您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家分享的是有關Python決策樹和隨機森林算法的示例分析的內容。小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,一起跟隨小編過來看看吧。
具體如下:
決策樹和隨機森林都是常用的分類算法,它們的判斷邏輯和人的思維方式非常類似,人們常常在遇到多個條件組合問題的時候,也通常可以畫出一顆決策樹來幫助決策判斷。
決策樹算法
決策樹表現了對象屬性和屬性值之間的一種映射關系。決策樹中的每個節點表示某個對象,而每個分叉路徑則表示某個可能的屬性值,而每個葉節點則對應從根節點到該葉節點所經歷的路徑所表現的對象值。在數據挖掘中,我們常常使用決策樹來進行數據分類和預測。
決策樹的helloworld
在這一小節,我們簡單使用決策樹來對iris數據集進行數據分類和預測。這里我們要使用sklearn下的tree的graphviz來幫助我們導出決策樹,并以pdf的形式存儲。具體代碼如下:
#決策樹的helloworld 使用決策樹對iris數據集進行分類
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
#導入iris數據集
iris = load_iris()
#初始化DecisionTreeClassifier
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
#適配數據
clf = clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
#將決策樹以pdf格式可視化
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file=None)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_pdf("iris.pdf")iris數據集得到的可視化決策樹如下圖所示:
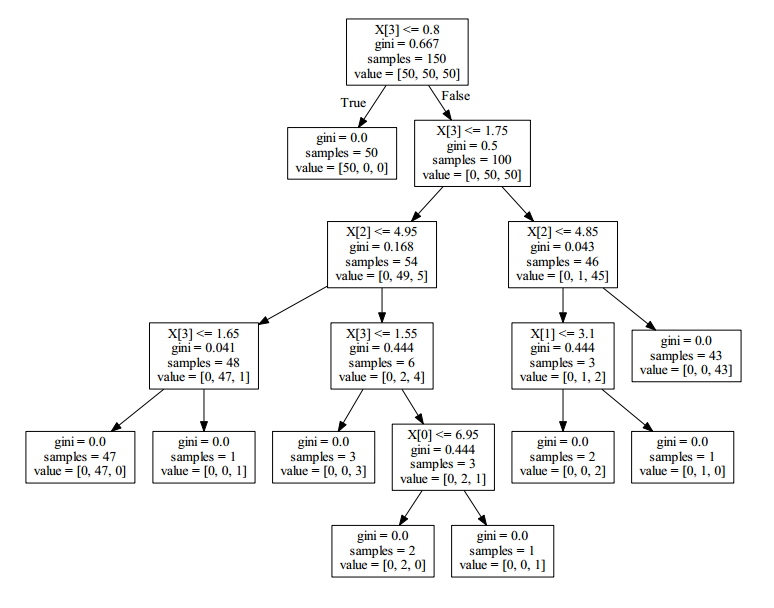
通過這個小例子,我們可以初步感受到決策樹的工作過程和特點。相較于其他的分類算法,決策樹產生的結果更加直觀也更加符合人類的思維方式。
使用決策樹檢測POP3暴力破解
在這里我們是用KDD99數據集中POP3相關的數據來使用決策樹算法來學習如何識別數據集中和POP3暴力破解相關的信息。關于KDD99數據集的相關內容可以自行google一下。下面是使用決策樹算法的源碼:
#使用決策樹算法檢測POP3暴力破解
import re
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import os
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
#加載kdd數據集
def load_kdd99(filename):
X=[]
with open(filename) as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip('\n')
line = line.split(',')
X.append(line)
return X
#找到訓練數據集
def get_guess_passwdandNormal(x):
v=[]
features=[]
targets=[]
#找到標記為guess-passwd和normal且是POP3協議的數據
for x1 in x:
if ( x1[41] in ['guess_passwd.','normal.'] ) and ( x1[2] == 'pop_3' ):
if x1[41] == 'guess_passwd.':
targets.append(1)
else:
targets.append(0)
#挑選與POP3密碼破解相關的網絡特征和TCP協議內容的特征作為樣本特征
x1 = [x1[0]] + x1[4:8]+x1[22:30]
v.append(x1)
for x1 in v :
v1=[]
for x2 in x1:
v1.append(float(x2))
features.append(v1)
return features,targets
if __name__ == '__main__':
v=load_kdd99("../../data/kddcup99/corrected")
x,y=get_guess_passwdandNormal(v)
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
print(cross_val_score(clf, x, y, n_jobs=-1, cv=10))
clf = clf.fit(x, y)
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file=None)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_pdf("POP3Detector.pdf")隨后生成的用于辨別是否POP3暴力破解的的決策樹如下:
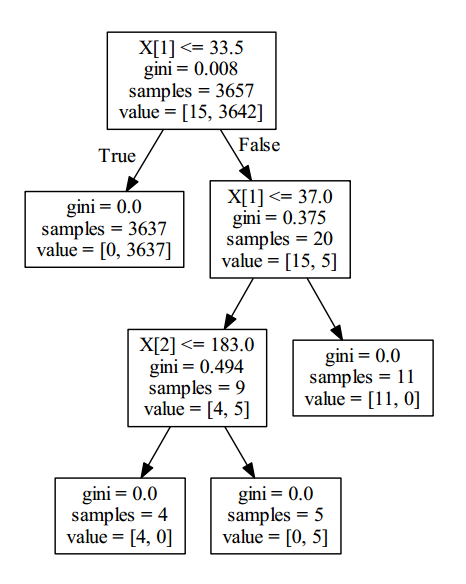
隨機森林算法
隨機森林指的是利用多棵樹對樣本進行訓練并預測的一種分類器。是一個包含多個決策樹的分類器,并且其輸出類別是由個別樹輸出的類別的眾數決定的。隨機森林的每一顆決策樹之間是沒有關聯的。在得到森林之后,當有一個新的輸入樣本進入的時候,就讓森林中的每一顆決策樹分別進行判斷,看看這個樣本屬于哪一類,然后看看哪一類被選擇最多,則預測這個樣本為那一類。一般來說,隨機森林的判決性能優于決策樹。
隨機森林的helloworld
接下來我們利用隨機生成的一些數據直觀的看看決策樹和隨機森林的準確率對比:
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
X,y = make_blobs(n_samples = 10000,n_features=10,centers = 100,random_state = 0)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth = None,min_samples_split=2,random_state = 0)
scores = cross_val_score(clf,X,y)
print("決策樹準確率;",scores.mean())
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10,max_depth = None,min_samples_split=2,random_state = 0)
scores = cross_val_score(clf,X,y)
print("隨機森林準確率:",scores.mean())最后可以看到決策樹的準確率是要稍遜于隨機森林的。

使用隨機森林算法檢測FTP暴力破解
接下來我們使用ADFA-LD數據集中關于FTP的數據使用隨機森林算法建立一個隨機森林分類器,ADFA-LD數據集中記錄了函數調用序列,每個文件包含的函數調用的序列個數都不一樣。相關數據集的詳細內容請自行google。
詳細源碼如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#使用隨機森林算法檢測FTP暴力破解
import re
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import os
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
def load_one_flle(filename):
x=[]
with open(filename) as f:
line=f.readline()
line=line.strip('\n')
return line
def load_adfa_training_files(rootdir):
x=[]
y=[]
list = os.listdir(rootdir)
for i in range(0, len(list)):
path = os.path.join(rootdir, list[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
x.append(load_one_flle(path))
y.append(0)
return x,y
def dirlist(path, allfile):
filelist = os.listdir(path)
for filename in filelist:
filepath = path+filename
if os.path.isdir(filepath):
#處理路徑異常
dirlist(filepath+'/', allfile)
else:
allfile.append(filepath)
return allfile
def load_adfa_hydra_ftp_files(rootdir):
x=[]
y=[]
allfile=dirlist(rootdir,[])
for file in allfile:
#正則表達式匹配hydra異常ftp文件
if re.match(r"../../data/ADFA-LD/Attack_Data_Master/Hydra_FTP_\d+/UAD-Hydra-FTP*",file):
x.append(load_one_flle(file))
y.append(1)
return x,y
if __name__ == '__main__':
x1,y1=load_adfa_training_files("../../data/ADFA-LD/Training_Data_Master/")
x2,y2=load_adfa_hydra_ftp_files("../../data/ADFA-LD/Attack_Data_Master/")
x=x1+x2
y=y1+y2
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df=1)
x=vectorizer.fit_transform(x)
x=x.toarray()
#clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, max_depth=None,min_samples_split=2, random_state=0)
clf = clf.fit(x,y)
score = cross_val_score(clf, x, y, n_jobs=-1, cv=10)
print(score)
print('平均正確率為:',np.mean(score))最后可以獲得一個準確率約在98.4%的隨機森林分類器。
感謝各位的閱讀!關于“Python決策樹和隨機森林算法的示例分析”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,讓大家可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到吧!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。