溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
使用Python怎么實現一個坐標線性插值應用?相信很多沒有經驗的人對此束手無策,為此本文總結了問題出現的原因和解決方法,通過這篇文章希望你能解決這個問題。
一、背景
在野外布設700米的測線,點距為10米,用GPS每隔50米測量一個坐標,再把測線的頭和為測量一個坐標。現在需使用線性插值的方法求取每兩個坐標之間的其他4個點的值。
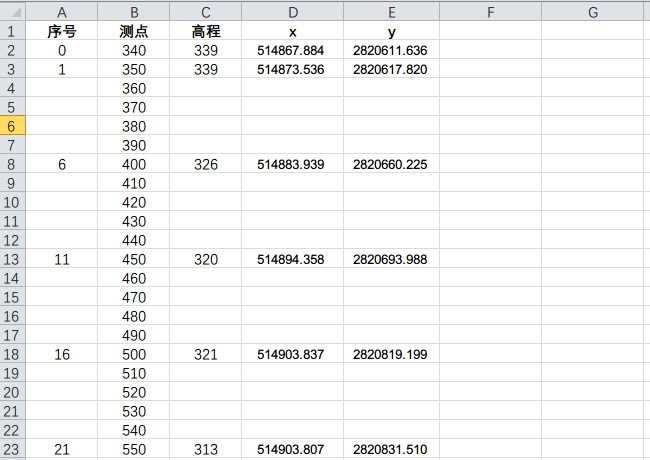
二、插值原理
使用等比插值的方法
起始值為 a
終止值為 b
步長值為 (a-b)/5
后面的數分別為 a+n, a+2n, a+3n, a+4n
三、代碼實習對 x 插值
interx.py
import numpy as np
f = np.loadtxt('datax.txt')
a = f[:, 0]
b = f[:, 1]
for j in np.arange(len(a)):
aa = a[j]*1000 # np.arrange()會自動去掉小數
bb = b[j]*1000
n = (bb-aa) / 5
x = np.arange(6)
x[0] = aa
print(x[0]/1000)
for i in range(1, 5, 1):
x[i] = x[i-1]+n
print(x[i]/1000)
i = i+1
# print(bb/1000)
# print("\n")datax.txt
514873.536 514883.939 514883.939 514894.358 514894.358 514903.837 514903.837 514903.807 514903.807 514907.179 514907.179 514911.356 514911.356 514913.448 514913.448 514913.315 514913.315 514917.344 514917.344 514923.684 514923.684 514924.801 514924.801 514929.697 514929.697 514916.274
對 y 插值
intery.py
import numpy as np
f = np.loadtxt('datay.txt')
a = f[:, 0]
b = f[:, 1]
for j in np.arange(len(a)):
aa = (a[j] - 2820000)*1000 # 數據太長會溢出
bb = (b[j]-2820000)*1000
n = (bb-aa) / 5
x = np.arange(6)
x[0] = aa
print(x[0]/1000+2820000)
for i in range(1, 5, 1):
x[i] = x[i-1]+n
print(x[i]/1000+2820000)
i = i+1
# print(bb/1000)
# print("\n")datay.txt
2820617.820 2820660.225 2820660.225 2820693.988 2820693.988 2820819.199 2820819.199 2820831.510 2820831.510 2820858.666 2820858.666 2820973.487 2820973.487 2821017.243 2821017.243 2821019.518 2821019.518 2821058.223 2821058.223 2821097.575 2821097.575 2821144.436 2821144.436 2821173.356 2821173.356 2821218.889
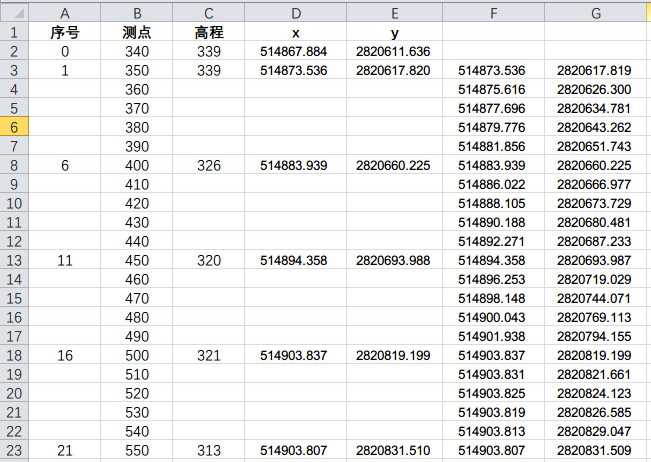
四、最終成果
手動把兩次插值結果復制到dataxy中
dataxy.txt
514873.536 2820617.819 514875.616 2820626.300 514877.696 2820634.781 514879.776 2820643.262 514881.856 2820651.743 514883.939 2820660.225 514886.022 2820666.977 514888.105 2820673.729 514890.188 2820680.481 514892.271 2820687.233 514894.358 2820693.987 514896.253 2820719.029 514898.148 2820744.071 514900.043 2820769.113 514901.938 2820794.155 514903.837 2820819.199 514903.831 2820821.661 514903.825 2820824.123 514903.819 2820826.585 514903.813 2820829.047 514903.807 2820831.509 514904.481 2820836.940 514905.155 2820842.371 514905.829 2820847.802 514906.503 2820853.233 514907.179 2820858.666 514908.014 2820881.630 514908.849 2820904.594 514909.684 2820927.558 514910.519 2820950.522 514911.356 2820973.487 514911.774 2820982.238 514912.192 2820990.989 514912.610 2820999.740 514913.028 2821008.491 514913.448 2821017.242 514913.421 2821017.697 514913.394 2821018.152 514913.367 2821018.607 514913.340 2821019.062 514913.315 2821019.518 514914.120 2821027.259 514914.925 2821035.000 514915.730 2821042.741 514916.535 2821050.482 514917.344 2821058.223 514918.612 2821066.093 514919.880 2821073.963 514921.148 2821081.833 514922.416 2821089.703 514923.684 2821097.575 514923.907 2821106.947 514924.130 2821116.319 514924.353 2821125.691 514924.576 2821135.063 514924.801 2821144.436 514925.780 2821150.219 514926.759 2821156.002 514927.738 2821161.785 514928.717 2821167.568 514929.697 2821173.356 514927.012 2821182.462 514924.327 2821191.568 514921.642 2821200.674 514918.957 2821209.780
五、畫圖對比
dataxy.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 解決中文字體顯示不出來
mpl.rcParams["font.sans-serif"]=["SimHei"]
mpl.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
a = np.loadtxt("datax.txt")
b = np.loadtxt('datay.txt')
c = np.loadtxt('dataxy.txt')
x = a[: ,0]
y = b[: ,0]
xx = c[:,0]
yy = c[:,1]
plt.plot(x,y,color = 'orange',
label = '插值線段')
plt.scatter(xx,yy,marker='o',
c = 'deepskyblue',
alpha = 0.6,
label = '實測點位')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Python坐標插值')
plt.grid()
# 保存高清圖片,dpi表示分辨率
plt.savefig('out.png',dpi = 600)
plt.show()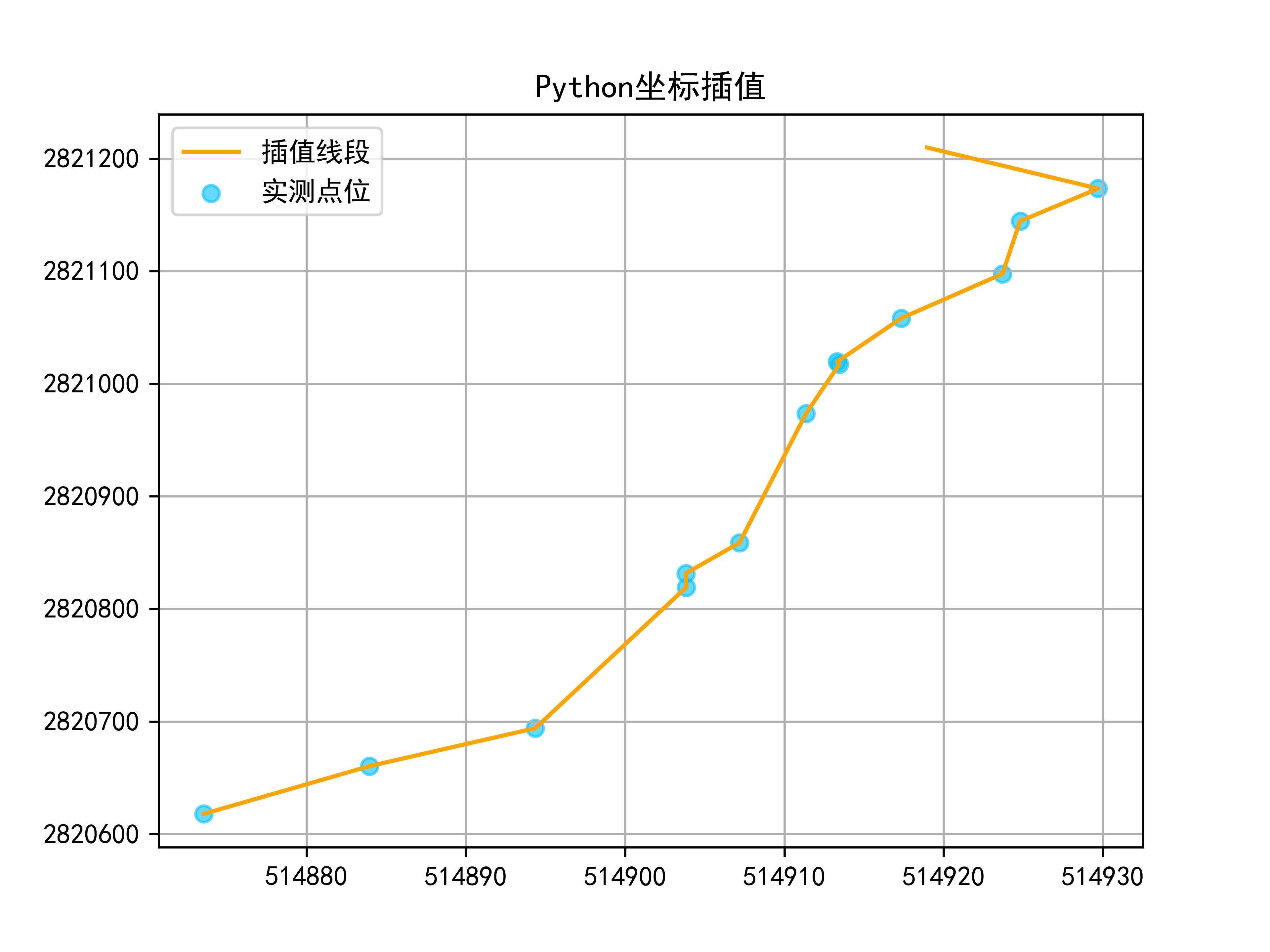
文件結構
看完上述內容,你們掌握使用Python怎么實現一個坐標線性插值應用的方法了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或想了解更多相關內容,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝各位的閱讀!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。