溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
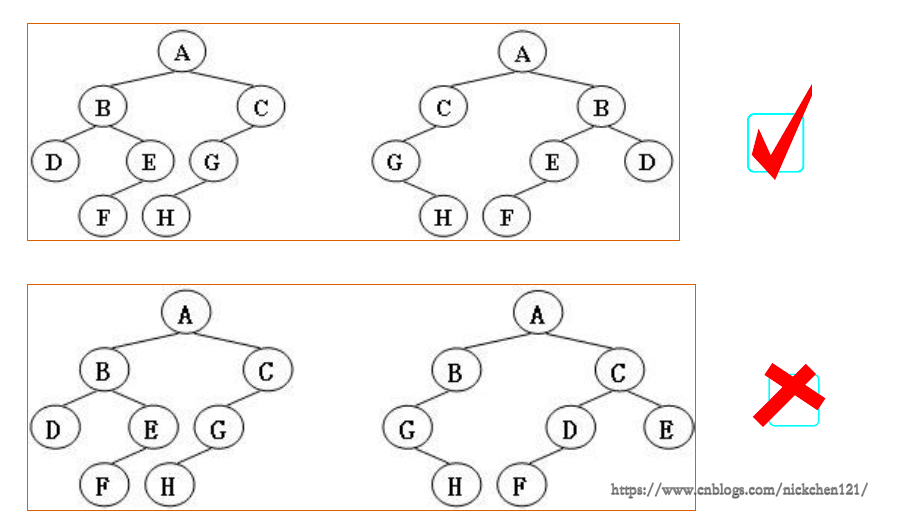
一、題意理解
給定兩棵樹T1和T2。如果T1可以通過若干次左右孩子互換就變成T2,則我們稱兩棵樹是“同構的”。現給定兩棵樹,請你判斷它們是否是同構的。
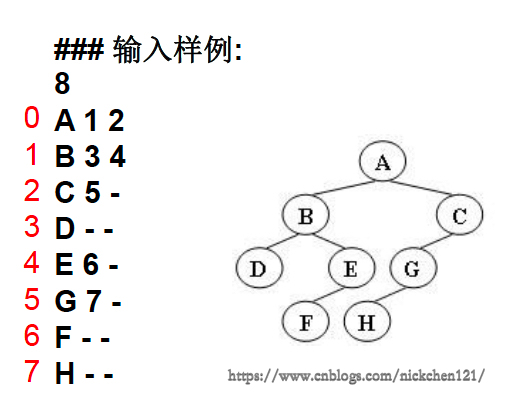
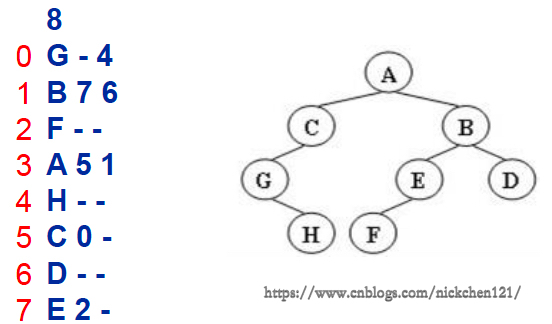
輸入格式:輸入給出2棵二叉樹的信息:
先在一行中給出該樹的結點樹,隨后N行
第i行對應編號第i個結點,給出該結點中存儲的字母、其左孩子結點的編號、右孩子結點的編號
如果孩子結點為空,則在相應位置給出“-”
如下圖所示,有多種表示的方式,我們列出以下兩種:
二、求解思路
搜到一篇也是講這個的,但是那篇并沒有完全用到單向鏈表的方法,所以研究了一下,寫了一個是完全用單向鏈表的方法:
其實應該有更優雅的刪除整個單向列表的方法,比如頭設為none,可能會改進下?
# python語言實現
L1 = list(map(int, input().split()))
L2 = list(map(int, input().split()))
# 節點
class Node:
def __init__(self, coef, exp):
self.coef = coef
self.exp = exp
self.next = None
# 單鏈表
class List:
def __init__(self, node=None):
self.__head = node
# 為了訪問私有類
def gethead(self):
return self.__head
def travel(self):
cur1 = self.__head
cur2 = self.__head
if cur1.next != None:
cur1 = cur1.next
else:
print(cur2.coef, cur2.exp, end="")
return
while cur1.next != None:
print(cur2.coef, cur2.exp, end=" ")
cur1 = cur1.next
cur2 = cur2.next
print(cur2.coef, cur2.exp, end=" ")
cur2 = cur2.next
print(cur2.coef, cur2.exp, end="")
# add item in the tail
def append(self, coef, exp):
node = Node(coef, exp)
if self.__head == None:
self.__head = node
else:
cur = self.__head
while cur.next != None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
def addl(l1, l2):
p1 = l1.gethead()
p2 = l2.gethead()
l3 = List()
while (p1 is not None) & (p2 is not None):
if (p1.exp > p2.exp):
l3.append(p1.coef, p1.exp)
p1 = p1.next
elif (p1.exp < p2.exp):
l3.append(p2.coef, p2.exp)
p2 = p2.next
else:
if (p1.coef + p2.coef == 0):
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next
else:
l3.append(p2.coef + p1.coef, p1.exp)
p2 = p2.next
p1 = p1.next
while p1 is not None:
l3.append(p1.coef, p1.exp)
p1 = p1.next
while p2 is not None:
l3.append(p2.coef, p2.exp)
p2 = p2.next
if l3.gethead() == None:
l3.append(0, 0)
return l3
def mull(l1, l2):
p1 = l1.gethead()
p2 = l2.gethead()
l3 = List()
l4 = List()
if (p1 is not None) & (p2 is not None):
while p1 is not None:
while p2 is not None:
l4.append(p1.coef * p2.coef, p1.exp + p2.exp)
p2 = p2.next
l3 = addl(l3, l4)
l4 = List()
p2 = l2.gethead()
p1 = p1.next
else:
l3.append(0, 0)
return l3
def L2l(L):
l = List()
L.pop(0)
for i in range(0, len(L), 2):
l.append(L[i], L[i + 1])
return l
l1 = L2l(L1)
l2 = L2l(L2)
l3 = List()
l3 = mull(l1, l2)
l3.travel()
print("")
l3 = List()
l3 = addl(l1, l2)
l3.travel()
以上就是本次介紹的全部內容知識點,相關內容可以參閱下方知識點,感謝大家對億速云的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。