasPtr.h"
using namespace std;
HasPtr::HasPtr(int i, int *p)
{
val = i;
ptr = p;
}
int HasPtr::get_ptr_value()
{
return *ptr;
}
void HasPtr::set_ptr_value(int *p)
{
ptr = p;
}
int HasPtr::get_val()
{
return val;
}
void HasPtr::set_val(int v)
{
val = v;
}
HasPtr::~HasPtr()
{
cout << "destructor of HasPtr " << endl;
delete ptr;
}
ClassWithPointer 代碼如下:
// ClassWithPointer.cpp : 定義控制臺應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "HasPtr.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int temp = 100;
HasPtr ptr(2,&temp);
cout << ptr.get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr.get_val() << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
執行一下,正常打印結束后,拋出錯誤:
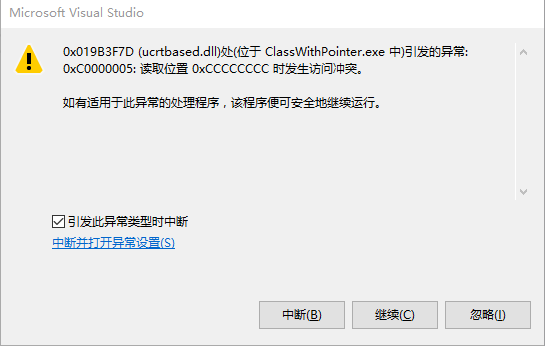
這里說明delete 不能刪除stack 上的指針值。
現在在ClassWithPointer傳入一個動態指針來測試一下。
// ClassWithPointer.cpp : 定義控制臺應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "HasPtr.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int temp = 100;
HasPtr ptr(2,&temp);
cout << ptr.get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr.get_val() << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
執行后析構函數正常運行。所以這里有兩個結論:
默認拷貝構造函數和默認賦值操作:
這里我們調用默認的構造函數和默認的賦值操作,看看會出現什么,為了方便查看,我在析構函數中打印了當前對象的地址,以及在main方法中打印了對象地址,這樣就可以看到哪個對象調用了析構函數:
HasPtr.cpp 代碼如下:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "HasPtr.h"
using namespace std;
HasPtr::HasPtr(int i, int *p)
{
val = i;
ptr = p;
}
int HasPtr::get_ptr_value()
{
return *ptr;
}
void HasPtr::set_ptr_value(int *p)
{
ptr = p;
}
int HasPtr::get_val()
{
return val;
}
void HasPtr::set_val(int v)
{
val = v;
}
HasPtr::~HasPtr()
{
cout << "destructor of HasPtr " << this << endl;
delete ptr;
}
ClassWithPointer 代碼如下:
// ClassWithPointer.cpp : 定義控制臺應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "HasPtr.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *temp = new int(100);
HasPtr ptr(2,temp);
cout << "ptr-------------->" << &ptr << endl;
cout << ptr.get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr.get_val() << endl;
HasPtr ptr2(ptr);
cout << "ptr2-------------->" << &ptr2 << endl;
cout << ptr2.get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr2.get_val() << endl;
HasPtr ptr3 = ptr;
cout << "ptr3-------------->" << &ptr3 << endl;
cout << ptr3.get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr3.get_val() << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
運行結果如下,最后還是報錯了:
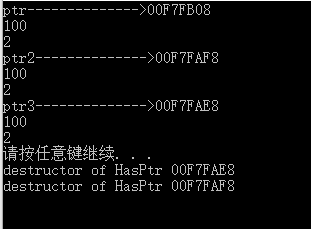
其實程序運行到第二個析構函數時,報錯了。報錯原因是,ptr 其實已經是pending指針了,因為這個ptr 指針所指向的地址已經被delete了。
不過我們這里最起碼可以知道默認的拷貝構造函數和賦值操作,也是會直接復制指針值的,不是指針所指向的值。是指針變量的值,也就是地址。
所以這里引申出來的問題是:如何管理對象中指針成員的內存? 這個是一個核心問題。
上面的例子,就是默認的方式,但是管理失敗了,因為析構函數到最后會刪除pending 指針,導致異常發生。
智能指針:
引入一個類U_Ptr,用來管理我們需要在業務對象中需要的指針變量,假設為int *p。頭文件如下:
#pragma once
#ifndef __UPTR__
#define __UPTR__
#include "HasPtr.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class U_Ptr
{
friend class HasPtr;
int *ip;
size_t use;
U_Ptr(int *p):ip(p),use(1) {}
~U_Ptr()
{
cout << "destruction:"<< *ip << endl;
delete ip;
}
};
#endif // !__UPTR__
現在我們的業務對象還是HasPtr。頭文件如下:
#pragma once
#ifndef __HASPTR__
#define __HASPTR__
#include "U_Ptr.h"
class HasPtr
{
public:
HasPtr(int *p, int i):ptr(new U_Ptr(p)),val(i){}
HasPtr(const HasPtr &orgi) :ptr(orgi.ptr), val(orgi.val)
{
++ptr->use;
cout << "coming into copy construction:" << ptr->use << endl;
}
HasPtr& operator=(const HasPtr &rhs);
~HasPtr();
int get_ptr_value() const;
int get_int() const;
void set_ptr(int *p);
void set_int(int i);
private:
U_Ptr *ptr;
int val;
};
#endif // !__HASPTR__
HasPtr.cpp 實現如下:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "HasPtr.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
HasPtr& HasPtr::operator=(const HasPtr &rhs)
{
++rhs.ptr->use;
if (--ptr->use == 0)
{
delete ptr;
}
ptr = rhs.ptr;
val = rhs.val;
return *this;
}
HasPtr::~HasPtr()
{
cout << "destruction:" << ptr->use << endl;
if (--ptr->use == 0)
{
delete ptr;
}
}
int HasPtr::get_ptr_value() const
{
return *ptr->ip;
}
int HasPtr::get_int() const
{
return val;
}
void HasPtr::set_ptr(int *p)
{
ptr->ip = p;
}
void HasPtr::set_int(int i)
{
val = i;
}
測試類如下:
// SmartPointer.cpp : 定義控制臺應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "HasPtr.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *temp = new int(100);
HasPtr ptr(temp,22);
cout << "ptr------------>" << endl;
cout << ptr.get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr.get_int() << endl;
HasPtr ptr2(ptr);
cout << "ptr2------------>" << endl;
cout << ptr2.get_ptr_value() << endl;
cout << ptr2.get_int() << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
我們把U_Ptr 叫做智能指針,用于幫我們管理需要的指針成員。我們的業務對象HasPtr對象包含一個智能指針,這個指針在HasPtr 對象創建時創建,智能指針的use 變量用來記錄業務對象HasPtr對象被復制了多少次,也就是說,有多少個相同的指針指向了ptr所指向的地方。如果要記錄HasPtr對象一共有多少個一樣的,那么就需要在拷貝構造函數和賦值操作處進行對use變量加一操作,在析構函數處進行減一操作。當減到0時,刪除指針。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。