您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章為大家展示了如何在Python怎么中使用heapq模塊,內容簡明扼要并且容易理解,絕對能使你眼前一亮,通過這篇文章的詳細介紹希望你能有所收獲。
heapq 模塊實現了適用于Python列表的最小堆排序算法。
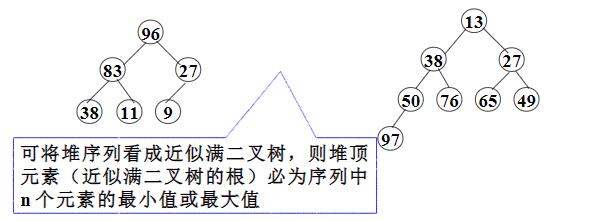
堆是一個樹狀的數據結構,其中的子節點都與父母排序順序關系。因為堆排序中的樹是滿二叉樹,因此可以用列表來表示樹的結構,使得元素 N 的子元素位于 2N + 1 和 2N + 2 的位置(對于從零開始的索引)。
本文內容將分為三個部分,第一個部分簡單介紹 heapq 模塊的使用;第二部分回顧堆排序算法;第三部分分析heapq中的實現。
heapq 的使用
創建堆有兩個基本的方法:heappush() 和 heapify(),取出堆頂元素用 heappop()。
heappush() 是用來向已有的堆中添加元素,一般從空列表開始構建:
import heapq
data = [97, 38, 27, 50, 76, 65, 49, 13]
heap = []
for n in data:
heapq.heappush(heap, n)
print('pop:', heapq.heappop(heap)) # pop: 13
print(heap) # [27, 50, 38, 97, 76, 65, 49]如果數據已經在列表中,則使用 heapify() 進行重排:
import heapq
data = [97, 38, 27, 50, 76, 65, 49, 13]
heapq.heapify(data)
print('pop:', heapq.heappop(data)) # pop: 13
print(data) # [27, 38, 49, 50, 76, 65, 97]回顧堆排序算法
堆排序算法基本思想是:將無序序列建成一個堆,得到關鍵字最小(或最大的記錄;輸出堆頂的最小 (大)值后,使剩余的 n-1 個元素 重又建成一個堆,則可得到n個元素的次小值 ;重復執行,得到一個有序序列,這個就是堆排序的過程。
堆排序需要解決兩個問題:
如何由一個無序序列建立成一個堆?
如何在輸出堆頂元素之后,調整剩余元素,使之成為一個新的堆?
新添加元素和,如何調整堆?
先來看看第二個問題的解決方法。采用的方法叫“篩選”,當輸出堆頂元素之后,就將堆中最后一個元素代替之;然后將根結點值與左、右子樹的根結點值進行比較 ,并與其中小者進行交換;重復上述操作,直至葉子結點,將得到新的堆,稱這個從堆頂至葉子的調整過程為“篩選”。
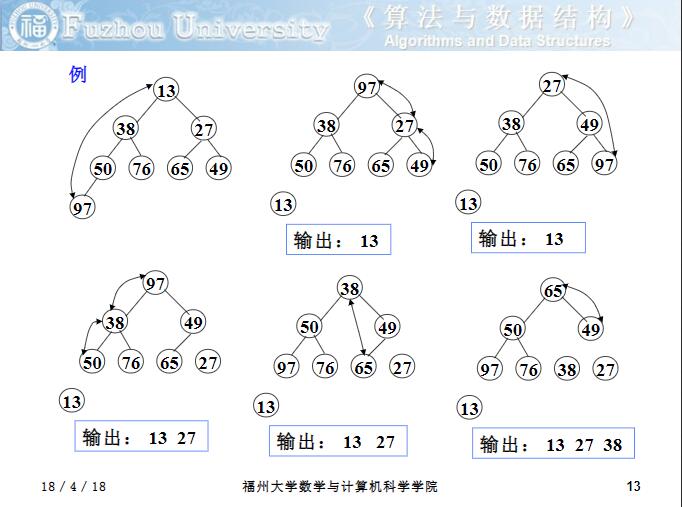
如上圖所示,當堆頂 13 輸出后,將堆中末尾的 97 替代為堆頂,然后堆頂與它的子節點 38 和 27 中的小者交換;元素 97 在新的位置上在和它的子節點 65 和 49 中的小者交換;直到元素97成為葉節點,就得到了新的堆。這個過程也叫 下沉 。
讓堆中位置為 pos 元素進行下沉的如下:
def heapdown(heap, pos): endpos = len(heap) while pos < endpos: lchild = 2 * pos + 1 rchild = 2 * pos + 2 if lchild >= endpos: # 如果pos已經是葉節點,退出循環 break childpos = lchild # 假設要交換的節點是左節點 if rchild < endpos and heap[childpos] > heap[rchild]: childpos = rchild if heap[pos] < heap[childpos]: # 如果節點比子節點都小,退出循環 break heap[pos], heap[childpos] = heap[childpos], heap[pos] # 交換 pos = childpos
再來看看如何解決第三個問題:新添加元素和,如何調整堆?這個的方法正好與 下沉 相反,首先將新元素放置列表的最后,然后新元素與其父節點比較,若比父節點小,與父節點交換;重復過程直到比父節點大或到根節點。這個過程使得元素從底部不斷上升,從下至上恢復堆的順序,稱為 上浮 。
將位置為 pos 進行上浮的代碼為:
def heapup(heap, startpos, pos): # 如果是新增元素,startpos 傳入 0 while pos > startpos: parentpos = (pos - 1) // 2 if heap[pos] < heap[parentpos]: heap[pos], heap[parentpos] = heap[parentpos], heap[pos] pos = parentpos else: break
第一個問題:如何由一個無序序列建立成一個堆?從無序序列的第 n/2 個元素 (即此無序序列對應的完全二叉樹的最后一個非終端結點 )起 ,至第一個元素止,依次進行下沉:
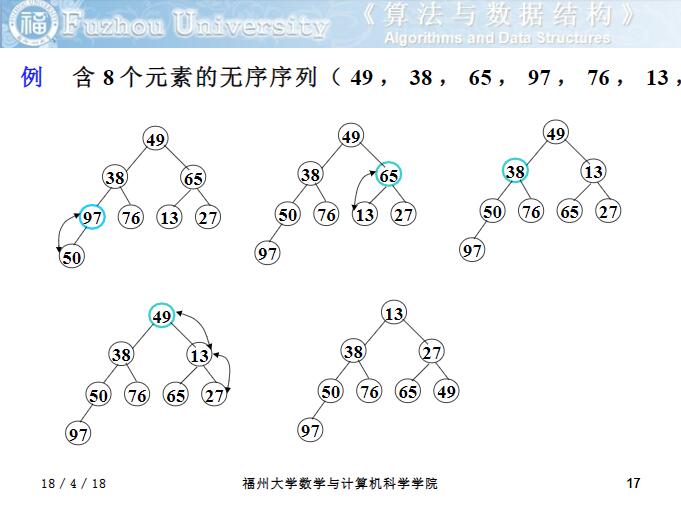
for i in reversed(range(len(data) // 2)): heapdown(data, i)
heapq 源碼分析
添加新元素到堆中的 heappush() 函數:
def heappush(heap, item): """Push item onto heap, maintaining the heap invariant.""" heap.append(item) _siftdown(heap, 0, len(heap)-1)
把目標元素放置列表最后,然后進行上浮。盡管它命名叫 down ,但這個過程是上浮的過程,這個命名也讓我困惑,后來我才知道它是因為元素的索引不斷減小,所以命名 down 。下沉的過程它也就命名為 up 了。
def _siftdown(heap, startpos, pos): newitem = heap[pos] # Follow the path to the root, moving parents down until finding a place # newitem fits. while pos > startpos: parentpos = (pos - 1) >> 1 parent = heap[parentpos] if newitem < parent: heap[pos] = parent pos = parentpos continue break heap[pos] = newitem
一樣是通過 newitem 不斷與父節點比較。不一樣的是這里缺少了元素交換的過程,而是計算出新元素最后所在的位置 pos 并進行的賦值。顯然這是優化后的代碼,減少了不斷交換元素的冗余過程。
再來看看輸出堆頂元素的函數 heappop():
def heappop(heap): """Pop the smallest item off the heap, maintaining the heap invariant.""" lastelt = heap.pop() # raises appropriate IndexError if heap is empty if heap: returnitem = heap[0] heap[0] = lastelt _siftup(heap, 0) return returnitem return lastelt
通過 heap.pop() 獲得列表中的最后一個元素,然后替換為堆頂 heap[0] = lastelt ,再進行下沉:
def _siftup(heap, pos): endpos = len(heap) startpos = pos newitem = heap[pos] # Bubble up the smaller child until hitting a leaf. childpos = 2*pos + 1 # 左節點,默認替換左節點 while childpos < endpos: # Set childpos to index of smaller child. rightpos = childpos + 1 # 右節點 if rightpos < endpos and not heap[childpos] < heap[rightpos]: childpos = rightpos # 當右節點比較小時,應交換的是右節點 # Move the smaller child up. heap[pos] = heap[childpos] pos = childpos childpos = 2*pos + 1 # The leaf at pos is empty now. Put newitem there, and bubble it up # to its final resting place (by sifting its parents down). heap[pos] = newitem _siftdown(heap, startpos, pos)
這邊的代碼將準備要下沉的元素視為新元素 newitem ,將其當前的位置 pos 視為空位置,由其子節點中的小者進行取代,反復如此,最后會在葉節點留出一個位置,這個位置放入 newitem ,再讓新元素進行上浮。
再來看看讓無序數列重排成堆的 heapify() 函數:
def heapify(x): """Transform list into a heap, in-place, in O(len(x)) time.""" n = len(x) for i in reversed(range(n//2)): _siftup(x, i)
上述內容就是如何在Python怎么中使用heapq模塊,你們學到知識或技能了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或者豐富自己的知識儲備,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。