您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹解析Mybatis的會話機制是什么,文中介紹的非常詳細,具有一定的參考價值,感興趣的小伙伴們一定要看完!
坐在我旁邊的鐘同學聽說我精通Mybatis源碼(我就想不通,是誰透漏了風聲),就順帶問了我一個問題:在同一個方法中,Mybatis多次請求數據庫,是否要創建多個SqlSession會話?
可能最近擼多了,當時腦子里一片模糊,眼神迷離,雖然我當時回答他:如果多個請求同一個事務中,那么多個請求都在共用一個SqlSession,反之每個請求都會創建一個SqlSession。這是我們在平常開發中都習以為常的常識了,但我卻沒有從原理的角度給鐘同學分析,導致鐘同學茶飯不思,作為老司機的我,感到深深的自責,于是我暗自下定決心,要給鐘同學一個交代。
不服跑個demo
測試在方法中不加事務時,每個請求是否會創建一個SqlSession:
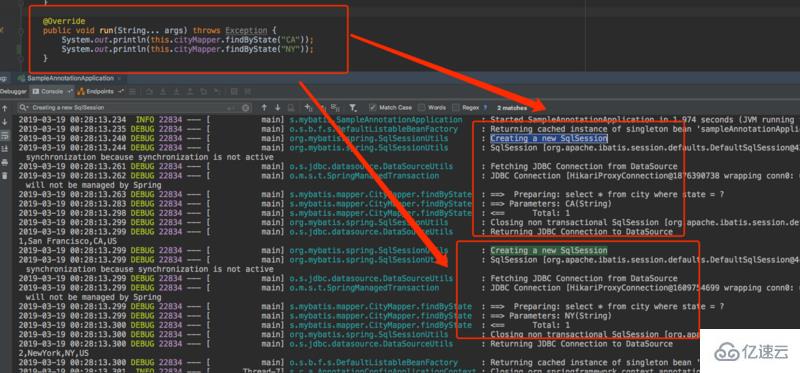
從日志可以看出,在沒有加事務的情況下,確實是Mapper的每次請求數據庫,都會創建一個SqlSession與數據庫交互,下面我們再看看加了事務的情況:

從日志可以看出,在方法中加了事務后,兩次請求只創建了一個SqlSession,再次證明了我上面的回答,但是僅僅這樣回答是體現完全不出一個老司機應有的職業素養的,所以,我要發車了。
什么是SqlSession
在發車之前,我們必須得先搞明白,什么是SqlSession?
簡單來說,SqlSession是Mybatis工作的最頂層API會話接口,所有的數據庫操作都經由它來實現,由于它就是一個會話,即一個SqlSession應該僅存活于一個業務請求中,也可以說一個SqlSession對應這一次數據庫會話,它不是永久存活的,每次訪問數據庫時都需要創建它。
因此,SqlSession并不是線程安全,每個線程都應該有它自己的 SqlSession 實例,千萬不能將一個SqlSession搞成單例形式,或者靜態域和實例變量的形式都會導致SqlSession出現事務問題,這也就是為什么多個請求同一個事務中會共用一個SqlSession會話的原因,我們從SqlSession的創建過程來說明這點:
每次創建一個SqlSession會話,都會伴隨創建一個專屬SqlSession的連接管理對象,如果SqlSession共享,就會出現事務問題。
從源碼的角度分析
源碼分析從哪一步作為入口呢?如果是看過我之前寫的那幾篇關于mybatis的源碼分析,我相信你不會在Mybatis源碼前磨磨蹭蹭,遲遲找不到入口。
在之前的文章里已經說過了,Mapper的實現類是一個代理,真正執行邏輯的是MapperProxy.invoke(),該方法最終執行的是sqlSessionTemplate。
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate:
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}這個是創建SqlSessionTemplate的最終構造方法,可以看出sqlSessionTemplate中用到了SqlSession,是SqlSessionInterceptor實現的一個動態代理類,所以我們直接深入要塞:
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
// release the connection to avoid a deadlock if the translator is no loaded. See issue #22
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}Mapper所有的方法,最終都會用這個方法來處理所有的數據庫操作,茶飯不思的鐘同學眼神迷離不知道是不是自暴自棄導致擼多了,眼神空洞地望著我,問我spring整合mybatis和mybatis單獨使用是否有區別,其實沒區別,區別就是spring封裝了所有處理細節,你就不用寫大量的冗余代碼,專注于業務開發。
該動態代理方法主要做了以下處理:
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils#getSqlSession:
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Creating a new SqlSession");
}
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}是不是看到了不服跑個demo時看到的日志“Creating a new SqlSession”了,那么證明我直接深入的地方挺準確的,沒有絲毫誤差。在這個方法當中,首先是從TransactionSynchronizationManager(以下稱當前線程事務管理器)獲取當前線程threadLocal是否有SqlSessionHolder,如果有就從SqlSessionHolder取出當前SqlSession,如果當前線程threadLocal沒有SqlSessionHolder,就從sessionFactory中創建一個SqlSession,具體的創建步驟上面已經說過了,接著注冊會話到當前線程threadLocal中。
先來看看當前線程事務管理器的結構:
public abstract class TransactionSynchronizationManager {
// ...
// 存儲當前線程事務資源,比如Connection、session等
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
// 存儲當前線程事務同步回調器
// 當有事務,該字段會被初始化,即激活當前線程事務管理器
private static final ThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>> synchronizations =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transaction synchronizations");
// ...
}這是spring的一個當前線程事務管理器,它允許將當前資源存儲到當前線程ThreadLocal中,從前面也可看出SqlSessionHolder是保存在resources中。
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils#registerSessionHolder:
private static void registerSessionHolder(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator, SqlSession session) {
SqlSessionHolder holder;
// 判斷當前是否有事務
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Environment environment = sessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment();
// 判斷當前環境配置的事務管理工廠是否是SpringManagedTransactionFactory(默認)
if (environment.getTransactionFactory() instanceof SpringManagedTransactionFactory) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
// 綁定當前SqlSessionHolder到線程ThreadLocal中
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
// 注冊SqlSession同步回調器
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
holder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
// 會話使用次數+1
holder.requested();
} else {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(environment.getDataSource()) == null) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because DataSource is not transactional");
}
} else {
throw new TransientDataAccessResourceException(
"SqlSessionFactory must be using a SpringManagedTransactionFactory in order to use Spring transaction synchronization");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active");
}
}
}注冊SqlSession到當前線程事務管理器的條件首先是當前環境中有事務,否則不注冊,判斷是否有事務的條件是synchronizations的ThreadLocal是否為空:
public static boolean isSynchronizationActive() {
return (synchronizations.get() != null);
}每當我們開啟一個事務,會調用initSynchronization()方法進行初始化synchronizations,以激活當前線程事務管理器。
public static void initSynchronization() throws IllegalStateException {
if (isSynchronizationActive()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot activate transaction synchronization - already active");
}
logger.trace("Initializing transaction synchronization");
synchronizations.set(new LinkedHashSet<TransactionSynchronization>());
}所以當前有事務時,會注冊SqlSession到當前線程ThreadLocal中。
Mybatis自己也實現了一個自定義的事務同步回調器SqlSessionSynchronization,在注冊SqlSession的同時,也會將SqlSessionSynchronization注冊到當前線程事務管理器中,它的作用是根據事務的完成狀態回調來處理線程資源,即當前如果有事務,那么當每次狀態發生時就會回調事務同步器,具體細節可移步至Spring的org.springframework.transaction.support包。
回到SqlSessionInterceptor代理類的邏輯,發現判斷會話是否需要提交要調用以下方法:
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils#isSqlSessionTransactional:
public static boolean isSqlSessionTransactional(SqlSession session, SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
notNull(session, NO_SQL_SESSION_SPECIFIED);
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
return (holder != null) && (holder.getSqlSession() == session);
}取決于當前SqlSession是否為空并且判斷當前SqlSession是否與ThreadLocal中的SqlSession相等,前面也分析了,如果當前沒有事務,SqlSession是不會保存到事務同步管理器的,即沒有事務,會話提交。
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils#closeSqlSession:
public static void closeSqlSession(SqlSession session, SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
notNull(session, NO_SQL_SESSION_SPECIFIED);
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
if ((holder != null) && (holder.getSqlSession() == session)) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Releasing transactional SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
holder.released();
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Closing non transactional SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
session.close();
}
}方法無論執行結果如何都需要執行關閉會話邏輯,這里的判斷也是判斷當前是否有事務,如果SqlSession在事務當中,則減少引用次數,沒有真實關閉會話。如果當前會話不存在事務,則直接關閉會話。
寫在最后
雖說鐘同學問了我一個Mybatis的問題,我卻中了Spring的圈套,猛然發現整個事務鏈路都處在Spring的管控當中,這里涉及到了Spring的自定義事務的一些機制,其中當前線程事務管理器是整個事務的核心與中軸,當前有事務時,會初始化當前線程事務管理器的synchronizations,即激活了當前線程同步管理器,當Mybatis訪問數據庫會首先從當前線程事務管理器獲取SqlSession,如果不存在就會創建一個會話,接著注冊會話到當前線程事務管理器中,如果當前有事務,則會話不關閉也不commit,Mybatis還自定義了一個TransactionSynchronization,用于事務每次狀態發生時回調處理。
以上是解析Mybatis的會話機制是什么的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!希望分享的內容對大家有幫助,更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。